A) Bowman's capsule → distal convoluted tubule → loop of Henle ��→ proximal convoluted tubule → collecting duct
B) Bowman's capsule → proximal convoluted tubule → loop of Henle → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct
C) Bowman's capsule → loop of Henle → proximal convoluted tubule → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct
D) Bowman's capsule → collecting duct → proximal convoluted tubule → loop of Henle → distal convoluted tubule
E) collecting duct → proximal convoluted tubule → loop of Henle → distal convoluted tubule→ Bowman's capsule
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gary has a kidney stone lodged in his ureter.Where will the radiologist find the kidney stone on an x-ray?
A) between the end of a nephron and the renal pelvis
B) between the bladder and the outside of the body
C) between a kidney and the bladder
D) between a Bowman's capsule and a loop of Henle
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most vertebrates maintain homeostasis in regard to the total solute concentrations of their extracellular fluids and the concentrations of specific inorganic ions.The kidneys participate in regulating the extracellular fluid concentration of all ions below EXCEPT
A) Fe2+ ions.
B) Ca2+ ions.
C) K+ ions.
D) Na+ ions.
E) Cl- ions.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where are the receptors that respond to elevated blood osmolarity?
A) in the adrenal cortex
B) in the adrenal medulla
C) in the hypothalamus
D) in the kidneys
E) in the heart
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You put a solution of sucrose into a bag of dialysis tubing,which is permeable to water but not to sucrose.You then put this bag into a beaker of water.An hour later,you observe that the bag has swelled due to
A) active transport of water molecules.
B) the osmotic pressure of the sucrose solution.
C) the pressure exerted on the bag by the surrounding water.
D) passive transport of sucrose molecules.
E) the high osmolarity of the surrounding water.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What response would correct for a drop in glomerular blood pressure?
A) angiotensin II-mediated inhibition of the adrenal cortex
B) inhibition of osmoreceptors in the brain,leading to decreased thirst
C) dilation of the afferent renal arterioles by angiotensin II
D) inhibition of antidiuretic hormone release by the posterior pituitary gland
E) stimulation of sodium secretion by the distal convoluted tubules
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the incorrectly-matched vertebrate and its urine concentration relative to its blood.
A) amphibians-isotonic
B) marine reptiles-isotonic
C) desert mammals-strongly hypertonic
D) marine mammals-strongly hypertonic
E) terrestrial birds-weakly hypertonic
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers.This means that
A) that their body fluids contain the exact same solutes in the same concentration as their cells.
B) the osmolarity of their body fluids is the same as their seawater environment.
C) that their body fluids contain the exact same solutes in the same concentration as their surroundings.
D) the osmolarity of their body fluids is equal to that of the osmoregulators who inhabit the same environments.
E) the osmolarity of their body fluids fluctuates between hypertonic to hypotonic depending on the season and the tides.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the loop of Henle enable the mammalian kidney to produce hypertonic urine? I-The ascending limb of the loop actively extrudes Na+. II-The descending limb interacts with the ascending limb to raise the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid in the renal medulla. III-The concentration is further enhanced by the presence of urea,which draws water out of the collecting ducts by osmosis.
A) just I
B) II and III
C) just III
D) I and II
E) I,II,and III
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Release of what protein is directly subject to negative feedback inhibition when blood volume rises?
A) renin
B) aldosterone
C) angiotensin II
D) angiotensinogen
E) atrial natriuretic hormone
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the production of ADH affects the kidney tubules by
A) inhibiting reabsorption of sodium ion in the collecting duct.
B) decreasing the permeability of the glomerulus to water.
C) causing the walls of the collecting duct to become more permeable to water.
D) inhibiting the reabsorption of water in the glomerulus.
E) decreasing the insertion of aquaporins into the membranes of cells that line the collecting ducts.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are animal mechanisms to cope with the problem of water balance EXCEPT
A) coupling of water/salt removal with metabolic waste removal.
B) contractile vacuoles.
C) passage of water and waste of the body across a layer of cells into a tubular structure.
D) kidneys used as filtering organs.
E) secretion of regulatory hormones into the tubule.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of a loop of Henle in nephrons is an evolutionary adaptation that enables mammals and birds to reabsorb water efficiently and produce a(n) ________ urine.
A) hypertonic
B) hypotonic
C) osmolar
D) isotonic
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What animal has kidneys that are so efficient that it never has to drink water and can obtain all of its water from its food?
A) camel
B) gerbil
C) kangaroo rat
D) pocket mouse
E) desert lizard
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the key factors in vertebrate colonization of many diverse environments is
A) the flexibility provided by selective reabsorption of different solutes.
B) not requiring a lot of water due to their closed systems.
C) the ability to eat foods with lots of water.
D) the ability to control water loss by controlling perspiration.
E) the ability to decrease metabolic needs.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the incorrectly-matched organism and its primary nitrogenous waste product.
A) most fish-ammonia
B) mammals-urea
C) reptiles-uric acid
D) birds-uric acid
E) insects-ammonia
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In vertebrates,most of the fluid that ultimately exits the body as urine first enters the nephron tubules by the process of ________.
A) reabsorption
B) absorption
C) secretion
D) filtration
E) excretion
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If uric acid accumulates in joints of humans the condition is referred to as
A) atherosclerosis.
B) gout.
C) hypertension.
D) distal convoluted tubule dysfunction.
E) diabetes insipidus.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
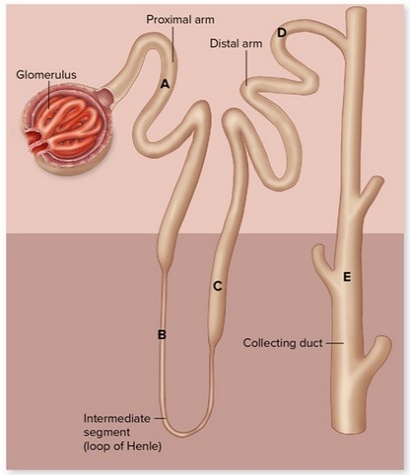 According to the above figure,which letter corresponds to the area where amino acids are most likely to be reabsorbed?
According to the above figure,which letter corresponds to the area where amino acids are most likely to be reabsorbed?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The kidneys are both protected and held in place by cushions of fat.In cases of rapid weight loss,the kidneys may drop to a lower position,possibly causing kinks in a nearby tubular organ.If this happens,urine will back up into the kidneys,severely damaging them.What organ(s) is/are most-likely kinked in this situation?
A) urethra
B) ureters
C) renal arteries
D) nephrons
E) renal veins
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 46
Related Exams