A) olfactory bulb
B) cilia (olfactory hairs)
C) olfactory neuron
D) axon of olfactory neuron
E) olfactory tract
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The receptor cells for which of the following special senses are bipolar neurons?
A) equilibrium
B) hearing
C) smell
D) taste
E) touch
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for a molecule to be detected by the olfactory neurons, it must
A) be present in high concentrations.
B) be one of the seven primary classes of odors.
C) be dissolved in fluid covering the olfactory epithelium.
D) interact with the mechanoreceptors of the olfactory hair membrane.
E) enter the nose slowly.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Light and dark adaptation involves
A) pupillary reflexes.
B) variations in rod and cone function.
C) changes in the amount of available rhodopsin.
D) pupillary reflexes and changes in the amount of available rhodopsin.
E) pupillary reflexes, variations in rod and cone function and changes in the amount of available rhodopsin.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures is part of the vascular tunic?
A) iris
B) retina
C) optic disc
D) fovea centralis
E) cornea
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When you try to focus on the tip of your nose,
A) the pupils dilate.
B) the ciliary muscles relax.
C) the lens becomes more spherical.
D) the tension on the suspensory ligament increases.
E) the lens becomes flatter.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ability of the olfactory system to adapt to a particular odor may involve
A) sensitivity of the olfactory cortex.
B) an increase in the sensitivity at the receptor sites.
C) neurons from the medial olfactory area stimulating mitral cells and tufted cells.
D) the intermediate olfactory area sending inhibiting impulses to the olfactory bulb.
E) molecules that do not bind to receptors anymore.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of taste has the lowest threshold?
A) sweet
B) bitter
C) salty
D) sour
E) umami
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the description with the most appropriate structure. -auditory tube
A) structures that produce earwax
B) fluid in the membranous labyrinth
C) fluid between the membranous and bony labyrinth
D) ossicles connect this structure to eardrum
E) connects the middle ear to the pharynx
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -visual cortex
A) the area that can be seen with the eyes open
B) opening in the orbit through which the optic nerve passes
C) the cerebral area that integrates messages from retina
D) area where medial ganglion cell axons cross over
E) the route of the ganglionic axons beyond the chiasma
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the description with its correct name. -myopia
A) difficulty seeing distant objects
B) a type of refractory error
C) clouding of the lens of the eye
D) increased intraocular pressure that can lead to loss of vision
E) loss of acute central vision
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
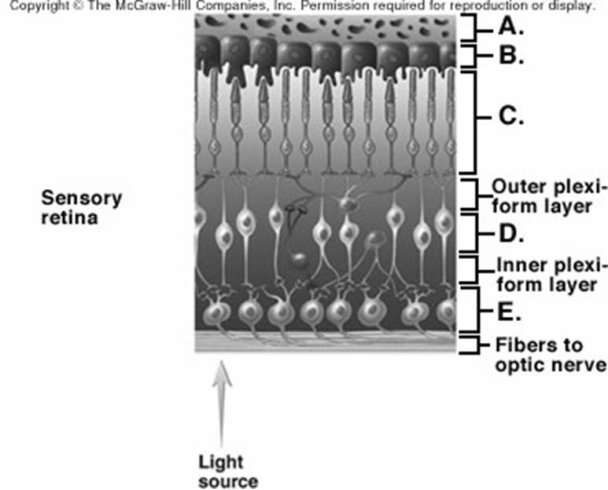 -What is layer "E" on the diagram of the retina?
-What is layer "E" on the diagram of the retina?
A) bipolar layer
B) ganglionic layer
C) choroid
D) pigmented layer
E) photoreceptor layer
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -palpebral conjunctiva
A) the angle where the eyelids join
B) the space between the two eyelids
C) another name for the eyelids
D) the membrane that covers the inner surface of the eyelids
E) the membrane that covers the anterior sclera of the eye
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a primary odor class?
A) umami
B) floral
C) putrid
D) pepperminty
E) ethereal
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A ringing in the ears is considered
A) tinnitus.
B) trachoma.
C) nystagmus.
D) mydriasis.
E) otitis media.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What is layer "A" on the diagram of the retina?
-What is layer "A" on the diagram of the retina?
A) bipolar layer
B) ganglionic layer
C) choroid
D) pigmented layer
E) photoreceptor layer
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The utricle and saccule are involved in
A) static balance.
B) kinetic balance.
C) hearing low intensity sounds.
D) hearing high intensity sounds.
E) evaluating movements of the head.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A) sclera - ciliary body
B) iris - sphincter pupillae
C) retina - canal of Schlemm
D) vitreous humor - anterior chamber
E) aqueous humor - vitreous chamber
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The outermost tunic of the eyeball is the
A) iris.
B) sclera.
C) retina.
D) choroid.
E) conjunctiva.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the structure with the appropriate description. -iris
A) photoreceptor cells that function in black and white vision
B) photoreceptor cells that function in color vision
C) the opening in the iris
D) the innermost tunic of the eye
E) a pigmented contractile structure
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 195
Related Exams