A) Lesser omentum
B) Falciform ligament
C) Mesentery proper
D) Mesocolon
E) Intraperitoneal ligament
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mechanical & chemical processes of digestion. 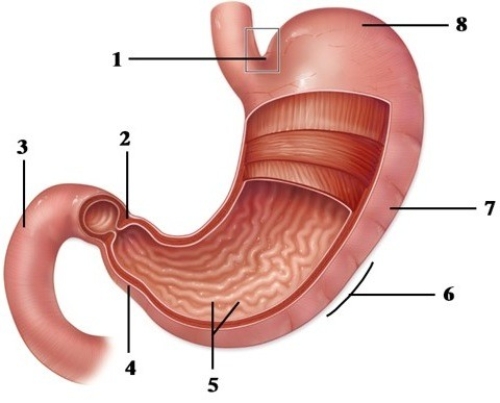 -This figure shows the stomach. What mesentery is attached to the region indicated by number 6?
-This figure shows the stomach. What mesentery is attached to the region indicated by number 6?
A) Falciform ligament
B) Mesentery proper
C) Gastric ligament
D) Greater omentum
E) Lesser omentum
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which organ is not considered an accessory digestive organ?
A) Tongue
B) Teeth
C) Pancreas
D) Salivary glands
E) Pharynx
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gross & microscopic anatomy of the alimentary canal. 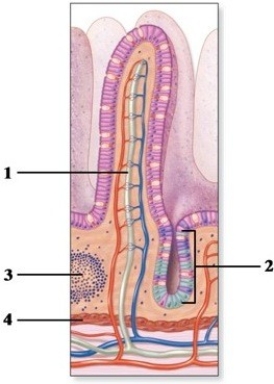 -This figure shows an intestinal villus. What is the invagination indicated by the number 2?
-This figure shows an intestinal villus. What is the invagination indicated by the number 2?
A) Gastric gland
B) Lymphatic nodule
C) Intestinal gland
D) Endocrine gland
E) Peyer patch
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is an accurate description of glucose and sucrose?
A) Glucose is a monosaccharide, sucrose is a polysaccharide, both molecules are starches.
B) Glucose is a monosaccharide, sucrose is a disaccharide, both molecules are carbohydrates.
C) Glucose is a disaccharide, sucrose is a monosaccharide, both molecules are lipids.
D) Glucose is a disaccharide, sucrose is a glycolipid, both molecules are essential nutrients.
E) Glucose is a monoamine, sucrose is a dipeptide, both molecules are acidic.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The deciduous teeth are the ________ teeth, and there are a total of ________ deciduous teeth.
A) milk; 8
B) milk; 20
C) wisdom; 4
D) permanent; 20
E) permanent; 28
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The transverse colon is part of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term "retroperitoneal" may be used to describe the location of certain abdominal organs. This means that such organs are located
A) between the visceral and parietal layers of the peritoneum.
B) posterior to the parietal peritoneum.
C) in the peritoneal cavity.
D) between folds of the parietal peritoneum.
E) deep to the visceral peritoneum.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nucleic acids are digested within the
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) small intestine.
D) pancreas.
E) large intestine.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gross & microscopic anatomy of the alimentary canal.  -This figure shows an intestinal villus. What is the structure indicated by the number 1?
-This figure shows an intestinal villus. What is the structure indicated by the number 1?
A) Intestinal artery
B) Lacteal
C) Microvillus
D) Intestinal vein
E) Flagellum
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vagus nerve activity ________ release of pancreatic juice.
A) stimulates
B) inhibits
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mastication center is located in the ________ of the brain.
A) hippocampus and amygdala
B) medulla and pons
C) hypothalamus
D) entorhinal cortex and basal nuclei
E) solitary nucleus
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carboxypeptidase is an enzyme that helps digest
A) amino acids within the stomach.
B) complex carbohydrates within the small intestine.
C) peptides within the small intestine.
D) disaccharides within the duodenum.
E) starch within the stomach.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The pancreas is part of the alimentary canal.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which layer(s) of the wall of the GI tract contain a nerve plexus?
A) Muscularis only
B) Mucosa and serosa
C) Adventitia only
D) Mucosa and muscularis
E) Submucosa and muscularis
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increased secretion of watery saliva will result when the
A) basal nuclei of the brainstem activate sympathetic pathways to salivary glands.
B) basal nuclei of the cerebrum activate somatic pathways to salivary glands.
C) salivary nuclei of the brainstem activate parasympathetic pathways to salivary glands.
D) salivary nuclei of the cerebrum activate sympathetic pathways to salivary glands.
E) glossopharyngeal nuclei of the pons activate somatic and sympathetic pathways to the salivary glands.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The process of swallowing is also called ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mastication is a process that facilitates
A) propulsion of materials through the intestine, and it involves simultaneous secretion of enzymes.
B) mixing of food within the stomach, and it occurs with simultaneous hormone secretion there.
C) swallowing of food, and it increases the surface area of the food for exposure to enzymes.
D) absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream, and it involves carrier proteins in the epithelium.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lysozyme within saliva primarily functions to
A) moisten and disperse food.
B) initiate the chemical breakdown of starch.
C) inhibit bacterial growth.
D) wash materials off teeth.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The esophagus is part of the gastrointestinal tract.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 141
Related Exams