A) thoracic volume increases.
B) pleural pressure increases.
C) the alveolar pressure increases.
D) expiration occurs.
E) thoracic volume decreases.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Increasing ventilation will increase the PO2 and decrease the PCO2, which promotes gas exchange.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each lobe of each lung is supplied by a
A) primary bronchus.
B) secondary bronchus.
C) tertiary bronchus.
D) bronchiole.
E) segmental bronchus.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ventral respiratory group
A) is located in the pons.
B) stimulates the intercostal and abdominal muscles.
C) is part of the pontine respiratory group.
D) is active only in exhalation.
E) stimulates the diaphragm.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mr. Jones has a blood pH of 7.00 and a temperature of 100.5 F. His oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve would
A) shift to the right, causing more O2 to be released to his cells.
B) shift to the left, allowing less O2 to be released to his cells.
C) show no change, allowing the O2 concentration to remain stable.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Constriction of smooth muscle in the bronchioles
A) occurs during periods of exercise.
B) restricts the flow of air into the lungs.
C) decreases ciliary action.
D) increases airflow out of the lungs.
E) does not affect airflow.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Contraction of respiratory muscles are responsible for the movement of air out of the lungs in quiet expiration.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
A decrease in the surface area of the respiratory membrane will cause the diffusion rate to A. increase. B. decrease. C. remain unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will cause a decrease in the surface area of the respiratory membrane?
A) emphysema
B) tuberculosis
C) pneumonia
D) All of the choices will reduce surface area of the respiratory membrane
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an effect of aging on the respiratory system?
A) vital capacity is unchanged
B) minute ventilation rates increase
C) residual volume increases
D) gas exchange in the lungs remains unchanged
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gas exchange between the air in the lungs and the blood takes place in the
A) alveoli.
B) primary bronchi.
C) terminal bronchioles.
D) trachea.
E) respiratory bronchi.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blood oxygen levels
A) are more important than carbon dioxide levels in the regulation of respiration.
B) need to change only slightly to cause a change in respiration rate.
C) within the normal PO2 range have little effect on regulation of respiration.
D) in venous blood and arterial blood are about the same.
E) never change enough to influence respiration.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person has severe damage or disease in the upper area of their right lung. Surgery is necessary. The doctor would need to remove
A) the entire right lung.
B) the superior lobe of the right lung.
C) the apical bronchopulmonary segment of the right lung.
D) only the damaged area of the apical bronchopulmonary segment.
E) the apical, anterior, and posterior segments of the superior lobe.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A molecule of air enters the nose through the external nares. Which of the following is the correct pathway to the trachea?
A) nasal cavity, larynx, pharynx, trachea
B) oral cavity, nasal cavity, larynx, pharynx, trachea
C) nasopharynx, nasal cavity, laryngopharynx, trachea
D) nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea
E) nasal cavity, trachea, larynx, pharynx
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of cells make up about 90% of the alveolar surface?
A) ciliated simple squamous epithelial cells
B) Type I pneumocytes
C) Type II pneumocytes
D) macrophages
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following respiratory membrane layers is closest to air in the alveolus?
A) alveolar epithelium
B) alveolar basement membrane
C) capillary basement membrane
D) capillary endothelium
E) alveolar fluid (with surfactant)
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT part of the respiratory membrane?
A) simple squamous epithelium of the alveolus and its basement membrane
B) interstitial space
C) pulmonary capillary simple squamous epithelium and its basement membrane
D) thick layer of mucus lining the alveolus
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
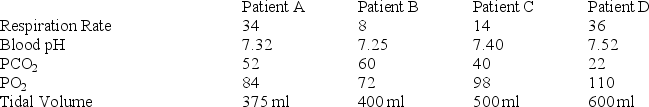 -Which of the patients above is suffering from emphysema?
-Which of the patients above is suffering from emphysema?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The volume of air inspired or expired with each breath is the
A) residual volume.
B) inspiratory reserve volume.
C) tidal volume.
D) expiratory reserve volume.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the disorder of the respiratory system with the best description. -pulmonary fibrosis
A) destruction of the alveolar walls
B) inflammation of the bronchii
C) inherited disease that affects secretory cells lining the lungs
D) replacement of lung tissue with fibrous connective tissue
E) infant stops breathing during sleep
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 178
Related Exams