A) systemic blood pressure by signaling for a decrease in heart rate through blood-borne hormones.
B) urine production by signaling for a decrease in urine production through the hormone ADH.
C) NaCl concentration in tubular fluid by signaling for afferent arteriole constriction with local chemical messengers.
D) glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure by signaling for afferent arterioles to constrict and increase filtration rate.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Micturition
A) is another name for urination.
B) is a reflex triggered by stretch receptors in the urinary bladder.
C) requires the opening of two sphincters.
D) requires contraction of the muscularis layer of the urinary bladder.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is an increase in systemic blood pressure, the resulting stretch of afferent arterioles results in reflexive
A) vasoconstriction of efferent arterioles to raise GFR.
B) vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles to keep GFR normal.
C) vasodilation of efferent arterioles to lower GFR.
D) vasodilation of afferent arterioles to keep GFR normal.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Renal plasma clearance
A) is lower than GFR for substances that are both filtered and secreted.
B) is the same as GFR for substances that are both filtered and secreted.
C) is the amount of water loss from the plasma to the urine over the course of one hour.
D) is the volume of plasma that can be entirely cleared of a substance in one minute.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Glucose and protein are common solutes within urine.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The ball of capillaries in the renal corpuscle is called the ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Peritubular capillaries tend to exhibit
A) high hydrostatic pressure and high colloid pressure.
B) high hydrostatic pressure and low colloid pressure.
C) low hydrostatic pressure and low colloid pressure.
D) low hydrostatic pressure and high colloid pressure.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sympathetic stimulation of the kidney results in
A) constriction of afferent arterioles and an increase in the surface area of the glomerulus.
B) constriction of afferent arterioles and a decrease in the surface area of the glomerulus.
C) dilation of afferent arterioles and an increase in the surface area of the glomerulus.
D) dilation of afferent arterioles and a decrease in the surface area of the glomerulus.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The capsular hydrostatic pressure is generally ________ than the glomerular hydrostatic pressure; increases in capsular hydrostatic pressure ________ the formation of additional filtrate.
A) larger; facilitate
B) larger; impede
C) smaller; facilitate
D) smaller; impede
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Tubuloglomerular feedback and myogenic response are both components of renal autoregulation.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Substances that are both filtered and reabsorbed have a renal plasma clearance that is ________ the GFR.
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) the same as
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pain from the kidneys is usually referred by way of the
A) autonomic pathways to the inferior pelvic organs.
B) sympathetic pathways to the T11-L2 dermatomes.
C) somatic pathways to the left shoulder.
D) parasympathetic pathways to the T1-T2 dermatomes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Passive movement of water and solutes from the plasma to the capsular space of kidney corpuscles is a process known as ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gross & microscopic anatomy of the urinary tract, including detailed histology of the nephron. 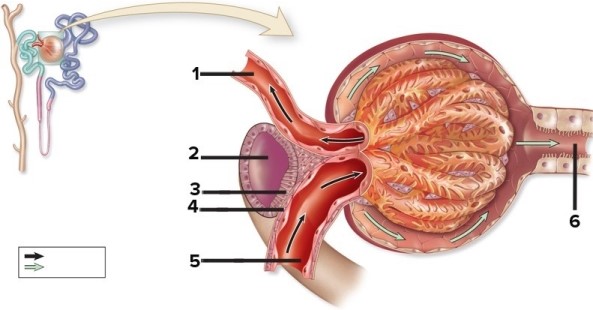 -This figure shows a renal corpuscle. What structure does number 1 indicate?
-This figure shows a renal corpuscle. What structure does number 1 indicate?
A) Distal convoluted tubule
B) Glomerulus
C) Afferent arteriole
D) Proximal convoluted tubule
E) Efferent arteriole
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hormone ANP is released from the heart and causes the urinary system to
A) increase urine volume and blood volume.
B) increase urine volume and decrease blood volume.
C) decrease urine volume and blood volume.
D) decrease urine volume and increase blood volume.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Urination is triggered by a complex sequence of events called the ________ reflex.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which class of nephron is crucially important in establishing a salt concentration gradient in the kidney so that urine concentration can be regulated?
A) Intercalated nephrons
B) Juxtamedullary nephrons
C) Adrenal nephrons
D) Cortical nephrons
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The normal pH for urine
A) is anything below 7.0.
B) is anything above 7.0
C) ranges between 4.5 and 8.0.
D) ranges between 3.0 and 6.0.
E) ranges between 8.0 and 9.0 for someone with a diet high in protein.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gross & microscopic anatomy of the urinary tract, including detailed histology of the nephron.  -This figure shows a renal corpuscle. What structure does number 6 indicate?
-This figure shows a renal corpuscle. What structure does number 6 indicate?
A) Efferent arteriole
B) Distal convoluted tubule
C) Proximal convoluted tubule
D) Afferent arteriole
E) Nephron loop
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Immediately before blood enters arterioles of the kidney, it travels through small arteries that project peripherally into the renal cortex. These arteries are the
A) arcuate arteries.
B) interlobular arteries.
C) segmental arteries.
D) lobar arteries.
E) peritubular arteries.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 161
Related Exams