A) astrocytes
B) microglial cells
C) oligodendrocytes
D) macrophages
E) ependymal cells
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptor molecules in synapses
A) tend to concentrate on presynaptic terminals.
B) bind irreversibly with neurotransmitter.
C) have a high degree of specificity.
D) serve as channel proteins.
E) can bind to any molecule in the synapse.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the correct definition. -Resting Membrane Potential
A) a small change in the resting membrane potential confined to a small area
B) a charge difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in an unstimulated state
C) a larger change in resting membrane potential that spreads over entire surface of a cell
D) membrane becomes more positive when sodium ions diffuse into cell
E) return to the resting membrane potential
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two action potentials arrive simultaneously at two different presynaptic terminals that synapse with the same postsynaptic neuron,
A) the direction of the action potential is reversed.
B) temporal summation occurs.
C) spatial summation occurs.
D) hyperpolarization occurs.
E) threshold is never reached.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The motor neurons responsible for making a fist are
A) tripolar.
B) bipolar.
C) multipolar.
D) pseudo-unipolar.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the neuroglial cell with its function. -ependymal cells
A) influence function of blood-brain barrier
B) macrophages in CNS
C) produce cerebrospinal fluid
D) form myelin sheath around axons in CNS
E) form myelin sheath around part of the axon in the PNS
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding voltage-gated K+ channels is true?
A) These channels have only one gate.
B) These channels open more slowly than Na+ channels.
C) Once open,these channels remain open until repolarization is complete.
D) These channels are specific for potassium.
E) All of these statements are true.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the only neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction?
A) serotonin
B) acetylcholine
C) dopamine
D) glutamate
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to a postsynaptic membrane would
A) increase neurotransmitter release.
B) decrease the release of neurotransmitter.
C) increase neurotransmitter production.
D) interfere with the ability to respond to neurotransmitter.
E) destroy vesicles containing neurotransmitter.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential) ,there is a
A) net movement of sodium ions out of the cells.
B) net movement of chloride ions into the cells.
C) decrease in action potential amplitude.
D) local hyperpolarization.
E) local depolarization.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in the number of voltage-gated Ca2+ ion channels in the presynaptic terminal would
A) enhance transmission across the synapse.
B) reduce or inhibit transmission across the synapse.
C) have no effect on transmission across the synapse.
D) alter receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
E) increase exocytosis.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
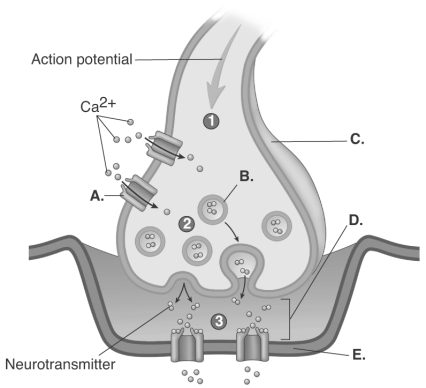 -The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse.What does "E" represent?
-The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse.What does "E" represent?
A) postsynaptic membrane
B) synaptic cleft
C) synaptic vesicle
D) voltage-gated calcium channel
E) presynaptic terminal
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
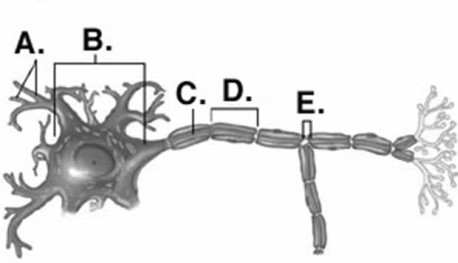 -Identify structure "D" on the neuron.
-Identify structure "D" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) neuron cell body (soma)
D) dendrites
E) axon
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enkephalins produce presynaptic inhibition in neurons transmitting pain signals.Increased levels of enkephalins will
A) increase awareness of pain.
B) decrease awareness of pain.
C) increase amount of pain.
D) decrease amount of pain.
E) have no effect on awareness or amount of pain.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The function of acetylcholinesterase is to
A) open voltage-gated sodium gates.
B) breakdown acetylcholine in the synapse.
C) produce an IPSP on the postsynaptic membrane.
D) metabolize norepinephrine.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
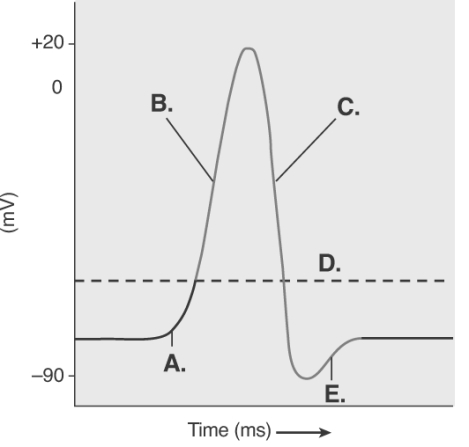 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "E" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "E" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rapid removal or destruction of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
A) may affect the ability of the postsynaptic membrane to generate action potentials.
B) generates local potentials in the presynaptic terminal.
C) is necessary for synaptic transmission.
D) may lead to action potentials.
E) may stop exocytosis.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describe events that occur as a result of a local potential reaching threshold?
A) Activation gates of Na+ ion channels begin to close.
B) Inactivation gates of Na+ ion channels begin to open.
C) A positive feedback cycle develops in which depolarization causes activation gates of Na+ ion channels to open.
D) K+ ion channels begin to close.
E) Inactivation gates of Na+ ion channels begin to open and a positive feedback cycle develops in which depolarization causes activation gates of Na+ ion channels to open.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The resting plasma membrane is more permeable to Na+ than K+.
B) The resting membrane potential never reaches an equilibrium point.
C) The resting membrane potential is proportional to the tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell.
D) Negatively charged Cl- ions are attracted by negative charges in the cell.
E) The purpose of the sodium-potassium exchange pump is to create an equilibrium of ion concentrations.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Gray matter has little myelination,whereas white matter has abundant myelination.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 155
Related Exams