A) inflationary expenditure gap is ed.
B) inflationary expenditure gap is BC.
C) recessionary expenditure gap is eg.
D) economy is in equilibrium, but at less than full employment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Actual investment is $62 billion at an equilibrium output level of $620 billion in a private closed economy.The average propensity to save at this level of output:
A) is 0.10.
B) is 10.
C) is 0.62.
D) cannot be determined on the basis of the information given.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information is consumption and investment data for a private closed economy.Figures are in billions of dollars.C = 60 + .6Y I = I0 = 30 Refer to the above data.In equilibrium, the level of consumption spending will be:
A) 170
B) 270
C) 160
D) 195
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the $180 billion equilibrium level of income, saving is $38 billion in a private closed economy.Planned investment must be:
A) $138 billion.
B) $126 billion.
C) $38 billion.
D) $180 billion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If APC = .6 and MPC = .7, the immediate impact of an increase in personal taxes of $20 will be to:
A) have no effect on consumption.
B) decrease consumption by $14.
C) decrease consumption by $12.
D) increase consumption by $14.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an increase in aggregate expenditures results in no increase in real GDP we can conclude that the:
A) economy is in a deep recession.
B) MPC equals 1.
C) economy is already operating at full employment.
D) price level has fallen.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the multiplier in an economy is 5, a $20 billion increase in net exports will:
A) increase GDP by $100 billion.
B) reduce GDP by $20 billion.
C) decrease GDP by $100 billion.
D) increase GDP by $20 billion.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a mixed closed economy:
A) government purchases and saving are injections, while investment and taxes are leakages.
B) taxes and government purchases are leakages, while investment and saving are injections.
C) taxes and savings are leakages, while investment and government purchases are injections.
D) taxes and investment are injections, while saving and government purchases are leakages.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
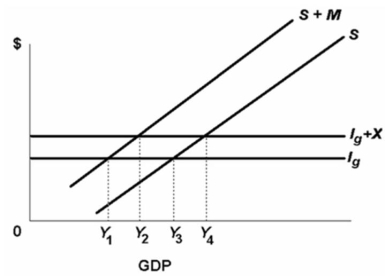 Refer to the above diagram.The equilibrium condition for a private open economy is S + M = Ig + X.
Refer to the above diagram.The equilibrium condition for a private open economy is S + M = Ig + X.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Given the economy's MPS, a $15 billion reduction in government spending will reduce the equilibrium GDP by more than would a $15 billion increase in taxes.
B) Other things unchanged, a tax reduction of $10 billion will increase the equilibrium GDP by $25 billion when the MPS is 0.4.
C) If the MPC is 0.8 and GDP has declined by $40 billion, this was caused by a decline in aggregate expenditures of $8 billion.
D) A government surplus is anti-inflationary; a government deficit is expansionary.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete the following table and answer the next question(s) on the basis of the resulting data.All figures are in billions of dollars. 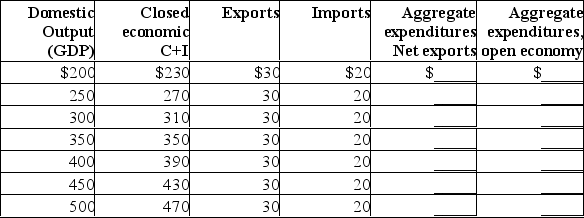 Other things equal, an increase in an economy's exports will:
Other things equal, an increase in an economy's exports will:
A) lower the marginal propensity to import.
B) have no effect on domestic GDP because imports will change by an offsetting amount.
C) decrease its domestic aggregate expenditures and therefore decrease its equilibrium GDP.
D) increase its domestic aggregate expenditures and therefore increase its equilibrium GDP.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The letters Y, C, Ig, X, and M stand for GDP, consumption, gross investment, exports, and imports respectively.Figures are in billions of dollars.C = 26 + .75Y Ig = 60 X = 24 M = 10 The equilibrium level of GDP for the above open economy is:
A) $390
B) $375
C) $320
D) $400
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information is for a closed economy: 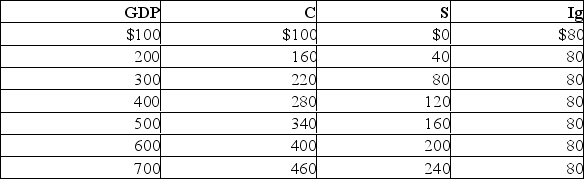 Refer to the above information.If government now spends $80 billion at each level of GDP and taxes remain at zero, the equilibrium GDP:
Refer to the above information.If government now spends $80 billion at each level of GDP and taxes remain at zero, the equilibrium GDP:
A) will rise to $700.
B) will rise to $600.
C) will rise to $500.
D) may either rise or fall.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If government decreases its purchases by $20 billion and the MPC is 0.8, equilibrium GDP will decrease by $100 billion.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a recessionary expenditure gap, the equilibrium level of real GDP is:
A) less than planned investment.
B) equal to full-employment GDP.
C) greater than full-employment GDP.
D) less than full-employment GDP.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
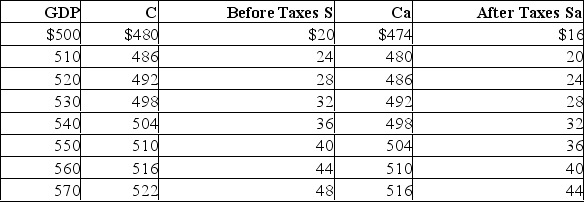 The tax in the above economy is a:
The tax in the above economy is a:
A) 10 percent proportional tax.
B) lump-sum tax of $20.
C) lump-sum tax of $10.
D) progressive tax.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows a private, open economy.All figures are in billions of dollars. 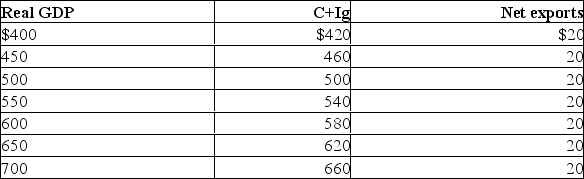 Refer to the above table.If the marginal propensity to consume in this economy is 0.8, a $10 increase in its net exports would increase its equilibrium real GDP by:
Refer to the above table.If the marginal propensity to consume in this economy is 0.8, a $10 increase in its net exports would increase its equilibrium real GDP by:
A) $25
B) $50
C) $100
D) $200
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the above diagram, which applies to a private closed economy.If the initial gross investment Ig1 increases to Ig2, the equilibrium GDP will increase by:
A) FE.
B) AB.
C) AD.
D) GE.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The level of aggregate expenditures in the private closed economy is determined by the:
A) expenditures of consumers and businesses.
B) intersection of the saving schedule and the 45-degree line.
C) equality of the MPC and MPS.
D) intersection of the saving and consumption schedules.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Refer to the diagram below.The equilibrium condition for a private closed economy is Ig = S. 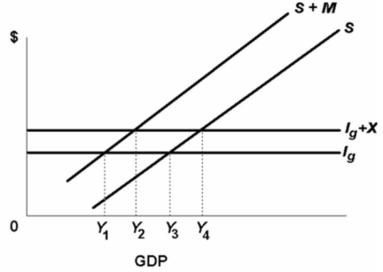
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 238
Related Exams