A) a tight monetary policy
B) a contractionary fiscal policy
C) an increase in aggregate demand
D) an increase in aggregate supply
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economists reject the idea of a long-run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of disinflation?
A) It is a reduction in the inflation rate from year to year.
B) It is used to describe instances when the inflation rate is negative.
C) It refers to misinformation about the real and nominal rates of inflation.
D) It refers to miscalculations about the inflation rates.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Statistical data for the 1970s and 1980s suggest that:
A) the Phillips Curve was stable.
B) the Phillips Curve was unstable.
C) low levels of unemployment were consistently associated with high rates of inflation.
D) the inflation rate was highly stable.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming prices and wages are flexible, a recession will decrease the price level, which:
A) raises nominal wages, and which eventually decreases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus decreasing real output to its original level.
B) raises nominal wages, and which eventually increases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus increasing real output to its original level.
C) reduces nominal wages, and which eventually decreases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus decreasing real output to its original level.
D) reduces nominal wages, and which eventually increases the short-run aggregate supply curve, thus increasing real output to its original level.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
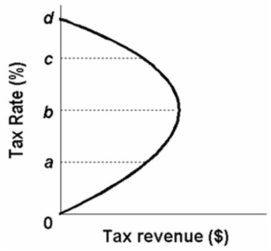 The above diagram describes the notion that as tax:
The above diagram describes the notion that as tax:
A) revenues increase from zero to 100 percent, tax rates will increase from zero to some maximum level and then decline to zero.
B) rates increase from zero to 100 percent, tax revenue will increase from zero to some maximum level and decline to zero.
C) rates decrease from 100 to zero percent, tax revenue will decrease from 100 percent to a maximum level.
D) rates increase from zero to 100 percent, tax revenue will increase from zero to a maximum level.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
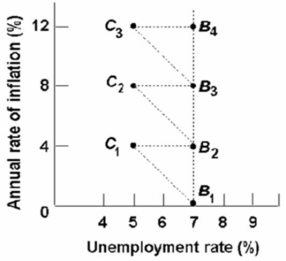 Refer to the above diagram and assume the economy is initially at point b1.According to the adaptive expectations theorists, the long-run relationship between the unemployment rate and the rate of inflation is represented by:
Refer to the above diagram and assume the economy is initially at point b1.According to the adaptive expectations theorists, the long-run relationship between the unemployment rate and the rate of inflation is represented by:
A) the line connecting B1 and C1.
B) the line through B1, B2, B3, and B4.
C) the line connecting C1 and B2.
D) any line parallel to the horizontal axis.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy enters the long run once:
A) nominal wages become real wages.
B) real wages become nominal wages.
C) input prices start to change from being inflexible to fully flexible.
D) sufficient time has elapsed for real GDP to increase and unemployment to decrease.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most significantly contributed to the 1970s' and the early 1980s' stagflation in Canada?
A) An appreciation of the Canadian dollar
B) A sharp drop in the prices of farm products
C) A dramatic increase in energy prices
D) Rising productivity in manufacturing
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demand-pull inflation in the short run increases the price level and:
A) real wages.
B) real output.
C) unemployment.
D) nominal wages.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in inflation is likely to occur when government:
A) counters cost-push inflation with a stimulative fiscal policy or monetary policy.
B) adopts a hands-off approach to cost-push inflation.
C) increases aggregate supply by lowering nominal wages.
D) increases aggregate demand by raising nominal wages.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, an increase in the price level will:
A) shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) cause a movement up along a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) cause a movement down a short run aggregate supply curve.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
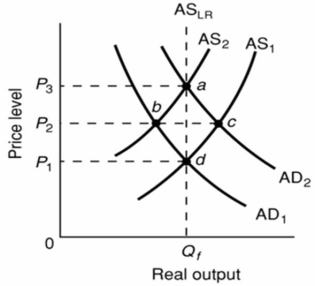 Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.If government offsets the decline in real output resulting from short-run cost-push inflation by increasing aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2:
Refer to the above diagram.The initial aggregate demand curve is AD1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS1.If government offsets the decline in real output resulting from short-run cost-push inflation by increasing aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2:
A) real output will rise above Qf.
B) the price level will rise from P1 to P2.
C) it is possible that aggregate supply will shift rightward from AS2 because nominal wage demands will rise.
D) the price level will rise from P2 to P3.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
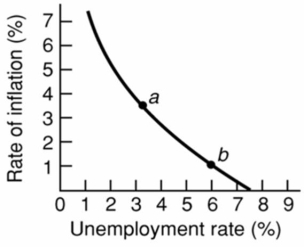 Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Stagflation will:
Refer to the above diagram for a specific economy.Stagflation will:
A) shift this curve outward.
B) shift this curve inward.
C) move this economy southeast along the curve.
D) move this economy northwest along the curve.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adverse aggregate supply shocks would result in:
A) a lower rate of inflation and a higher rate of unemployment.
B) a higher rate of inflation and a lower rate of unemployment.
C) a lower rate of inflation and a lower rate of unemployment.
D) a higher rate of inflation and a higher rate of unemployment.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economists often recommend active monetary policy, and perhaps fiscal policy, to counteract the recessions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long run, cost-push inflation results in a simultaneous decrease in the price level and real output.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the conventional view, outward shifts of the Phillips Curve in the 1970s and early 1980s were caused by:
A) adverse shocks to aggregate supply.
B) adverse shocks to aggregate demand.
C) an increase in the misery index.
D) the Vietnam War.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Supply-side economists say that:
A) lower tax rates on businesses will shift the aggregate supply curve rightward.
B) demand creates its own supply.
C) tariffs should be imposed on imports to shift the Canadian aggregate supply curve rightward.
D) the federal budget deficit should be eliminated through increases in taxes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If prices and wages are flexible, a recession arising from a decrease in aggregate demand will:
A) decrease the price level.
B) increase the price level.
C) increase the interest rate.
D) increase net exports.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 122
Related Exams