A) leftward shift of the production possibilities curve.
B) movement from a point inside to a point outside of the production possibilities curve.
C) movement from a point near the vertical axis to a point near the horizontal axis on the production possibilities curve.
D) rightward shift of the production possibilities curve.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Real GDP in any year is equal to:
A) the quantity of labour divided by resource outputs.
B) labour productivity multiplied by the quality of labour.
C) worker-hours divided by labour productivity.
D) worker-hours multiplied by labour productivity.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Recently, the changes in the educational attainment of the Canadian labour force indicate that the percentage of those:
A) completing high school has been rising, but the percentage of those attending university has declined.
B) attending university have increased.
C) completing college has been constant, and the percentage of those attending university has declined.
D) attending university and community colleges have decreased.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nominal GDP was $9,500 billion in Year 1 and $10,000 billion in Year 2.The GDP price index was 170 in Year 1 and 175 in Year 2.Between Years 1 and 2, the rate of growth in real GDP was approximately:
A) 1.6 percent.
B) 2.3 percent.
C) 4.4 percent.
D) 5.3 percent.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a nation's real GDP is growing by 5 percent per year, its real GDP will double in approximately:
A) 22 years.
B) 20 years.
C) 14 years.
D) 8 years.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Real GDP or total output in any year is equal to:
A) labour inputs divided by resource outputs.
B) labour productivity multiplied by real output.
C) worker-hours multiplied by labour productivity.
D) worker-hours divided by labour productivity.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The historical reallocation of labour from agriculture to manufacturing in Canada has:
A) been inflationary.
B) had no effect upon the average productivity of labour.
C) increased the average productivity of labour.
D) reduced the average productivity of labour.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The rise in productivity seen in the last decade is believed to be due to a significant new wave of technological advance coupled with global competition.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic growth can be portrayed as a(n) :
A) outward shift of the production possibilities curve.
B) inward shift of the production possibilities curve.
C) movement from a point on to a point inside a production possibilities curve.
D) movement from one point to another point on a production possibilities curve.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economic growth can be shown as a movement from a point on one production possibility curve to a point on a curve located farther from the origin.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is an efficiency factor in economic growth?
A) an efficient allocation of resources
B) natural resources
C) the quantity and quality of labour
D) technological knowledge
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be a source of economies of scale?
A) the social environment
B) the quantity of labour
C) decreasing returns
D) more specialized inputs
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A rightward shift of a nation's production possibilities curve is a necessary but not sufficient condition for economic growth.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The countries which have begun modern economic growth later than the others can catch up because:
A) for them, it is quicker to adopt technology rather than inventing one.
B) for them, it is harder to adopt technology rather than inventing one.
C) for them, it is as hard to adopt technology as it is to invent one.
D) for them, it is very easy to invent a new technology with lower cost.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
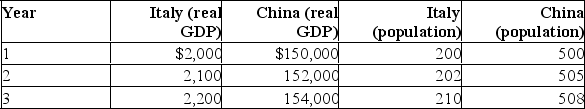 Refer to the above table.Between years 1 and 2, real GDP per capita grew by _____ percent in Italy:
Refer to the above table.Between years 1 and 2, real GDP per capita grew by _____ percent in Italy:
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 10
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using Image 8.1 Global Perspective, which of the following nations is the most competitive nation in the world according to the global competitiveness index calculated for 2016-2017?
A) Switzerland
B) Singapore
C) United States
D) Germany
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Canada, the lowest increase in the average annual rates of productivity growth was observed during the period of:
A) 1981-1989.
B) 1946-2015.
C) 1973-1981.
D) 2000-2015.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nation's "infrastructure" refers to:
A) its ability to realize economies of scale.
B) its stock of technological knowledge.
C) public capital goods such as highways and utilities.
D) the productivity of its labour force.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most important contributor to increases in the productivity of Canadian labour is:
A) the reallocation of labour from agriculture to manufacturing.
B) improvements in labour quality.
C) increases in the quantity of capital.
D) technological advance.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Show me a pastoral society with an untouched environment, an abundance of leisure, and nonsecular values, and I will show you an underdeveloped, poverty-ridden country.This statement is most likely to be made by a(n) :
A) advocate of learning by doing.
B) advocate of network effects.
C) proponent of economic growth.
D) critic of economic growth.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 122
Related Exams