A) Choose this if the first item is greater than the second item.
B) Choose this if the first item is less than the second item.
C) Choose this if the first item is equal or nearly equal to the second item.
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following results in an increase in shunted blood (blood not completely oxygenated) ?
A) exercise
B) pulmonary edema
C) increased heart rate
D) increased respiration rate
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) As thoracic volume increases, alveolar pressure (Palv) increases.
B) In expiration, the thoracic volume increases.
C) Constriction of bronchioles assists breathing.
D) As alveolar volume increases, alveolar pressure (Palv) decreases.
E) Pressure is directly proportional to volume.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is transfused blood discarded after about 6 weeks of storage?
A) It can not bind to oxygen anymore.
B) It becomes too thick.
C) The BPG levels are too low for adequate release of oxygen to tissues.
D) The percent oxygen saturation is too low.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diameter of bronchioles can change because their walls contain
A) smooth muscle.
B) skeletal muscle.
C) fibrous cartilage.
D) hyaline cartilage.
E) elastic cartilage.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the appropriate description or definition. -vital capacity "Enter the letter of the correct description below"
A) sum of the inspiratory reserve, expiratory reserve, tidal, and residual volumes
B) volume of air inspired during a normal inspiration
C) volume of air remaining in lungs after the most forceful expiration
D) sum of the expiratory reserve, inspiratory reserve, and tidal volumes
E) the amount of air that can be forcefully expired after expiration of the normal tidal volume
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During swallowing, the opening into the larynx is covered by the
A) epiglottis.
B) thyroid cartilage.
C) cricoid cartilage.
D) arytenoid cartilage.
E) the "Adam's apple".
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning the dorsal and ventral respiratory groups is false?
A) They are located in the reticular activating system.
B) There is cross communication between these two groups.
C) These groups establish the basic rate and depth of breathing.
D) These groups increase the number of action potentials to the respiratory muscles during inspiration.
E) Two dorsal and two ventral respiratory groups make up the medullary respiratory center.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
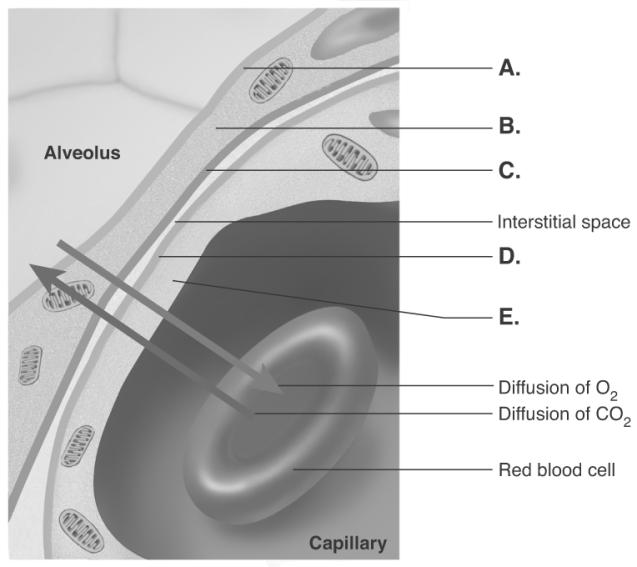 -The diagram illustrates the respiratory membrane. What layer is "D"?
-The diagram illustrates the respiratory membrane. What layer is "D"?
A) basement membrane of capillary endothelium
B) capillary endothelium
C) alveolar epithelium
D) alveolar fluid
E) basement of alveolar epithelium
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does carbon monoxide affect red blood cells (RBCs) ?
A) It causes them to shrivel.
B) The hemoglobin within the RBC bind to carbon monoxide.
C) The hemoglobin rejects carbon monoxide.
D) The RBCs clump together.
E) The carbon monoxide converts to carbon dioxide.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following structures in the order air passes through them during inhalation: (1) alveolar ducts (2) alveolus (3) respiratory bronchiole (4) terminal bronchiole
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 2, 1, 3, 4
C) 4, 3, 1, 2
D) 3, 2, 1, 4
E) 4, 3, 2, 1
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The part of the respiratory system where gas exchange does not occur is called __________ space.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nasal septum
A) divides the nose into superior and inferior chambers.
B) forms the floor of the nasal cavity.
C) is the opening of the nose to the outside environment.
D) is the part of the nose responsible for the sense of smell.
E) divides the nose into right and left chambers.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Direct stimulation of neurons within the dorsal respiratory group would cause an increase in the frequency of action potential in the
A) glossopharyngeal nerve that innervates the pharyngeal muscles.
B) phrenic nerve that innervates the diaphragm.
C) vagus nerve that innervates the smooth muscle of the bronchioles.
D) intercostal nerves to internal intercostals muscles.
E) intercostal nerves to external intercostals muscles.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A greater than normal amount of CO2 in the blood is called
A) hypercapnia.
B) hypoxia.
C) hyperdioxemia.
D) hypodioxemia.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The diagram illustrates the respiratory membrane. What layer is "E"?
-The diagram illustrates the respiratory membrane. What layer is "E"?
A) basement membrane of capillary endothelium
B) capillary endothelium
C) alveolar epithelium
D) alveolar fluid
E) basement of alveolar epithelium
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major regulator of respiration is the plasma concentration of
A) oxygen.
B) carbon dioxide.
C) water vapor.
D) nitrogen.
E) chloride.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pitch of the sound produced by the vocal folds is controlled by the
A) frequency of the vibrations.
B) amplitude of the vibrations.
C) thickness of the thyroid cartilage.
D) size of the glottis.
E) force of air moving past them.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The volume of air available for gas exchange per minute is called the
A) vital capacity.
B) alveolar ventilation.
C) minute respiratory volume.
D) functional residual capacity.
E) respiratory rate.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the appropriate description or definition. -total lung capacity "Enter the letter of the correct description below"
A) sum of the inspiratory reserve, expiratory reserve, tidal, and residual volumes
B) volume of air inspired during a normal inspiration
C) volume of air remaining in lungs after the most forceful expiration
D) sum of the expiratory reserve, inspiratory reserve, and tidal volumes
E) the amount of air that can be forcefully expired after expiration of the normal tidal volume
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 178
Related Exams