A) are ductless glands.
B) are the organs of the endocrine system.
C) secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
D) help maintain homeostasis.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two hormones released from the posterior pituitary are
A) oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone.
B) thyrotropin-releasing hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone.
C) prolactin and growth hormone.
D) prolactin and vasopressin.
E) follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not characteristic of the endocrine system?
A) Effects: causes metabolic activity changes in target cells
B) Response time: slow reaction time = seconds to hours
C) Duration of response: long-lasting = minutes to weeks
D) Recovery time: rapid, immediate return to prestimulation level
E) Communication method: hormones in the bloodstream
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intracellular signaling pathways within target cells are organized such that
A) each step allows for amplification of the signal where one molecule can activate many.
B) each step involves one molecule activating or synthesizing exactly one other molecule for precise control.
C) enzymes are used up and degraded after each individual reaction they catalyze.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Until thyroid hormone needs to be secreted, precursors to it are stored in a viscous, protein-rich fluid within the center of thyroid follicles. This viscous fluid is known as ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the signal transduction pathway that results in the formation of inositol triphosphate, the G protein directly activates
A) phospholipase C.
B) protein kinase A.
C) calmodulin.
D) adenylate cyclase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A G protein is
A) a type of water-soluble hormone.
B) a second messenger activated by a steroid hormone.
C) a molecule that binds a guanine nucleotide and helps transduce a signal inside a target cell.
D) a receptor for a water-soluble hormone that causes arachidonic acid to be extracted from a phospholipid.
E) an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of ATP into cyclic AMP.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary function of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is to
A) regulate salt and water balance by acting on the renal system.
B) stimulate glucocorticoid release from the adrenal glands.
C) stimulate adrenaline release from the adrenal medulla.
D) stimulate cell growth and cell division in muscle and bone.
E) stimulate the development of the folds on the surface of the brain.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hypothalamic hormone that triggers the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is
A) cortisol.
B) corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) .
C) vasopressin.
D) adrenal follicle-stimulating hormone.
E) cortical stimulating factor (CSF) .
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a chemical messenger helps initiate an inflammatory response by causing cellular changes in neighboring cells, it is demonstrating ________ signaling.
A) autocrine
B) paracrine
C) allomone
D) pheromone
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to the liver might impair enzymatic degradation of some hormones. The levels of such hormones in the blood would therefore be expected to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which order would blood flow through these structures as it travels from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland? A: Primary plexus B: Secondary plexus C: Hypophyseal portal veins
A) a - b - c
B) a - c - b
C) c - a - b
D) b - a - c
E) c - b - a
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to young adults, the elderly usually have ________ levels of circulating growth hormone and ________ levels of circulating sex hormones.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As someone starts to develop in puberty, most cells in their reproductive organs are probably starting to express
A) more receptors for sex hormones.
B) fewer receptors for sex hormones.
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Insulin causes a(n) ________ in glycogenesis in the liver and a(n) ________ in lipogenesis in adipose.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a tropic hormone?
A) Thyroid-stimulating hormone
B) Adrenocorticotropic hormone
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone
D) Prolactin
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not correct regarding the pancreas?
A) It is located posterior to the stomach, between the small intestine and the spleen.
B) It is a heterocrine, or mixed, gland.
C) It is elongated in shape, spongy, and nodular.
D) The majority of cells in the pancreas are pancreatic acini.
E) It does not begin to secrete its hormones until puberty.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Alpha cells of the pancreas secrete the hormone ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lipophilic hormones bind to ________ receptors of target cells.
A) intracellular
B) membrane-bound
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identity, source, secretory control, & functional roles of the major hormones produced by the body. 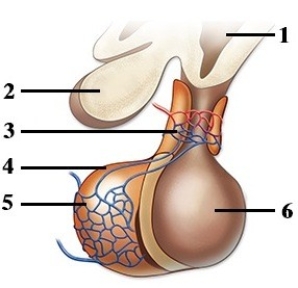 -This figure shows the pituitary gland. Which number indicates the posterior pituitary?
-This figure shows the pituitary gland. Which number indicates the posterior pituitary?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 127
Related Exams