A) contraction cannot occur.
B) relaxation cannot occur.
C) sodium ions will be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum instead.
D) the active sites are left exposed.
E) the action potential travels into the muscle anyway.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about skeletal muscle?
A) Sensory neurons stimulate muscles to contract.
B) There are very few blood vessels in skeletal muscle.
C) Every muscle fiber receives a branch of an axon from the nerve.
D) There are very few nerve fibers in a muscle.
E) All of these are true.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plasma membrane of an excitable cell is more permeable to potassium ions because
A) of its positive electrical charge.
B) there are more leak ion channels for K+ than Na+.
C) protein molecules cannot exit through the cell membrane.
D) calcium ions block Na+ and Cl- channels.
E) there are more gated channels for K+.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Actin myofilaments
A) resemble bundles of minute golf clubs.
B) contain both myosin and tropomyosin.
C) are held in place by the M line.
D) contain strands of fibrous actin.
E) are the thickest proteins in muscle.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following changes have the potential to dramatically affect the potential difference across the plasma membrane?
A) increased permeability of the membrane to sodium ions
B) increased intracellular concentration of potassium ions
C) any change in the rate at which the sodium-potassium pump works
D) increased permeability of the membrane to sodium ions and increased intracellular concentration of potassium ions
E) increased permeability of the membrane to sodium ions,increased intracellular concentration of potassium ions and any change in the rate at which the sodium-potassium pump works
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In excitation-contraction coupling,
A) calcium ions must bind with myosin to expose active sites on actin.
B) myosin heads bind to exposed active sites on actin.
C) cross-bridges form between myosin heads and calcium ions.
D) movement of the troponin-tropomyosin complex causes actin myofilaments to slide.
E) ATP binds to actin myofilaments.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscle hypertrophy results from increased numbers of
A) myofibrils and sarcomeres.
B) muscle fibers.
C) motor units.
D) muscles.
E) muscle cells.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth muscle
A) responds in an all-or-none fashion.
B) depolarizes when both sodium and calcium ions diffuse into the cell.
C) has fast waves of depolarization.
D) has fast waves of repolarization.
E) has a resting membrane potential that is more negative than skeletal muscle fibers.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electrical properties of cells are the result of
A) ion concentration differences across the plasma membrane.
B) receptor sites that are present on the plasma membrane.
C) phosphorylation reactions within the cytoplasm.
D) phospholipids in the cell membrane.
E) None of these choices is correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue has cells that branch?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
D) both skeletal and cardiac muscle
E) both cardiac and smooth muscle
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A waste product of anaerobic respiration in muscle cells is
A) uric acid.
B) hydrochloric acid.
C) lactic acid.
D) carbonic acid.
E) pyruvic acid.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aerobic exercise
A) increases vascularity of muscle.
B) develops fatigue-resistant fast-twitch fibers.
C) can increase the efficiency of slow-twitch fibers.
D) can increase the number of mitochondria in muscle cells.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a known effect of illegal use of anabolic steroids in large dosages?
A) increased muscle size
B) kidney damage
C) diminished testosterone secretion
D) increased cardiovascular fitness
E) sterility
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are similar in that they both
A) are under involuntary control.
B) are striated.
C) are widely distributed in the body.
D) have multiple nuclei.
E) are under voluntary control.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When skeletal muscle is producing carbon dioxide and water while making ATP,which chemical processes could be active at this time?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) aerobic respiration
C) both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
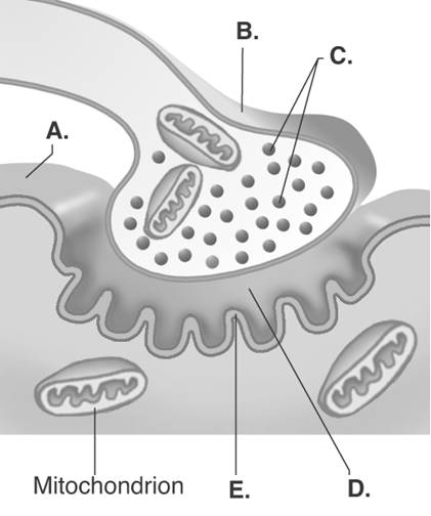 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "C" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "C" represent?
A) synaptic vesicles
B) synaptic cleft
C) sarcolemma
D) presynaptic terminal
E) postsynaptic membrane
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Callie is a world class marathon runner.Which of the descriptions about her dominant type of skeletal muscle is FALSE?
A) They split ATP slowly.
B) They have large deposits of myoglobin.
C) They are well adapted to anaerobic activity.
D) They have a well developed blood supply.
E) They have low glycogen stores.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth muscle is regulated by all of the following except
A) the autonomic nervous system.
B) neurotransmitters.
C) the somatic nervous system.
D) hormones.
E) prostaglandins.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "B" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "B" represent?
A) synaptic vesicles
B) synaptic cleft
C) sarcolemma
D) presynaptic terminal
E) postsynaptic membrane
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "D" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction.What does "D" represent?
A) synaptic vesicles
B) synaptic cleft
C) sarcolemma
D) presynaptic terminal
E) postsynaptic membrane
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 189
Related Exams