A) inflammation of the liver
B) watery feces
C) bad breath
D) enlargement or inflammation of the vein of the anal canal
E) chronic acid in the esophagus
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the process or term with the best description. -bolus
A) swallowing
B) chewing
C) ball of food
D) semifluid material
E) phagocytosis
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
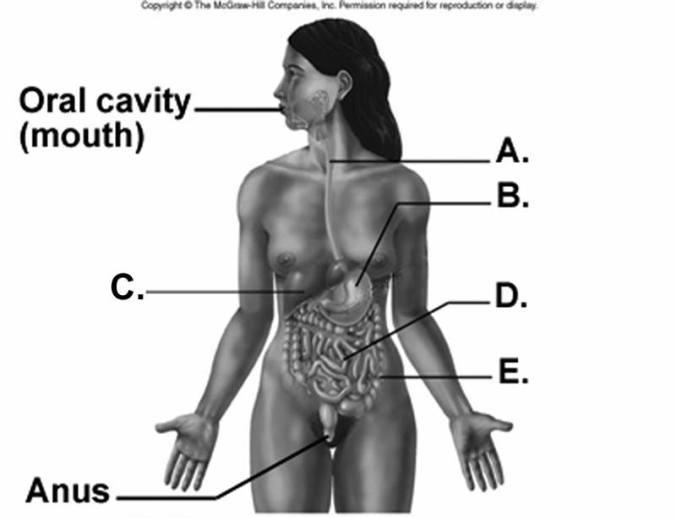 -What does "E" represent on the diagram?
-What does "E" represent on the diagram?
A) small intestine
B) large intestine
C) esophagus
D) stomach
E) liver
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the key to choose the best answer. -(1) number of villi in small intestine; (2) number of villi in large intestine
A) Choose this if the first item is greater than the second item.
B) Choose this if the first item is less than the second item.
C) Choose this if the first item is equal or nearly equal to the second item.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding swallowing is true?
A) The voluntary phase begins in the pharynx.
B) In the pharyngeal phase, food is moved through the pharynx.
C) The uvula rises during the esophageal phase.
D) Peristalsis occurs in all phases of swallowing.
E) Breathing occurs during swallowing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gastritis, peptic ulcers and gastric cancer can all be caused by
A) Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium.
B) increased secretion of gastric bicarbonate.
C) pH of the stomach contents continuously greater than 4.
D) increased mucus production by the neck cells.
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Serum cholesterol levels are solely dependent on a person's dietary intake of cholesterol.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is the uvula located?
A) on the hard palate
B) hanging in the fauces
C) lateral walls of the fauces
D) under the tongue
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inability of the pyloric sphincter to open would prevent
A) food from entering the stomach.
B) stomach acid from being released.
C) digestive enzymes from being released.
D) food from entering the small intestine.
E) the making of chyme.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bile would flow directly from the
A) gallbladder into the hepatic duct.
B) hepatic ducts into the common hepatic duct.
C) bile canaliculus into the cystic duct.
D) common bile duct into the gallbladder.
E) cystic duct into the hepatic ducts.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell needs a receptor in order to absorb LDL's. A disease that interferes with the functioning of these LDL receptors would
A) increase serum cholesterol levels.
B) decrease serum cholesterol levels.
C) halt endocytosis.
D) promote endocytosis.
E) have no effect on serum cholesterol or endocytosis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is located closest to the rectum?
A) ascending colon
B) descending colon
C) transverse colon
D) sigmoid colon
E) cecum
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the function with its appropriate description. -peristalsis
A) movement of molecules from digestive tract into blood
B) chewing of food
C) muscular contractions that propel food
D) removal of undigested wastes from body
E) breakdown of organic molecules with digestive enzymes
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning cholecystokinin is correct?
A) Cholecystokinin stimulates relaxation of the gallbladder.
B) Cholecystokinin stimulates secretion of mucus by the gastric glands.
C) Cholecystokinin stimulates the pancreas to release an enzyme-rich solution.
D) Cholecystokinin stimulates the intestine to secrete trypsin.
E) Cholecystokinin stimulates gastric secretions.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In comparison to a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) , a high density lipoprotein (HDL) contains
A) less lipid.
B) less protein.
C) more cholesterol.
D) more carbohydrate.
E) more amino acids.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Small droplets of digested lipids surrounded by bile salts are called
A) chylomicrons.
B) micelles.
C) monoglycerides.
D) diglycerides.
E) lacteals.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gallbladder
A) produces bile.
B) is attached to the pancreas.
C) stores bile.
D) produces secretin.
E) breaks down red blood cells.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the muscularis layer of the esophagus differ from the rest of the digestive tract?
A) it is all skeletal muscle
B) the superior part is skeletal muscle
C) the inferior part is skeletal muscle
D) it has alternating smooth and skeletal muscle sections
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bile
A) digests proteins in the small intestine.
B) emulsifies fats in the small intestine.
C) is made by the gallbladder and stored by the liver.
D) activates trypsin in the small intestine.
E) activates the pancreas.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events occurs because of the low pH of the stomach?
A) activation of salivary amylase
B) enhanced carbohydrate digestion
C) proper environment for functioning of pepsin
D) protein synthesis
E) lipid digestion
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 258
Related Exams