A) directional selection
B) assortive mating
C) natural selection
D) an increase of recessive alleles
E) no evolutionary changes
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Antigens on red blood cells are hereditary traits that allow blood to be typed in different ways.One system is based on a gene with two alleles,M and N.If the frequency of the M allele in a population is 0.4,then according to the Hardy-Weinberg rule,the expected frequency of the heterozygous MN genotype is ________.
A) 0) 16
B) 0) 24
C) 0) 36
D) 0) 48
E) 0) 6
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many male songbirds are brightly colored.However,the color of the birds is determined by a balance of
A) natural selection against bright colors by predation and sexual selection in favor of bright colors.
B) mutations that reduce bright colors and gene flow in favor of bright colors.
C) natural selection against bright colors by predation and mutations that introduce bright colors.
D) mutations that reduce bright colors and sexual selection in favor of bright colors.
E) gene flow that reduces bright colors and natural selection in favor of bright colors.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a small population of cockroaches living in your kitchen,only a few roaches mate in one year.This can lead to random changes in allele frequency in the population through ________
A) mutation.
B) migration.
C) genetic drift.
D) nonrandom mating.
E) selection.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
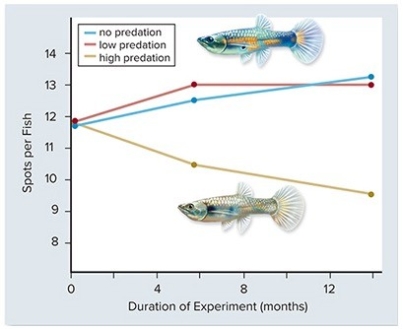 In the experiment above,guppy color patterns (spots) were measured in populations exposed to increasing amounts of predation.From this you could conclude that ________.
In the experiment above,guppy color patterns (spots) were measured in populations exposed to increasing amounts of predation.From this you could conclude that ________.
A) predators are more likely to catch and eat brightly colored guppies
B) predators are less likely to catch and eat brightly colored guppies
C) brightly colored guppies are more likely to reproduce in the presence of predators
D) predators do not affect the color patterns of guppies
E) evolutionary changes take millions of years to appear
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the phalarope,or wadepiper bird,the male is unusual in playing the larger parenting role -- he performs all the egg incubation and chick care.What unusual behavior might you predict for the female of the species?
A) The female provides sperm to fertilize the male's eggs.
B) The female is part of a large harem of females,under the domain of a single male.
C) The females compete to mate with the males,who choose among them.
D) The females have dull,brown coloring that keeps them well-camouflaged.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The several hundred species of picture-winged fruit flies of the Hawaiian Islands are genetically very similar,yet they all differ markedly from their ancestral population in Asia.This is probably an example of ________
A) sexual selection.
B) directional selection.
C) disruptive selection.
D) founder effect.
E) gene flow.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the frequency of an autosomal recessive trait in humans is 1 out of 100 births,what would be the expected frequency of heterozygote carriers for the trait if we assume that the gene is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) 0) 01
B) 0) 10
C) 0) 18
D) 0) 81
E) 0) 90
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People homozygous for the sickle-cell anemia allele develop a life threatening disease,while those homozygous for the normal allele are at the highest risk of dying from malaria.Carriers have some resistance to malaria,but do not develop sickle cell anemia.This is an example of ________
A) founder effect.
B) genetic bottleneck.
C) point mutation.
D) heterozygote advantage.
E) heterozygosity.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ would produce the smallest evolutionary change in a given period of time in a population of birds.
A) Mutation
B) Natural selection
C) Migration
D) Assortive mating
E) Gene flow
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying a population of geese in which there are two color phases,brown and gray.Color in this species is controlled by a single gene,with brown dominant to gray.A random sample of 250 geese shows that 210 are brown.What percentage of the brown geese are heterozygous? (Assume that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.)
A) 36%
B) 43%
C) 48%
D) 57%
E) 84%
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a drought on the Galapagos islands,finches with larger beaks were able to crack the large tough seeds produced by plants that survived the dry conditions.This is an example of ________.
A) directional selection
B) stabilizing selection
C) disruptive selection
D) genetic drift
E) a founder effect
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
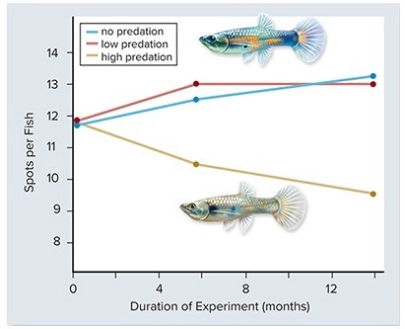 Based on the graph above,the color of male guppies can be seen as a balance between positive and negative selections.Bright colors are an advantage in ________,but a disadvantage in ________.
Based on the graph above,the color of male guppies can be seen as a balance between positive and negative selections.Bright colors are an advantage in ________,but a disadvantage in ________.
A) attracting mates; avoiding predators
B) avoiding predators; attracting mates
C) avoiding predators; finding food
D) attracting mates; finding food
E) finding food; attracting mates
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ would keep a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
A) Mutation
B) Gene flow
C) Random mating
D) Genetic drift
E) Selection
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a large population of randomly reproducing rabbits,a recessive allele r comprises 80% of the alleles for a gene.What percentage of the rabbits would you expect to have the recessive phenotype?
A) 4%
B) 32%
C) 64%
D) 80%
E) 100%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gene flow,defined as the movement of genes from one population to another,can take place by migration,as well as
A) mating with certain trait-containing individuals.
B) mating with dominant phenotypes.
C) mating between individuals of adjacent populations.
D) removing the barriers between the populations.
E) physical movement of genes within an individual by transposons.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An island is on the migration route of sea birds.This island also has abundant tree nesting birds that live on the island permanently and are not found on any other island.The tree nesting birds are more likely than the sea birds to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium because:
A) of high immigration in the sea bird population.
B) the sea bird population is larger.
C) there are fewer mutations in the sea birds.
D) mating is random in the tree nesting birds.
E) natural selection is stronger in the tree nesting birds.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Male Mormon crickets choose larger females as their mates.Which of the following statements best interprets the graph? 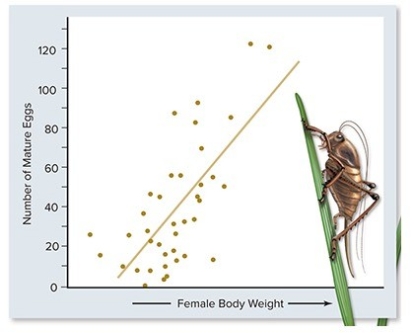
A) Larger females live longer and thus produce more eggs.
B) Larger females are capable of storing sperm.
C) Larger females reproduce earlier than smaller females.
D) Larger females lay more eggs.
E) Larger females defend themselves better.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Average human males are most likely to be attracted to women with a waist to hip ratio of 0.72.Women with this waist to hip ratio are also the most fertile.By being attracted to women with a waist to hip ratio,a male is increasing his chances of having children and thus improve his ________.
A) fitness
B) longevity
C) allele frequency
D) gene flow
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since females take on the larger parenting role in most species,what tendency do they have?
A) They produce large numbers of gametes.
B) They compete heavily for access to high fitness males.
C) They are the choosy sex.
D) They acquire polyandrous groups of male mates.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 78
Related Exams