A) systemic risk.
B) the risk premium.
C) idiosyncratic risk.
D) nondiversifiable risk.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
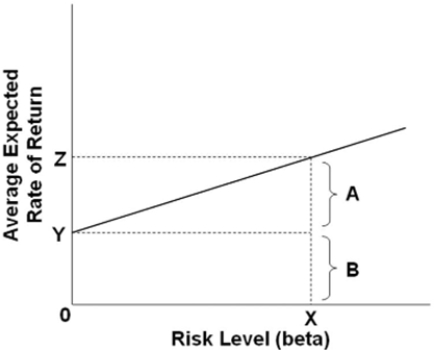 In the accompanying graph, bracket A represents the
In the accompanying graph, bracket A represents the
A) rate of return for an asset.
B) rate of return for the risk-free asset.
C) risk premium for an asset with a certain risk level.
D) compensation for time preference for an asset with a certain risk level.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is a feature of all investments?
A) They provide regular interest payments.
B) They are typically long term.
C) They have minimal risk for future payments to be made.
D) They give owners a chance to receive future payments.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not common to all investments?
A) Investors are required to pay some price to acquire them.
B) Owners are given the opportunity to receive future payments.
C) Future payments are typically risky.
D) The investment pays a positive rate of interest.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Before taking management and trading costs into account, arbitrage activities in the market ensure that the returns of actively managed funds are
A) significantly higher than those of index funds with similar risk.
B) significantly lower than those of index funds with similar risk.
C) about the same as those of index funds with similar risk.
D) more volatile than those of index funds with similar risk.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Risk in finance means that an asset
A) does not pay dividends.
B) does not pay capital gains.
C) has a present value that is negative.
D) has future payments that are uncertain.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Risk in financial economics refers mainly to the chance that an investment could lose value.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S.federal government is unlikely to default on its bond payments because
A) if necessary, it can print the money needed to make payments on time.
B) its bond payments are insured.
C) the U.S.federal budget usually runs a surplus, providing ample funds for repaying debt.
D) of all of these.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Owners of stock can receive from their shares; sellers of stock can receive from selling their shares.
A) capital gains; dividends
B) dividends; capital gains
C) interest; dividends
D) interest; capital gains
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market portfolio would have a beta of
A) 0.
B) 1.0.
C) 100.
D) any value.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an investment is 80 percent likely to gain 40 percent but also 20 percent likely to lose 10 percent, then its average expected rate of return is
A) 34 percent.
B) 32 percent.
C) 30 percent.
D) 12 percent.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Index funds are a portfolio of
A) bonds with rates of return fixed at 2 percentage points above the rate of inflation.
B) mutual funds that track different indexes.
C) stocks or bonds that exactly match a particular index.
D) stocks guaranteed rates of return in excess of growth in the GDP price index.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If an asset has a beta of 1.5, it has 50 percent more nondiversifiable risk than the market portfolio.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Arbitrage refers to the buying and selling activities that cause an equalization of the rates of return on assets that have substantially different characteristics.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compound interest describes increases in value when interest is paid, or compounded, on
A) only the original amount invested.
B) only the previously accumulated interest payments.
C) the original amount invested and previously accumulated interest payments.
D) the original amount invested minus any previously accumulated interest payments.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is an example of an economic investment?
A) putting money in a bank CD
B) buying a corporate bond or stock
C) purchasing shares of a mutual fund
D) building a new bank office
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that money has "time value" refers to the fact that
A) people prefer to receive a given sum of money in the future rather than in the present.
B) money can be used to purchase the services of labor, as measured in hourly units.
C) a specific amount of money is more valuable to a person the sooner it is received.
D) compound interest converts future dollars into a greater amount of current dollars.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The average expected rate of return on an asset can be fully understood as the rate that compensates for risk.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Karen holds a $100 bond that pays $10 per year in interest.The minimum price Karen would have to be offered before she would sell the bond
A) is $110.
B) is $125.
C) is $140.
D) depends on rates of return she could earn on other, similar investments.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two investments, X and Y, have beta values of 0.1 and 3.0 respectively.Based on this, we can claim that, relative to the market portfolio,
A) both have more nondiversifiable risk than the market portfolio.
B) both have less nondiversifiable risk than the market portfolio.
C) X has more nondiversifiable risk and Y has less nondiversifiable risk than the market portfolio.
D) X has less nondiversifiable risk and Y has more nondiversifiable risk than the market portfolio.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 323
Related Exams