A) government spending is more employment-intensive than is either consumption or investment spending.
B) government spending increases the money supply and a tax reduction does not.
C) a portion of a tax cut will be saved.
D) taxes vary directly with income.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC in an economy is .75, a $1 billion increase in taxes will reduce the GDP by:
A) $1 billion.
B) $.75 billion.
C) $3 billion.
D) $4 billion.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy is in equilibrium at the $400 billion level of GDP and the full-employment level of GDP is $500 billion:
A) real and nominal GDP will both increase.
B) economy does not reach full-employment unless aggregate expenditures increases.
C) real GDP will increase, but nominal GDP will decrease.
D) the price level will increase.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the aggregate expenditures model, an increase in government spending will:
A) decrease real GDP.
B) increase output and employment.
C) shift the aggregate expenditures schedule downward.
D) do all of the above.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram below for a private closed economy.Saving and planned investment are equal: 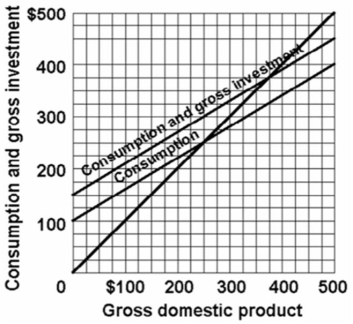
A) only at the $300 level of GDP.
B) only at the $250 level of GDP.
C) at all levels of GDP.
D) only at the $375 level of GDP.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Planned investment is $75 billion and saving is $62 billion in a private closed economy.In equilibrium actual investment must be:
A) $13 billion.
B) $75 billion.
C) $62 billion.
D) minus $13 billion.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the $180 billion equilibrium level of income, saving is $38 billion in a private closed economy.Planned investment must be:
A) $138 billion.
B) $126 billion.
C) $38 billion.
D) $180 billion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If S = -60 + 0.25Y and Ig = 60, where S is saving, Ig is gross investment, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP) , then the equilibrium level of GDP is:
A) $200.
B) $320.
C) $360.
D) $480.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A lump-sum tax causes the after-tax consumption schedule to be flatter than the before-tax consumption schedule.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a recessionary expenditure gap, the equilibrium level of real GDP is:
A) less than planned investment.
B) equal to full-employment GDP.
C) greater than full-employment GDP.
D) less than full-employment GDP.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram.If the full-employment level of GDP is B and aggregate expenditures are at AE1, the: 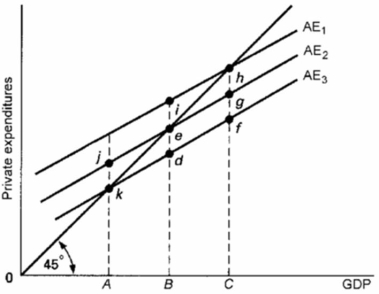
A) inflationary expenditure gap is hg.
B) recessionary expenditure gap is BC.
C) inflationary expenditure gap is zero.
D) inflationary expenditure gap is ed.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal propensity to consume is.80 and both taxes and government purchases increase by $50 billion, GDP will:
A) increase by $50 billion.
B) decrease by $50 billion.
C) increase by $10 billion.
D) decrease by $10 billion.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, the effect of a downward shift of the economy's net export schedule on equilibrium GDP will be similar to a(n) :
A) rightward shift in the investment-demand schedule.
B) downward shift in the consumption schedule.
C) upward shift in the consumption schedule.
D) upward shift in the investment schedule.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which event would most likely decrease an economy's exports?
A) a decline in the tariff on products imported from abroad
B) an increase the prosperity of trading partners for this economy
C) an appreciation of a nation's currency relative to foreign currencies
D) a depreciation of a nation's currency relative to foreign currencies
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a mixed closed economy:
A) government purchases and saving are injections, while investment and taxes are leakages.
B) taxes and government purchases are leakages, while investment and saving are injections.
C) taxes and savings are leakages, while investment and government purchases are injections.
D) taxes and investment are injections, while saving and government purchases are leakages.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in government expenditures will shift the aggregate expenditures schedule ____ and ____ the equilibrium GDP.
A) upward; raise
B) downward; raise
C) downward; lower
D) upward; lower
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the recession of 2008 - 2009:
A) the federal government undertook various policies intended to stimulate private spending and investment.
B) the federal government undertook various policies that ultimately resulted in an inflationary expenditure gap.
C) the federal government was able to achieve a balanced budget even though it undertook various policies to stimulate the economy.
D) the federal government took no action to stimulate the economy, and instead left it to the private sector to try to eliminate the recessionary gap.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If government increases its tax revenues by $15 billion and the MPC is 2/3, then we can expect the equilibrium GDP to:
A) decrease by $30 billion.
B) decrease by $45 billion.
C) decrease by $35 billion.
D) decrease by $55 billion.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 238 of 238
Related Exams