A) Sensory neurons stimulate muscles to contract.
B) There are very few blood vessels in skeletal muscle.
C) Every muscle fiber receives a branch of an axon from the nerve.
D) There are very few nerve fibers in a muscle.
E) All of these are true.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A drug that interferes with the active transport of calcium ions from the sarcoplasm back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum would result in
A) relaxation of the muscle fiber.
B) contraction with no relaxation.
C) muscle hypertrophy.
D) fibrosis of the muscle.
E) an imbalance of blood calcium.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscles exhibit the property of excitability. This means that the muscle
A) shortens its length.
B) recoils to its original resting length.
C) stretches beyond its normal length.
D) responds to stimulation by the nervous system.
E) excites itself.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
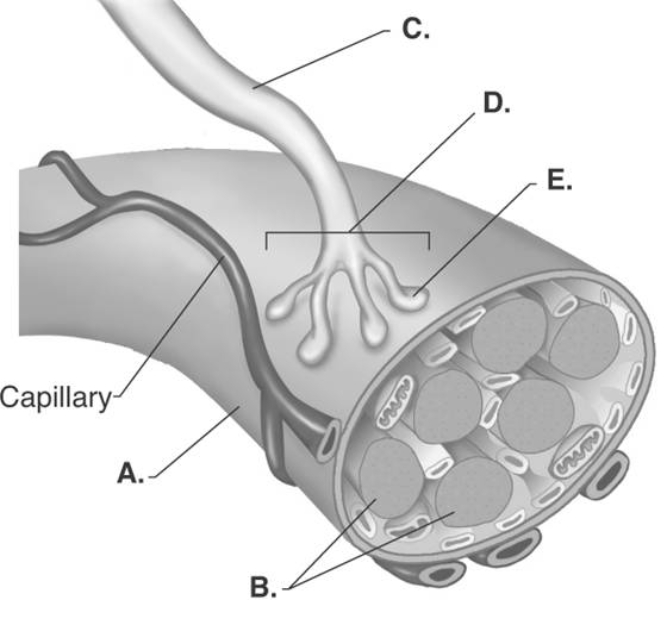 -The figure illustrates the neuromuscular junction. What does "B" represent?
-The figure illustrates the neuromuscular junction. What does "B" represent?
A) presynaptic terminal
B) muscle fiber
C) neuromuscular junction
D) axon branch
E) myofibrils
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Functionally, smooth muscle
A) is well adapted to anaerobic metabolism.
B) exhibits autorhythmic contractions.
C) contracts in response to slow increases in length.
D) is unable to maintain tone.
E) rapidly develops an oxygen debt.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
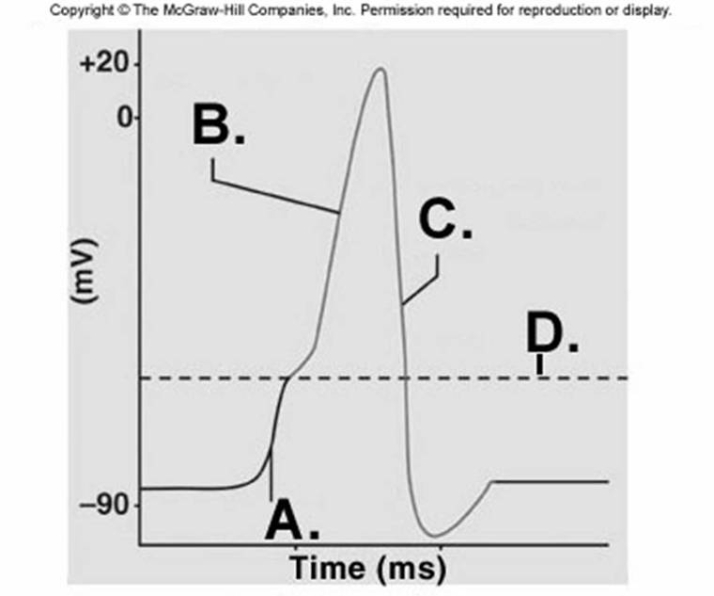 -What does "C" represent on the diagram?
-What does "C" represent on the diagram?
A) threshold
B) depolarization
C) depolarization phase of action potential
D) repolarization phase of action potential
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time between application of the stimulus to a motor neuron and the beginning of contraction is called the _____ phase.
A) contraction
B) relaxation
C) latent or lag
D) refractory
E) threshold
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The greater the overlap of actin and myosin, the stronger the contraction.
B) Overstretching a muscle will increase its tension.
C) Optimal actin and myosin overlap will produce maximal contraction.
D) The greatest amount of tension is achieved when actin and myosin do not overlap.
E) Tension is great when actin and myosin overlap as much as they can.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sarcoplasmic reticulum
A) stores calcium ions.
B) shortens during muscle contraction.
C) transmits nerve impulses to the myofibrils.
D) connects adjacent sarcomeres.
E) covers the muscle fiber.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lack of acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft would result in
A) a decrease in acetylcholine production by the motor neuron.
B) continuous stimulation of the postsynaptic membrane.
C) rapid degradation of acetylcholine.
D) relaxation of the muscle.
E) continuous stimulation of the presynaptic membrane.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
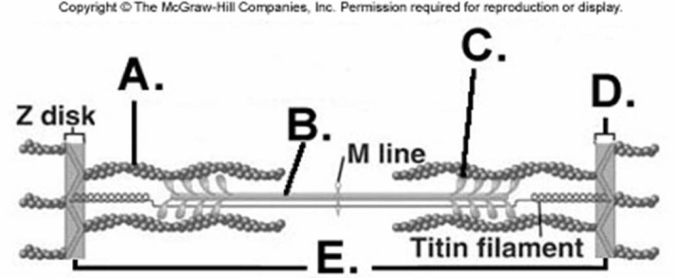 -What does "D" represent on the diagram?
-What does "D" represent on the diagram?
A) myosin myofilament
B) actin myofilament
C) sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) cross-bridge
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) Muscle fatigue has no influence on the force of contractions.
B) A threshold stimulus will cause contraction of a muscle fiber.
C) A subthreshold stimulus causes a muscle contraction.
D) Motor units do not obey the "all or none" law.
E) A threshold stimulus will not affect motor units.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In smooth muscle, most of the calcium needed for muscle contraction
A) is in the dense bodies.
B) enters from extracellular fluid.
C) is attached to the intermediate filaments.
D) must be activated by myosin kinase.
E) is stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue would cause flexion and extension of the arm?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rigor mortis occurs after death because
A) cross-bridges form but can't release.
B) calcium is actively transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) anaerobic respiration is occurring.
D) myosin levels decline at death.
E) cross-bridges never form.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sites where a chemical substance is transmitted from the presynaptic terminal of an axon to the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber are called
A) neuromuscular junctions.
B) sarcomeres.
C) myofilaments.
D) Z disks.
E) cell body of neuron.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations between contractions is called
A) complete tetanus.
B) incomplete tetanus.
C) involuntary paralysis.
D) all or none tetanus.
E) treppe.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue causes contraction of the heart?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a cross-bridge?
A) a protein found along the groove of the F-actin double helix
B) a T tubule and two adjacent terminal cisternae
C) the combination of myosin heads with active sites on actin molecules
D) the movement of myosin head while attached to actin myofilament
E) after exercise, the oxygen taken in that exceeds the oxygen required for resting metabolism
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are dense bodies and intermediate filaments in smooth muscle?
A) can rapidly develop action potentials
B) shallow invaginations of cell membrane
C) relatively constant tension maintained for a period of time
D) intracellular cytoskeleton
E) enzyme that removes phosphate from myosin
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 194
Related Exams