A) changes in the magnitude of the action potential.
B) the frequency of the action potentials.
C) the length of time action potentials are produced.
D) both the frequency and the length of time action potentials are produced.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A stimulus either causes an action potential or it doesn't.This is called
A) an all-or-none response.
B) a graded response.
C) a latent period response.
D) a relative refractory response.
E) a local response.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The junction of a neuron with another cell is a/an
A) synapse.
B) ganglion.
C) receptor.
D) effector.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in resting membrane potential confined to a small area is called a(n)
A) local potential.
B) action potential.
C) summated potential.
D) after potential.
E) resting membrane potential.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some cells,an afterpotential occurs because
A) the sodium ions continue to enter the cell after depolarization is finished.
B) there is prolonged,elevated permeability to potassium during repolarization.
C) the sodium-potassium pump is actively exchanging ions across the membrane.
D) the extracellular Na+ ion concentration is reduced.
E) the permeability to sodium continues longer than necessary.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A neuron with several dendrites and a single axon would be called a ____________ neuron.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each voltage-gated Na+ ion channel has two voltage sensitive gates: an activation gate and an inactivation gate.Which of the following would occur during depolarization?
A) Activation gates are open; inactivation gates are closed.
B) Activation gates are closed; inactivation gates are open.
C) Both activation and inactivation gates are open.
D) Both activation and inactivation gates are closed.
E) None of these events occurs during depolarization.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What inhibitory neurotransmitter is blocked in strychnine poisoning?
A) glycine
B) acetylcholine
C) glutamate
D) adenosine
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of neuroglial cells provide support and nutrition to sensory ganglia in the PNS?
A) Schwann cells
B) microglia
C) ependymal cells
D) satellite cells
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
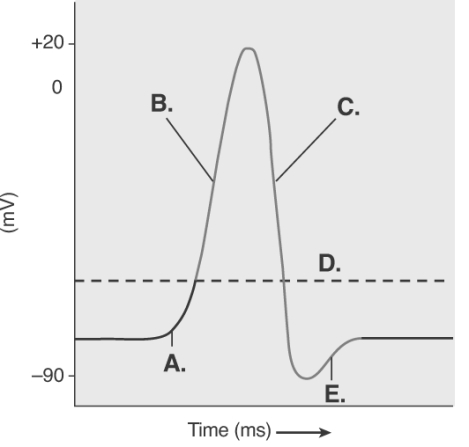 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "B" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "B" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nervous system
A) monitors internal and external stimuli.
B) transmits information in the form of action potentials.
C) interprets or assesses information.
D) maintains homeostasis.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical synapses are characterized by
A) the release of neurotransmitter by the presynaptic terminal.
B) connexons that connect the pre- and postsynaptic cells.
C) the presence of receptors for neurotransmitters on the presynaptic terminal.
D) the absence of gap junctions.
E) receptors located only on the presynaptic terminal.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurotransmitters are released from the
A) epineurium.
B) synaptic cleft.
C) presynaptic terminal.
D) postsynaptic membrane.
E) calcium channels.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person who has seizures might have a deficit of which of the following?
A) GABA
B) dopamine
C) glutamate
D) serotonin
E) histamine
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the neuroglial cell with its function. -oligodendrocyte
A) influence function of blood-brain barrier
B) macrophages in CNS
C) produce cerebrospinal fluid
D) form myelin sheath around axons in CNS
E) form myelin sheath around part of the axon in the PNS
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An IPSP is inhibitory because it
A) changes the threshold of the neuron.
B) hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane.
C) prevents Ca2+ entry into the presynaptic terminal.
D) reduces the amount of neurotransmitter released by the presynaptic terminal.
E) depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -higher inside cell
A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events will lead to depolarization?
A) an increase in K+ ions in the extracellular fluid
B) a decrease in K+ ions in the extracellular fluid
C) an increase in the rate of diffusion of K+ ions from cells
D) an increase in Na+ ions in the extracellular fluid
E) None of these events would cause depolarization.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blood-brain barrier
A) permits passage of foreign substances from the blood to the neurons.
B) prohibits the transport of amino acids and glucose to the neurons.
C) prohibits the removal of waste materials from the neurons.
D) protects neurons from toxic substances in the blood.
E) does not prevent fluctuations in the composition of the blood from affecting the functions of the brain.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The speed of an action potential depends upon
A) whether an axon is myelinated or not myelinated.
B) thickness of the myelin sheath.
C) the diameter of the axon.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 155
Related Exams