A) pegmatitic
B) porphyritic
C) glassy
D) aphanitic
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Slow cooling produces ________ crystals, whereas fast cooling produces ________ crystals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the geologic definition of texture?
A) How the sample feels to the touch
B) The mineral content of the sample
C) The percentage of silica in a sample
D) Size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains in the sample
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ describes the formation of one or more secondary magmas from a single parent magma.
A) Magmatic differentiation
B) Hydrothermal alteration
C) Decompression melting
D) Partial melting
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mineral crystals that form early in the crystallization process will have better-developed crystal faces than later crystals.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What creates the small holes found in a vesicular texture?
A) Liquid water
B) Volatiles
C) Soluble minerals
D) Weathering
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is a felsic igneous rock with a meringuelike vesicular texture, consisting of very small holes, created by small shards of volcanic glass.
A) Scoria
B) Obsidian
C) Granite
D) Pumice
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is molten rock that is below the Earth's surface and retains most of its volcanic gases.
A) Lava
B) Pumice
C) Magma
D) Volatiles
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
List the intrusive igneous textures below. Phaneritic, aphanitic, glassy, pyroclastic, pegmatitic
Correct Answer

verified
Phaneritic...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Will density increase or decrease with the crystallization of a magma?
A) Decrease
B) Increase
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which igneous texture has visible crystals that are a few millimeters across?
A) Phaneritic
B) Aphanitic
C) Pegmatitic
D) Porphyritic
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes a pegmatitic texture?
A) Large crystals that form in a fluid-rich environment late in crystallization
B) Porous texture resulting from escaping volatiles
C) Fine-grained texture composed of microscopic crystals
D) Several large crystals surrounded by a fine-grained matrix
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most sills are intrusive igneous structures that display a fine-grained texture.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between pressure and melting point in the Earth's Interior?
A) Higher pressure leads to lower melting points.
B) Melting points of rocks are not dependent on changes in pressure.
C) Higher melting points are determined by higher pressures.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Refer to the scenario above.How does this gradient compare to the average geothermal gradient?
Correct Answer

verified
It is slig...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
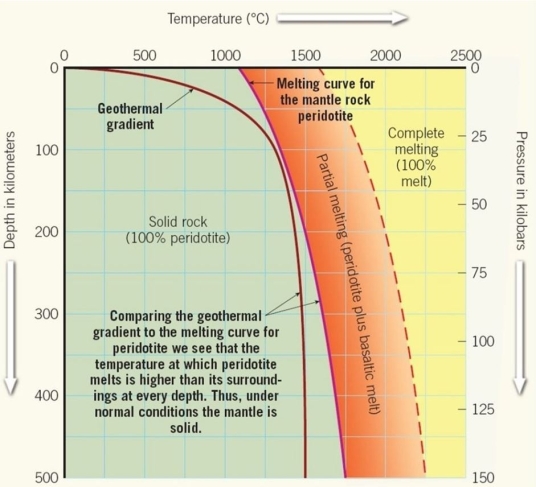 Follow the geothermal gradient to the depth of 100 km.In which state of matter will peridotite exist at 100 km?
Follow the geothermal gradient to the depth of 100 km.In which state of matter will peridotite exist at 100 km?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plutonic bodies that have a surface exposure less than 100 km2 are called ________.
A) dikes
B) stocks
C) swarms
D) batholiths
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
How does magma differ from lava?
Correct Answer

verified
Magma is molten rock below the...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
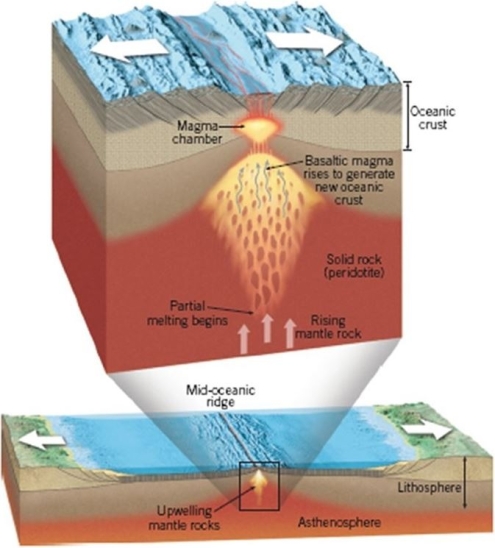 Explain the processes occurring in the figure above that are generating magma.At what kind of tectonic boundary are such processes common?
Explain the processes occurring in the figure above that are generating magma.At what kind of tectonic boundary are such processes common?
Correct Answer

verified
As rifting occurs at the diver...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
What three components make up most magmas?
A) Silicon, potassium feldspar, and muscovite
B) Water, melted rock, and solid crystals
C) Lava, ash, and gas
D) Liquid portion, solid portion, gaseous portion
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 76
Related Exams