B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -hippocampus A
A) the part of the brain involved in the actual declarative memory
B) the largest of the cerebral commissures
C) a factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) a series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) a part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a person is exposed to temperature extremes, why is it difficult to distinguish hot from cold objects?
A) Temperature perception requires more than one type of receptor.
B) Temperatures above 37 degrees centigrade actually stimulate the cold receptors.
C) At extremes, pain receptors are stimulated by both very hot and very cold objects.
D) Most temperature receptors cannot differentiate hot from cold.
E) Pain receptors are inhibited by both very hot and very cold objects.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to Wernicke area would result in
A) facial paralysis.
B) facial tics.
C) aphasia.
D) "seeing stars".
E) apraxia.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The conscious awareness of stimuli received by sensory receptors is called perception.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient with a lesion in the hippocampus may have decreased
A) sensory memory.
B) Pavlovian reflexes.
C) procedural memory.
D) declarative memory.
E) short term memory.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the sensation with the appropriate receptor type. -Pacinian corpuscles C
A) mechanoreceptors
B) thermoreceptors
C) nociceptors
D) chemoreceptors
E) photoreceptors
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
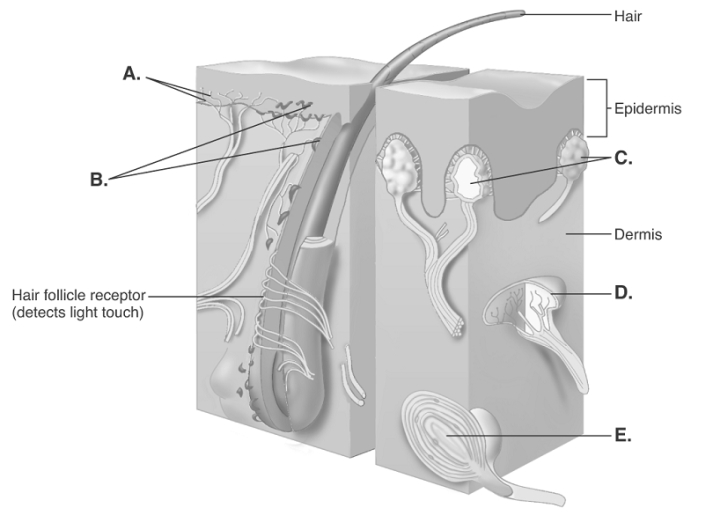 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "E" represent?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "E" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
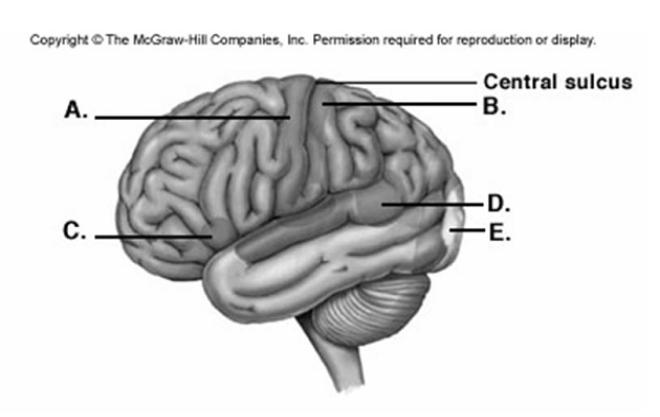 -Label area "D" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "D" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the kind of pain to the appropriate description. -peripheral sensitization D
A) may occur in amputees
B) migraine headaches are an example of this
C) pain from internal organs sensed in the skin
D) peripheral tissue damage causes increased sensitivity in area of damage
E) increased sensitivity of CNS to tissue damage
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "B" represent?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "B" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) corticospinal tract - movements, especially the hands
B) corticobulbar tract - movements in the head and face
C) rubrospinal tract - two-point discrimination
D) vestibulospinal tract - maintains upright posture
E) reticulospinal - posture adjustments and walking
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major source of sensory input into the limbic system is the sense of
A) vision.
B) taste.
C) touch.
D) smell.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary somatic sensory or general sensory area is located in
A) the postcentral gyrus.
B) the precentral gyrus.
C) the prefrontal gyrus.
D) the central sulcus.
E) the superior temporal gyrus.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a visceral sensation?
A) pain
B) touch
C) temperature
D) proprioception
E) balance
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of procedural or implicit memory?
A) remembering your name
B) riding a bicycle
C) locating Russia on a globe
D) being afraid of snakes
E) reciting a poem
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -memory engram D
A) the part of the brain involved in the actual declarative memory
B) the largest of the cerebral commissures
C) a factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) a series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) a part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The portion of the dorsal column/medial lemniscal tract that carries proprioceptive sensations from nerve endings in the feet and legs is the
A) nucleus gracilis.
B) nucleus cuneatus.
C) fasciculus gracilis.
D) fasciculus cuneatus.
E) fasciculus nucleus.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The perception of position and movement of body parts is
A) sensation.
B) kinesthesia.
C) proprioception.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of brain wave with its appropriate description. -delta waves C
A) usually occur in children or in adults experiencing frustration
B) observed in a person who is awake, quiet, and resting, with eyes closed
C) occur in deep sleep, infancy and patients with brain disorders
D) occur during intense mental activity
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 132
Related Exams