A) retailers using a price lining strategy will occasionally mark up items based on color, style, and expected consumer demand.
B) fewer people buy black-and-white shells, so the retailer has to charge a higher price to break even.
C) the retailer is using prestige pricing; black-and-white shells are more elegant.
D) the primary colors were priced using a penetration strategy, the pastels were priced using a skimming strategy, and the black-and-white shells were priced using prestige pricing.
E) the retailer is essentially using above-, at-, and below-market pricing for the three groupings.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Seasonal discounts are used by manufacturers to
A) get rid of dated merchandise.
B) prevent retailers from purchasing competitors' products.
C) prolong the peak seasonal selling season.
D) establish an immediate feeling of goodwill between the buyer and seller that hopefully will continue when prices return to normal.
E) entice dealers to purchase seasonal merchandise earlier in the selling season.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
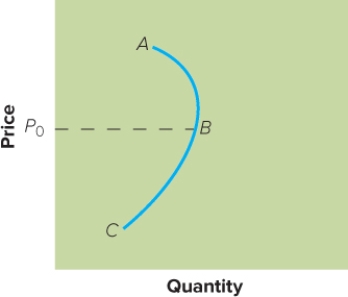 Figure 14-3
-The movement from point A to point B in Figure 14-3 above shows
Figure 14-3
-The movement from point A to point B in Figure 14-3 above shows
A) skimming demand.
B) penetration demand.
C) that buyers see the product as a bargain and buy more.
D) that buyers become dubious about the quality and prestige and buy less.
E) a downturn in the economy.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allowances, like discounts, are
A) rewards given to retailers to encourage early payment.
B) payment extensions given to cash-strapped consumers during the current recession.
C) list price deductions based on surges in consumer demand.
D) list price deductions based on sudden drops in consumer demand.
E) reductions from list or quoted prices to buyers for performing some activity.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The purpose of a cash discount is to
A) reward retailers for making large quantity purchases.
B) encourage purchasing items during periods of low demand.
C) prevent competitors from obtaining shelf space.
D) counteract the introduction of a new product by a competitor.
E) encourage retailers to pay their bills promptly.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The retail price of mobile phones (unsubsidized) has decreased from $4,000 in 1983 when Motorola commercialized the device, to less than $99 today as the volume increased from zero to millions of units sold. This is due in large part to which type of pricing approach?
A) skimming pricing
B) prestige pricing
C) experience-curve pricing
D) odd-even pricing
E) customary pricing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination is
A) the practice of charging different prices to different buyers for goods of like grade and quality.
B) an arrangement a manufacturer makes with a reseller to handle only its products and not those of a competitor.
C) the practice of charging a very low price for a product with the intent of driving competitors out of business.
D) a conspiracy among firms to set prices for a product or service.
E) a seller's requirement that the purchaser of one product also buy another product in the line.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of these are pricing practices that are closely scrutinized because of potential unethical or illegal actions except which?
A) price discrimination
B) predatory pricing
C) showrooming
D) price fixing
E) deceptive pricing
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Incremental analysis might take the form of such questions as, "Should we extend our hours to include Sundays?" or "What if we put more apples in the pie?" The basic principle is that
A) as long as a marketing action breaks even, the action is worth taking.
B) expected incremental revenues from pricing and other marketing actions must more than offset incremental costs.
C) you "don't rock the boat" if your program is making a profit; "leave well enough alone."
D) if you are not willing to take risks, even if the numbers tell you otherwise, your business will ultimately fail.
E) marketing and finance are two different animals: "If it feels right in your gut-go for it."
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting a market price for a product or product class based on a subjective feel for the competitors' price or market price as the benchmark is referred to as
A) customary pricing.
B) above-, at-, or below-market pricing.
C) standard markup pricing.
D) competitive margin pricing.
E) experience-curve pricing.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marketing two or more products in a single package price is referred to as
A) package pricing.
B) loss-leader pricing.
C) bundle pricing.
D) tie-in pricing.
E) multi-product pricing.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these businesses would be most likely to use target return-on-investment pricing?
A) a farmer
B) a supermarket chain
C) a book publisher
D) a veterinarian
E) an automobile manufacturer
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements regarding quantity discounts is most accurate?
A) Cumulative quantity discounts encourage repeat buying by a single customer to a far greater degree than do noncumulative quantity discounts.
B) Noncumulative quantity discounts encourage repeat buying by a single customer to a far greater degree than do cumulative quantity discounts.
C) Quantity discounts are primarily used to undercut competitors' prices.
D) Noncumulative quantity discounts encourage smaller long-term repeat purchases rather than less frequent large quantity purchases.
E) Quantity discounts are designed to reward wholesalers and retailers for marketing functions they will perform in the future.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Frito-Lay recognizes that its tortilla chip products are partial substitutes for one another. Its bean and cheese dips and salsa sauces complement its tortilla chips. Frito-Lay uses this knowledge to set prices for each item in order to ensure that the entire line is profitable. This pricing strategy is known as
A) bundle pricing.
B) price lining.
C) customary pricing.
D) product-line pricing.
E) loss-leader pricing.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Dell sells various laptops, it also pre-installs Microsoft Office and other software that customers order at a discount before a laptop is shipped. This is an example of
A) price lining.
B) product-line pricing.
C) bundle pricing.
D) customary pricing.
E) prestige pricing.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A penetration pricing policy is most likely to be effective when which of these is true?
A) Lowering the price has only a minor effect on increasing the sales volume and reducing the unit cost.
B) The high initial price will not attract competitors.
C) A low initial price discourages competitors from entering the market.
D) Customers interpret the high price as signifying high quality.
E) Enough prospective customers are willing to buy immediately at the high initial price to make these sales profitable.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
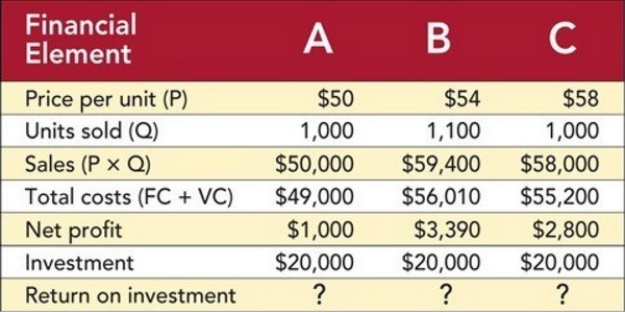 Figure 14-5
-Figure 14-5 above shows the results of a spreadsheet simulation to select a price to achieve a target return on investment (ROI) . What is the ROI for Scenario A?
Figure 14-5
-Figure 14-5 above shows the results of a spreadsheet simulation to select a price to achieve a target return on investment (ROI) . What is the ROI for Scenario A?
A) 2%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 14%
E) 17%
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting the highest initial price that customers really desiring the product are willing to pay when introducing a new or innovative product is referred to as
A) a skimming strategy.
B) a penetration strategy.
C) a price-lining strategy.
D) an experience-curve pricing strategy.
E) a prestige pricing strategy.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The practice of charging a very low price for a product with the intent of driving competitors out of business is referred to as
A) price fixing.
B) predatory pricing.
C) price discrimination.
D) deceptive pricing.
E) geographical pricing.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two forms of cost-plus pricing are
A) cost-plus-fixed-fee pricing and cost-plus-variable-fee pricing.
B) cost-plus-ROI pricing and cost-percentage-ROI pricing.
C) target return on sales pricing and target return on investment pricing.
D) cost-plus-percentage-of-cost pricing and cost-plus-fixed-fee pricing.
E) dynamic pricing and flexible pricing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 319
Related Exams