A) is located in the vascular tunic.
B) is the site of greatest visual acuity.
C) is also called the macula lutea.
D) is on the anterior surface of the eye.
E) contains no photoreceptor cells.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following in correct sequence: (1) gustatory cell depolarizes (2) action potential stimulated in gustatory neurons (3) food substance dissolves in saliva (4) neurotransmitter released by gustatory cell (5) food substance enters taste pore and attaches to receptor on gustatory hair
A) 5, 4, 1, 2, 3
B) 3, 5, 1, 4, 2
C) 5, 3, 1, 4, 2
D) 3, 1, 4, 5, 2
E) 3, 2, 1, 5, 4
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
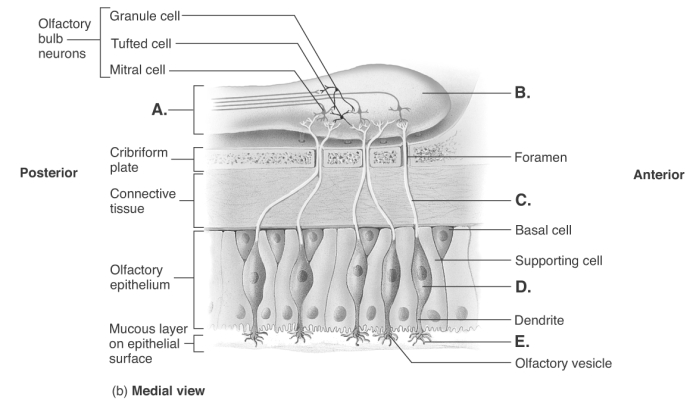 -Olfaction is the sense of smell. What does "E" represent?
-Olfaction is the sense of smell. What does "E" represent?
A) olfactory bulb
B) cilia (olfactory hairs)
C) olfactory neuron
D) axon of olfactory neuron
E) olfactory tract
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following to reflect the correct sequence an action potential would follow to reach the olfactory cortex of the brain: (1) olfactory bulb (2) olfactory cortex (3) olfactory epithelium (4) olfactory tract
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 3, 4, 1, 2
C) 1, 4, 2, 3
D) 3, 1, 4, 2
E) 4, 3, 2, 1
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
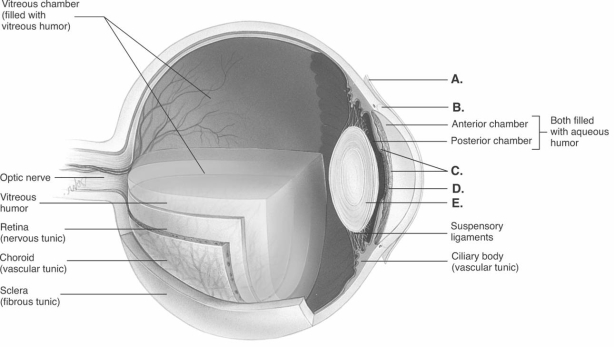 -The figure is a sagittal section of the eye. What does "D" represent?
-The figure is a sagittal section of the eye. What does "D" represent?
A) iris
B) pupil
C) lens
D) conjunctiva
E) cornea
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -tympanic membrane
A) eardrum
B) part of the ear that contains the organ of hearing
C) the pinna and external auditory meatus are part of this
D) fleshy portion of the external ear
E) air-filled space within the temporal bone
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which auditory ossicle is attached to the tympanic membrane?
A) labyrinth
B) incas
C) malleus
D) stapes
E) oval window
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The correct pathway for impulses leaving the retina is
A) photoreceptors, ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and optic nerve.
B) photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and optic nerve.
C) photoreceptors, bipolar cells, optic nerve, and ganglion cells.
D) photoreceptors, ganglion cells, optic nerve, and bipolar cells.
E) ganglion cells, bipolar cells, photoreceptors, and optic nerve.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vitreous humor
A) is produced on a daily basis.
B) is less viscous than aqueous humor.
C) does not contribute to intraocular pressure.
D) helps to hold the lens and retina in place.
E) is located in the anterior chamber.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oscillation of the eyes during the tracking of something in motion is called
A) nystagmus.
B) vertigo.
C) scotoma.
D) ptosis.
E) otitis media.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a part of the bony labyrinth?
A) malleus
B) vestibule
C) cochlear duct
D) tympanic membrane
E) ossicles
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -optic foramen
A) the area that can be seen with the eyes open
B) opening in the orbit through which the optic nerve passes
C) the cerebral area that integrates messages from retina
D) area where medial ganglion cell axons cross over
E) the route of the ganglionic axons beyond the chiasma
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Damage to the chorda tympani in the right ear could result in loss of taste on the right anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve would result in some loss of
A) hearing and balance.
B) hearing and taste.
C) smell.
D) taste.
E) hearing and sight.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is false?
A) Rods cannot detect color.
B) The visual pigment of cones is iodopsin.
C) Most of the optic tract axons terminate in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus.
D) Association neurons in the inner retinal layers modify signals of rods and cones.
E) Most of the optic tract axons terminate in the medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -olfactory vesicle
A) relay olfactory information to the brain and synapse with association neurons in the olfactory bulb
B) area of the brain where the olfactory tracts terminate
C) enlargements on the dendrites of olfactory neurons
D) fibers that connect the olfactory bulb to the cortex
E) the expanded anterior portions of the olfactory nerves
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which tastant is NOT correctly matched with its process of depolarization?
A) salty - Na+
B) umami - G protein
C) bitter - K+
D) sour - H+
E) sweet - G protein
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -palpebrae
A) the angle where the eyelids join
B) the space between the two eyelids
C) another name for the eyelids
D) the membrane that covers the inner surface of the eyelids
E) the membrane that covers the anterior sclera of the eye
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
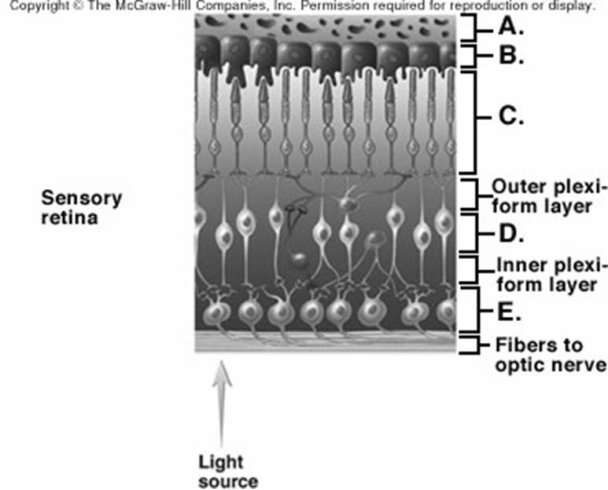 -What is layer "B" on the diagram of the retina?
-What is layer "B" on the diagram of the retina?
A) bipolar layer
B) ganglionic layer
C) choroid
D) pigmented layer
E) photoreceptor layer
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following functions is carried out by both aqueous and vitreous humor?
A) cleanses the eye
B) nourishment of the eye
C) refraction of light rays
D) generation of a visual image
E) control the amount of light entering the eye
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 195
Related Exams