B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What determines the difference between a variable and a fixed cost?
A) Whether the total cost changes when activity levels change.
B) Whether the total cost is relevant to a particular decision.
C) Whether the total cost can be traced to a specific cost object.
D) Whether the total cost is related to manufacturing or nonmanufacturing activities.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the primary goal of accounting?
A) To set long-term goals and objectives.
B) To arrange for the necessary resources to achieve a plan.
C) To provide information for decision making.
D) To motivate others to work towards a plan's success.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of reports is more characteristic of managerial accounting than financial accounting?
A) An internal report used by management.
B) An external report used by investors.
C) A report prepared according to GAAP.
D) A report prepared periodically (monthly,quarterly,annually) .
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Product costs are reported
A) only on the balance sheet.
B) only on the income statement.
C) on the balance sheet before goods are sold,and on the income statement after goods are sold.
D) on the income statement before goods are sold,and on the balance sheet after goods are solD.Product costs are counted as inventory (an asset) until the product is sold,at which point they are reported as Cost of Goods Sold on the income statement.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accounting is primarily intended to facilitate
A) starting a business.
B) decision making.
C) ethics investigations.
D) cost tracing.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a cost to be relevant,it must
A) differ between decision alternatives.
B) have already been incurred.
C) not influence a decision.
D) not be a differential cost.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Robin Company has the following balances for the current month: What is Robin's total manufacturing overhead?
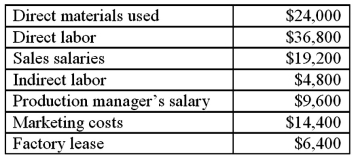
A) $14,400
B) $28,800
C) $20,800
D) $33,600
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Costs that can be traced to a specific cost object are
A) opportunity costs.
B) direct costs.
C) indirect costs.
D) irrelevant costs.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prime costs are the same as
A) Manufacturing costs minus non-manufacturing costs.
B) Manufacturing costs minus manufacturing overhead.
C) Manufacturing costs minus fixed costs.
D) Manufacturing costs minus direct materials.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Properly applied,ethics provide a clear right or wrong answer to the business situations facing accountants and managers.Ethics refers to the standards of conduct for judging right from wrong,honest from dishonest,and fair from unfair.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes one of the Directing/Leading functions of management?
A) Setting short and long-term objectives
B) Comparing actual to budgeted results and taking corrective action
C) Taking actions to implement the plan
D) Arranging the necessary resources to carry out the plan
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an indirect cost of manufacturing a table made of wood and glass,for a firm that manufactures furniture?
A) The cost of the wood in the table.
B) The cost of the labor used to assemble the table.
C) The cost of the glass in the table.
D) The cost of rent on the factory where the table is manufactureD.Costs that cannot be traced to a specific cost object,or that are not worth the effort of tracing,are indirect costs,such as the cost of rent on the factory.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Manufacturing costs are
A) always relevant.
B) always fixed.
C) the costs incurred to produce a final product.
D) split into prime costs and conversion costs.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Variable costs are
A) costs that are not worth the effort to trace to a specific cost object.
B) costs that change,in total,in direct proportion to changes in activity levels.
C) always irrelevant.
D) costs that remain constant no matter the activity level.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Financial accounting information is generally used exclusively by internal parties such as managers.Financial accounting information is used by external parties;managerial accounting information is used by internal business owners and manager.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To earn summer money,Joe could mow lawns in his neighborhood,or he could work at a local grocery store.Which of the following is an opportunity cost of mowing lawns?
A) Cash paid for gas to run the lawnmower.
B) The time spent mowing the lawns.
C) The wages he could have earned working at the grocery store.
D) Depreciation on the lawnmower.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What determines the difference between a product cost and a period cost?
A) Whether the cost changes when activity levels change.
B) Whether the cost is relevant to a particular decision.
C) Whether the cost can be traced to a specific cost object.
D) When the cost will be matched against revenue on the income statement.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning costs is incorrect?
A) Costs are treated differently depending on how the information will be used.
B) Out-of-pocket costs include the costs associated with not taking a particular course of action.
C) Any single cost can be classified in more than one way.
D) Costs can be categorized on the basis of relevant or irrelevant costs.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about product and period costs?
A) Product costs are usually manufacturing costs,and period costs are usually nonmanufacturing costs.
B) Product costs are usually nonmanufacturing costs,and period costs are usually manufacturing costs.
C) Both product and period costs are usually manufacturing costs.
D) Both product and period costs are usually nonmanufacturing costs.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 113
Related Exams