A) a Gantt chart.
B) a demand curve.
C) an ROI analysis.
D) a cross-tabulation.
E) a break-even chart.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
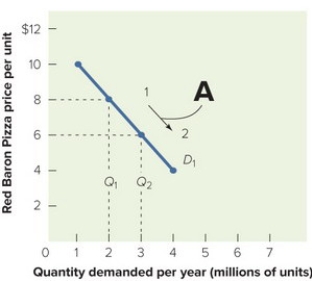 Figure 13-4A
-Figure 13-4A above shows that when the price for Red Baron frozen cheese pizzas moves from $8 to $6 per unit along the demand curve D1, the quantity demanded
Figure 13-4A
-Figure 13-4A above shows that when the price for Red Baron frozen cheese pizzas moves from $8 to $6 per unit along the demand curve D1, the quantity demanded
A) increases from 2 to 3 million units per year.
B) decreases from 3 to 2 million units per year.
C) stays the same.
D) increases from 6 to 8 million units per year.
E) decreases from 8 to 6 million units per year.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists have identified four types of competitive markets, which are
A) capitalistic, monopolistic, socialist, and communist.
B) pure monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and pure competition.
C) free market, restrained market, government-regulated, and command economy.
D) market economy, command economy, traditional economy, and controlled economy.
E) open market, consumer-dominated market, service market, and product market.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Basic to setting a product's price is the extent of ________. This information is used in estimating the revenues the firm expects to receive.
A) management's commitment to the product relative to other products in the line
B) the product line into which it will be introduced
C) customer demand for it
D) the firm's promotional budget
E) distribution requirements
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these would be an example of a fixed cost for a company that makes carbon monoxide monitoring systems for workers to wear in hazardous areas?
A) the lithium batteries that are used in each monitor
B) the chest harness used to wear the monitor
C) the insurance for the company's factory
D) the free training videos that are sent to each new customer
E) the stainless-steel, water-resistant cases in which the monitors are stored
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To reduce the price sensitivity for some of its products, Washburn Guitars
A) uses multiple suppliers for its raw materials.
B) offers three months of free music lessons with the purchase of each guitar.
C) uses endorsements by internationally known musicians who play Washburn signature guitars.
D) offers a lifetime, unconditional warranty on all its instruments regardless of the price of its guitars.
E) sponsors free music programs and special Washburn guitar camps for children.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Specifying the role of price in an organization's marketing and strategic plans is referred to as
A) choosing a pricing plan.
B) defining a profit mission.
C) developing pricing constraints.
D) setting pricing objectives.
E) determining the list or quoted price.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements about the product life cycle as a pricing constraint is most accurate?
A) The newer a product is, the higher the price that can usually be charged.
B) The later in the product life cycle a product is, the higher the price that can usually be charged.
C) Once a product is considered nostalgic, the price will continue to rise indefinitely.
D) Fads will generally have only two price points-high and low-but the values of those price points usually will be within 10 percent of each other.
E) Prices should not be changed until a product reaches its maturity stage.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
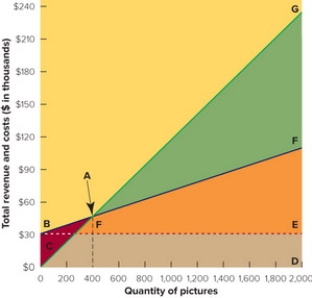 Figure 13-7B
-In the break-even chart in Figure 13-7 above, the wedge ABC represents the firm's
Figure 13-7B
-In the break-even chart in Figure 13-7 above, the wedge ABC represents the firm's
A) fixed costs.
B) break-even point.
C) loss.
D) profit.
E) total revenue.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Several pricing objectives relate to a firm's profit. In one known as ________, a company gives up immediate profit in exchange for achieving a higher market share in the hopes of penetrating competitive markets.
A) maximizing current profit
B) target return
C) break-even strategy
D) minimizing risk
E) managing for long-run profits
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these are elements of determining cost, volume, and profit relationships in the price-setting process?
A) objectives and constraints
B) estimation of demand, sales revenue, and price elasticity
C) cost estimation, marginal analysis, and break-even analysis
D) demand for the product class and brand, newness of the product, and competition
E) market segmentation targeting, and positioning
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inelastic demand exists when
A) a small percentage decrease in price produces a smaller percentage increase in quantity demanded.
B) a small percentage increase in price produces a larger percentage increase in quantity demanded.
C) an increase in price is impossible due to government restrictions.
D) the quantity demanded remains the same regardless of any changes in marketing strategies.
E) a small percentage decrease in price produces a smaller percentage increase in quantity supplied.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The unit variable cost (UVC) divided by selling price (P) is
A) contribution margin (CM) .
B) fixed costs (FC) .
C) total cost (TC) .
D) total revenue (TR) .
E) price per unit of the product (P) .
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
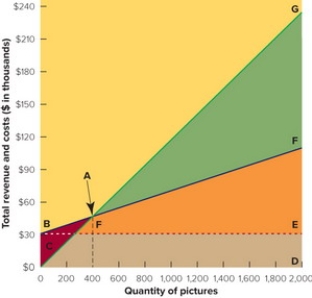 Figure 13-7B
-In the break-even chart in Figure 13-7 above, the rectangular area EBCD represents the firm's
Figure 13-7B
-In the break-even chart in Figure 13-7 above, the rectangular area EBCD represents the firm's
A) fixed costs.
B) break-even point.
C) variable costs.
D) profit.
E) total revenue.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the sake of simplicity and by convention, price elasticity figures are shown as
A) positive numbers (0.64, 1.25, etc.) .
B) negative numbers (−0.64, −1.25, etc.) .
C) Greek letters (∑, ∏, etc.) .
D) Roman numerals (I, V, X, etc.) .
E) English consonants (P, Q, R, etc.) .
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If competitive market circumstances are such that there is almost no price competition, no product differentiation, and the only advertising informs prospects that the product is available, then the competitive market in this industry must be
A) a pure monopoly.
B) pure competition.
C) an oligopoly.
D) monopolistic competition.
E) monopolistic oligopoly.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demand factors are
A) the various competitors that provide a substituable product or service.
B) the price levels that should be charged for a given product.
C) the elements that determine consumers' willingness and ability to pay for products.
D) the various groups of consumers who want to purchase a product.
E) the various groups of consumers who can purchase a product.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate a firm's profit using the following information: the unit price (P) for a product is $40; the quantity sold (Q) is 2,000; the fixed cost (FC) is $50,000; and the variable cost (VC) is $20,000.
A) $10,000
B) $50,000
C) $110,000
D) $150,000
E) cannot be determined with the information provided
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price elasticity of demand is determined by a number of factors, such as the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the product or service, and
A) the cash outlay of the purchase relative to a person's disposable income.
B) the stage of the product or service in its product life cycle.
C) the degree of carrying costs for the manufacturer or distributor.
D) the financial resources of the organization itself.
E) the ability of the organization to meet sudden increases in demand.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The break-even point for a large grain farming operation was calculated to be 2 million bushels of corn. Break-even analysis would take place during which step of the price-setting process?
A) identify pricing objectives and constraints
B) determine cost, volume, and profit relationships
C) estimate demand and revenue
D) select an approximate price level
E) make special adjustments to list or quoted price
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 237
Related Exams