A) supinator
B) triceps brachii
C) brachialis
D) pronator quadratus
E) brachioradialis
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which muscle fixes the clavicle or elevates the first rib?
A) levator scapulae
B) serratus anterior
C) pectoralis minor
D) subclavius
E) rhomboideus major
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following muscles of the leg,which one is on the anterior side of the leg?
A) gastrocnemius
B) soleus
C) tibialis anterior
D) tibialis posterior
E) peroneus longus
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The orbicularis oris muscle
A) puckers the mouth for kissing.
B) contributes to pouting.
C) contributes to laughing and smiling.
D) causes crow's feet wrinkles.
E) raises the eyelid.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
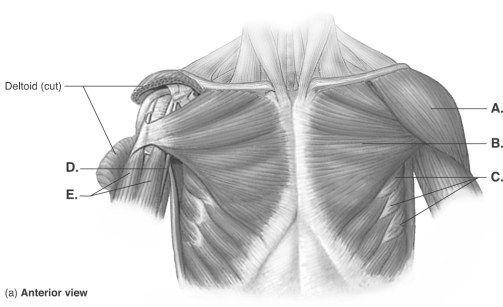 -What does "D" represent?
-What does "D" represent?
A) coracobrachialis
B) deltoid
C) pectoralis major
D) biceps brachii
E) serratus anterior
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An antagonist is
A) a muscle working in opposition to another muscle.
B) the end of the muscle where the action occurs.
C) the muscle that does most of the movement.
D) the stationary end of the muscle.
E) a group of muscles that work together to cause movement.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
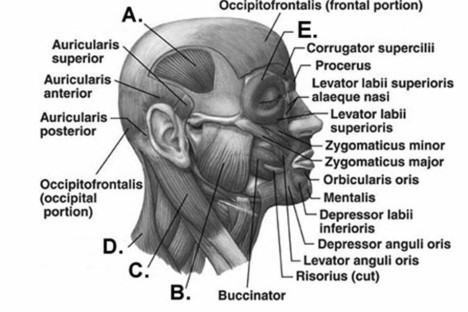 -Label muscle "E" on the diagram.
-Label muscle "E" on the diagram.
A) orbicularis oculi
B) temporalis
C) trapezius
D) sternocleidomastoid
E) masseter
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gluteus maximus
A) does most of the work in "sit-ups."
B) accounts for a sprinter's stance.
C) allows one to sit cross-legged.
D) is used in the knee-jerk reflex.
E) is a common site for injections.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which muscle extends the big toe?
A) tibialis anterior
B) soleus
C) extensor digitorum longus
D) extensor hallicus longus
E) fibularis brevis
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following muscles extends the forearm and has its insertion on the ulna?
A) deltoid
B) biceps brachii
C) triceps brachii
D) brachialis
E) coracobrachialis
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the body's lever systems,the
A) joint represents the fulcrum point.
B) force or pull is applied by the bone.
C) fulcrum is the part being moved.
D) weight is the muscle mass.
E) lever is a pivot point.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which muscle extends the four lateral toes?
A) tibialis anterior
B) soleus
C) extensor digitorum longus
D) extensor hallicus longus
E) fibularis brevis
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscles that change the shape of the tongue are called
A) extrinsic muscles.
B) deglutition muscles.
C) masseter muscles.
D) intrinsic muscles.
E) suprahyoid muscles.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The teres major and teres minor are not involved in
A) extension of the arm.
B) adduction of the arm.
C) medial rotation of the arm.
D) lateral rotation of the arm.
E) flexion and abduction of the arm.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bulge of the calf is caused by the ___ and___ muscles.
A) sartorius; piriformis
B) gastrocnemius; soleus
C) peroneus longus; plantaris
D) extensor hallucis longus; flexor hallucis longus
E) calcaneal; peroneal
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which muscle rotates and protracts the scapula,and elevates the ribs?
A) levator scapulae
B) serratus anterior
C) pectoralis minor
D) subclavius
E) rhomboideus major
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents a class I lever system?
A) crossing your legs
B) hyperextension of the head
C) standing on your tiptoes
D) flexion of the elbow to elevate the hand
E) lifting weight with your arm
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Contraction of the inferior rectus muscle directs the pupil to look
A) up.
B) obliquely.
C) to the side.
D) to the nose.
E) down.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans
A) back muscles are strong to maintain erect posture.
B) deep back muscles extend from the vertebrae to the ribs.
C) most of the muscle mass in the lower back is from the spinalis muscle.
D) back muscles are not very strong.
E) back muscles are similar in strength to the back muscles of cattle.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The prime mover is
A) a muscle working in opposition to another muscle.
B) the end of the muscle where the action occurs.
C) the muscle that does most of the movement.
D) the stationary end of the muscle.
E) a group of muscles that work together to cause movement.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 135
Related Exams