A) 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexene
B) 2,3-Dimethylcyclohexene
C) 1,6-Dimethylcyclohexene
D) 1,2-Dimethyl-3-cyclohexene
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major product of the following reaction? 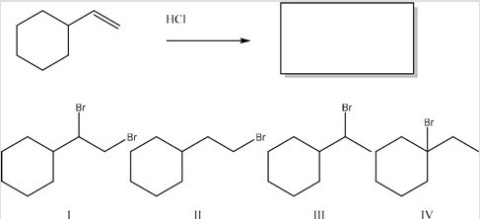
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the statements about the properties of the carbon-carbon double bond is not true?
A) There is restricted rotation around the carbon-carbon double bond.
B) Whenever the two groups on each end of a carbon-carbon double bond are the same,two diastereomers are possible.
C) Trans alkenes are generally more stable than cis alkenes.
D) The stability of the carbon-carbon double bond increases as the number of substituent groups increases.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Predict the product(s) of the following reaction. 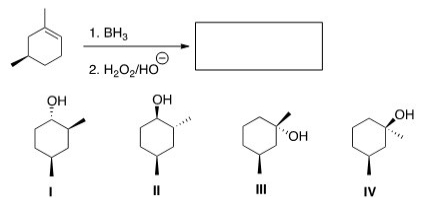
A) Only I and II
B) Only I and III
C) Only II and III
D) Only III and IV
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of reactive intermediate is formed in the reaction of an alkene with HI to give an iodoalkane?
A) Carbanion
B) Carbocation
C) Cyclic bromonium ion
D) Radical
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkenes is an E alkene? 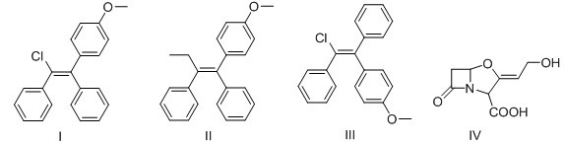
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the degree of unsaturation for a molecule with molecular formula C6H11Cl.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 0
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the degree of unsaturation for the following molecule: 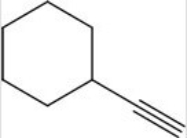
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkenes will undergo a carbocation rearrangement when reacting with H2O in the presence of a small amount of H2SO4? 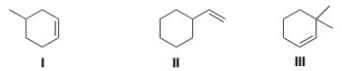
A) Only I and II
B) Only I and III
C) Only II and III
D) I,II,and III
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the starting material in the following reaction? 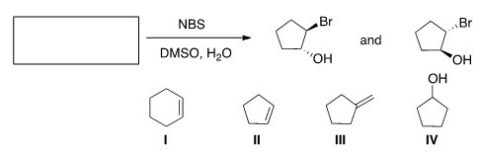
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound? 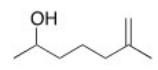
A) 5-Methyl-5-hexen-2-ol
B) 6-Methyl-6-hepten-2-ol
C) 6-Hydroxy-2-methylheptene
D) 6-Hydroxy-2-methyl-1-heptene
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about alkenes is true?
A) Alkenes react with nucleophiles and bases.
B) Alkenes contain double bonds from two sp-hybridized carbon atoms.
C) In the reactions of alkenes,the ![]() bond is not always broken.
bond is not always broken.
D) Alkenes react with electrophiles.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the carbocation in order of increasing stability,putting the least stable first. 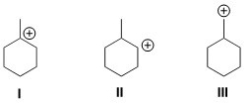
A) III < I < II
B) III < II < I
C) I < II < III
D) I < III < II
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Label each C-C double bond in Kavain,a naturally occurring relaxant,as E or Z. 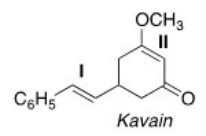
A) I = Z and II = Z
B) I = Z and II = E
C) I = E and II = E
D) I = E and II = Z
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 54 of 54
Related Exams