Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the site of primary sensory integration in the brain?
A) medulla oblongata
B) cerebrum
C) cerebellum
D) thalamus
E) corpus callosum
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which major regions compose the contemporary vertebrate brain?
A) rhombencephalon and prosencephalon only
B) mesencephalon and rhombencephalon only
C) prosencephalon and metencephalon only
D) metencephalon,rhombencephalon,and prosencephalon
E) rhombencephalon,mesencephalon,and prosencephalon
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following drugs has been discovered to bind to acetylcholine receptors?
A) serotonin reuptake inhibitors
B) thorazine
C) cocaine
D) codeine
E) nicotine
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three-quarters of the substantial amount of energy consumed by the brain is used to run a single molecular machine that maintains the resting potential of neurons.What is this machine called?
A) K+ leak channel
B) sodium-potassium pump
C) acetylcholine receptor
D) voltage-gated sodium channel
E) voltage-gated calcium channel
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To process information,postsynaptic neurons often add up simultaneous signals from several presynaptic neurons.Which structure and process allow them to do so?
A) axons; temporal summation
B) axons; spatial summation
C) dendrites; temporal summation
D) dendrites; spatial summation
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons both release acetylcholine (ACh) ,how can they have antagonistic effects? (Check all that apply.)
A) The target cells of each set of neurons respond differently to the same signal.
B) Each type of neuron secretes ACh bound to a different co-neurotransmitter.
C) Sympathetic neurons activate the adrenal gland,causing secretion of epinephrine.
D) The neurons release different forms of ACh.
E) Parasympathetic neurons activate the adrenal gland,causing secretion of epinephrine.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which diagram correctly illustrates the distribution of ions in a resting neuron? (Note: A larger symbol indicates a higher concentration of that ion.) 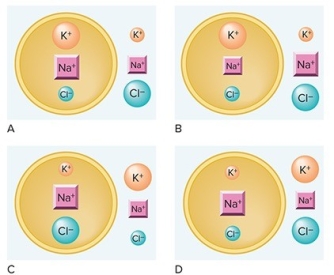
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The outside of a neuron is positively charged at resting potential.Why do K+ ions leave the cell when K+ channels open during an action potential?
A) The diffusion gradient is the only factor that affects ion movement.
B) K+ ions are actively pumped out by the sodium-potassium pump acting in reverse.
C) Voltage-gated K+ channels open when membrane potential reaches +50 mV during the depolarization phase.The diffusion gradient and electrical force cooperate to drive K+ ions out of the cell.
D) Negatively charged proteins leave the cell at the onset of the action potential.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the process in which impulses jump from node to node?
A) facilitated transmission
B) refractory action
C) incomplete transfer
D) repolarization
E) saltatory conduction
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can mutations in different genes,functioning in different cells,lead to the same disease? From the following,choose the best responses to complete the sentences: "Physiological function requires that multiple cells work together.Various defects in different cells can impair function,leading to ________ that are indistinguishable at the level of the whole organism.In Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease,motor nerve function can be impaired either by a problem within ________,or a problem in ________ causing ________."
A) defects; somatic cells; oligodendrocytes; demyelination
B) symptoms; motor neurons; Schwann cells; demyelination
C) symptoms; sensory neurons; Schwann cells; fast axonal transport
D) genotypes; dendrites; axons; fast axonal transport
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an action potential begins and sodium channels open,why does sodium rush into the cell? (Check all that apply.)
A) The inside of the cell is negatively charged.
B) The inside of the cell is positively charged.
C) Chloride ions are waiting to bind to the sodium inside the cell.
D) The diffusion gradient drives sodium into the cell.
E) Channels use energy to move ions across the membrane whenever they are open.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your roommate is on an ultra-low fat diet to try to lose weight.Given what you know about structure of the nervous system,what advice would you give him?
A) "You should drink large quantities of water,because the brain is mostly water."
B) "Good for you! Losing weight by any means necessary can only help your brain."
C) "You should eat some healthy unsaturated fats,like those found in fish,olive oil,and nuts,because your brain needs fatty acids to build the myelin sheaths around your axons."
D) "You should eat trans fats,from donuts,because 'trans' is short for neurotransmission."
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In contrast to these toxins,strychnine acts postsynaptically,to block glycine from binding to receptors on motor neurons.Would you expect the symptoms of strychnine poisoning to be more similar to those of botulinum or tetanus toxin?
A) botulinum
B) tetanus toxin
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What important resource do Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes provide to neurons?
A) oxygen
B) nutrients
C) physical strength from microtubules
D) Ca2+ currents
E) insulating layers of membrane
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which figure correctly illustrates the mechanism of action of the sodium-potassium pump? 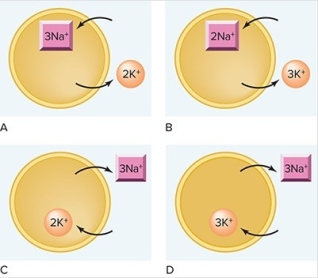
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient of yours is injured in a car accident.The surgeon reports that while there is damage to the dorsal roots,the spinal cord and nerves otherwise appear intact.What functions would you expect to be affected in the patient?
A) The patient may lose somatic function,but should retain autonomic function.
B) The patient may lose motor function,but should retain sensory perception.
C) The patient may lose some sensory perception,but should retain motor function.However,lack of proprioceptive input may make muscle control difficult.
D) The patient may lose parasympathetic function,but should retain sympathetic function.They should avoid stressful situations.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What additional factor is required to mediate the parasympathetic effects of acetylcholine?
A) G-protein coupled receptor
B) GABA
C) AMPAR
D) habituation
E) synaptic integration
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 78 of 78
Related Exams