A) frontal lobe.
B) temporal lobe.
C) occipital lobe.
D) parietal lobe.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary somatic sensory or general sensory area is located in
A) the postcentral gyrus.
B) the precentral gyrus.
C) the prefrontal gyrus.
D) the central sulcus.
E) the superior temporal gyrus.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Visceroreceptors are receptors associated with joints,tendons,and other connective tissue.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the nervous system ages
A) reflexes become faster.
B) cutaneous sensation becomes more acute.
C) blood pressure decreases.
D) reflexes become slower.
E) size and weight of the brain increases.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Amputees frequently perceive pain in the amputated structure.This type of pain is called
A) chronic pain.
B) phantom pain.
C) referred pain.
D) gate pain.
E) ghost pain.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
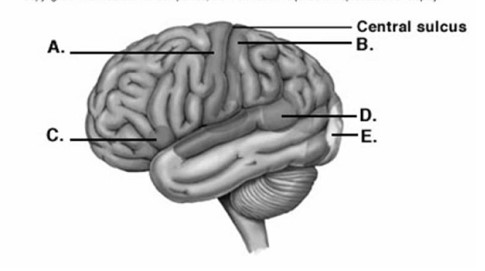 -Label area "A" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "A" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A series of neurons involved in long-term retention of a thought is called
A) an EEG.
B) a brain wave.
C) a memory engram.
D) short-term memory.
E) a memory trace.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Slowly adapting proprioceptors that would let you know the position of your thumb without looking at it are known as
A) phasic receptors.
B) primary receptors.
C) secondary receptors.
D) tonic receptors.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The extrapyramidal system
A) controls the speed of skilled movements.
B) maintains control of unconscious movements.
C) interprets cutaneous perception.
D) projects sensory information from the medulla to the cerebrum.
E) control facial expression,mastication,and tongue movements.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you feel someone touch you on the shoulder,the person has stimulated a(n) ____ sense.
A) special
B) somatic
C) visceral
D) undifferentiated
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following nerve endings are found in the skin EXCEPT
A) Pacinian corpuscles.
B) proprioceptors.
C) Ruffini end organs.
D) Merkel disks.
E) Meissner corpuscles.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A baseball pitcher was hit on the side of the head by a line drive.When he was revived,he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had.This was because
A) short-term memory had not been converted to working memory.
B) he lost both working and short-term memory.
C) long-term memory had not been converted to working memory.
D) he lost long-term memory.
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In short-term memory,
A) information is retained for less than a second.
B) the frontal lobe plays the most important role.
C) current information is lost when new information is presented.
D) there is increased synaptic activity by long-term potentiation.
E) there is consolidation of information.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wernicke area is necessary for
A) motivation.
B) understanding and formulating coherent speech.
C) initiating the muscular movements of speech.
D) processing visual images.
E) smiling.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Label area "B" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "B" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mechanoreceptors respond to
A) compression of receptors.
B) irritation of nerve endings.
C) light striking the receptors.
D) binding of molecules to membrane receptors.
E) a change in temperature.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the kind of pain to the appropriate description. -central sensitization E
A) may occur in amputees
B) migraine headaches are an example of this
C) pain from internal organs sensed in the skin
D) peripheral tissue damage causes increased sensitivity in area of damage
E) increased sensitivity of CNS to tissue damage
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary motor area
A) contains sensory neurons for the face in its inferior portion.
B) contains a smaller area for control of the hands than for control of the legs.
C) contains neurons that control smooth muscle.
D) contains more motor neurons for the thighs than the mouth.
E) contains a larger area for control of the hand and fingers than for control of the arm and elbow.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a descending pathway in the spinal cord?
A) fasciculus gracilis
B) corticospinal tract
C) spinothalamic tract
D) spinoreticular tract
E) trigeminothalamic tract
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
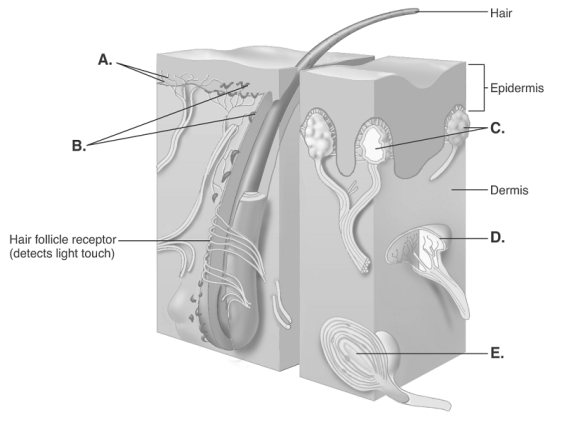 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin.What structure does "E" represent?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin.What structure does "E" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 132
Related Exams