A) to cause coughing
B) a mucus-cilia escalator
C) move dirt toward the alveoli
D) All of the choices are correct
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As temperature increases, how would this affect the oxyhemoglobin-dissociation curve?
A) shift it to the left
B) shift it to the right
C) no change
D) shift it up
E) None of these choices is correct
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The olfactory epithelium responsible for the sense of smell is located in the
A) floor of the nasal cavity.
B) wall of the nasal septum.
C) lining of the nasopharynx.
D) cavity of the paranasal sinuses.
E) roof of the nasal cavity.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The walls of the alveoli
A) are composed of simple squamous epithelium.
B) contain several layers of smooth muscle.
C) contain goblet cells.
D) are surrounded by cartilage.
E) are ciliated.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors keeps the alveoli expanded?
A) a pneumothorax
B) negative pleural pressure
C) alveolar pressure being equal to atmospheric pressure
D) a reduction in surfactant
E) negative intra-alveolar pressure
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
__________ is the volume of air inspired during a normal inspiration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mr. Huff and Puff exhales normally; then, using forced expiration, he exhales as much air as possible. The volume of air still remaining in his lungs is called
A) expiratory reserve volume.
B) tidal volume.
C) inspiratory reserve volume.
D) vital capacity.
E) residual volume.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
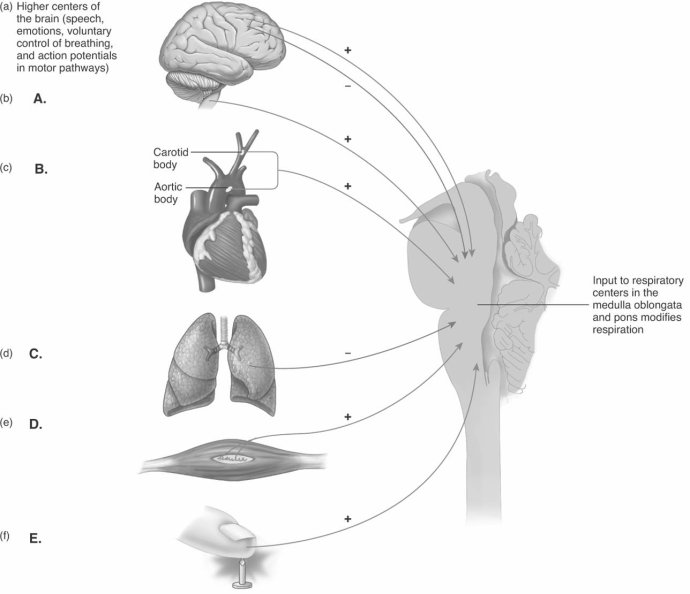 -The diagram illustrates the major regulatory mechanisms of ventilation. What mechanism does "A" represent?
-The diagram illustrates the major regulatory mechanisms of ventilation. What mechanism does "A" represent?
A) Hering-Breuer reflex
B) receptors for touch, temperature, pain stimule
C) medullary chemoreceptors
D) carotid and aortic body chemoreceptors
E) proprioceptors
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hemoglobin that has released its oxygen
A) loses its affinity for oxygen.
B) will dissolve in the plasma.
C) will bind more readily to carbon dioxide.
D) is broken down to heme and globin and excreted.
E) will bind more readily to oxygen.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air in the pleural cavity is called
A) emphysema.
B) respiratory distress syndrome.
C) a pneumothorax.
D) pneumonia.
E) forced expiration.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) levels increase, hemoglobin
A) releases less oxygen to tissues.
B) releases more carbon dioxide to tissues.
C) releases more oxygen to tissues.
D) releases less carbon dioxide to tissues.
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the disorder of the respiratory system with the best description. -cystic fibrosis
A) destruction of the alveolar walls
B) inflammation of the bronchii
C) inherited disease that affects secretory cells lining the lungs
D) replacement of lung tissue with fibrous connective tissue
E) infant stops breathing during sleep
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen is transported in the blood
A) bound to hemoglobin.
B) bound to albumin.
C) dissolved in the plasma.
D) as part of the bicarbonate ion.
E) dissolved in the plasma and bound to hemoglobin.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The auditory tubes open into the
A) fauces.
B) oropharynx.
C) nasopharynx.
D) laryngopharynx.
E) nasal cavity.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the volume of air that can be forcibly expired after expiration of the tidal volume?
A) residual volume
B) inspiratory reserve volume
C) vital capacity
D) expiratory reserve volume
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During exercise, the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
A) shifts to the right.
B) shifts to the left.
C) doesn't shift.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The trachea
A) is located in the pleural cavity.
B) has "C" shaped cartilages that form its anterior and lateral sides.
C) is lined with keratinized squamous epithelium.
D) bifurcates to form the bronchioles.
E) collapses when not in use.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rhythmicity of breathing involves
A) conscious effort and control.
B) stimulation of inspiration. Expiration is automatic.
C) pontine respiratory group as a necessary part.
D) a set pattern of inspiration - expiration that is always the same.
E) the pre-Bötzinger complex of the ventral respiratory group.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a process of respiration?
A) voice production
B) internal respiration
C) ventilation
D) external respiration
E) transport of blood gases in the blood
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pulmonary edema will cause the rate of gas diffusion to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 178
Related Exams