A) precision would be greater, and we would not need as many receptors to monitor the environment for stimuli.
B) precision would be greater, but we would need more receptors to monitor the environment for stimuli.
C) precision would be lessened, and we would need more receptors to monitor the environment for stimuli.
D) precision would be lessened, but we would not need as many receptors to monitor the environment for stimuli.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
These receptors respond to changes in temperature.
A) Chemoreceptors
B) Thermoreceptors
C) Photoreceptors
D) Mechanoreceptors
E) Baroreceptors
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After being funneled by the auricle, sound waves pass (in sequence) through the
A) external acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, ossicles, and oval window.
B) external acoustic meatus, oval window, ossicles, and cochlea.
C) external acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, internal acoustic meatus, and oval window.
D) internal acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, oval window, and ossicles.
E) internal acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, ossicles, and round window.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The entire area through which the sensitive ends of the receptor cells are distributed is the
A) sensory field.
B) receptive field.
C) stimulus area.
D) adaptative radius.
E) transducer field.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The flavor of food depends upon
A) olfaction.
B) gustation.
C) both olfaction and gustation.
D) neither olfaction nor gustation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conscious awareness of incoming sensory information is called
A) sensation.
B) receptor.
C) a stimulus.
D) adaptation.
E) transducer.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
________ receptors respond continuously to a stimulus at a constant rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which structure is not considered to be part of the membranous labyrinth?
A) Scala vestibuli
B) Semicircular duct
C) Saccule
D) Cochlear duct
E) Utricle
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What part of the retina lacks photoreceptors?
A) Optic disc
B) Macula lutea
C) Fovea centralis
D) Posterior retina
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gelatinous mass inside of the eye is called the
A) lacrimal secretion.
B) mucoid body.
C) vitreous humor.
D) hyaloid mass.
E) scleroid humor.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The middle and inner ear are housed within the ________ bone.
A) sphenoid
B) maxillary
C) frontal
D) occipital
E) temporal
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some prey animals, such as rabbits, have laterally placed eyes, and the images on their two retinas do not overlap. Such animals would be expected to show ________ depth perception.
A) excellent
B) poor
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The part of the thalamus that filters auditory information and relays some of it on to the temporal lobe of the cortex is the ________ geniculate nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When light strikes rhodopsin, the retinal is converted
A) from cis to trans, and retinal and opsin combine.
B) from cis to trans, and retinal and opsin disassociate.
C) from trans to cis, and retinal and opsin combine.
D) from trans to cis, and retinal and opsin disassociate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The eye measures about ________ in diameter.
A) 2.5 mm
B) 12.5 mm
C) 2.5 cm
D) 12.5 cm
E) 22.5 cm
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sensory receptors AND their roles. 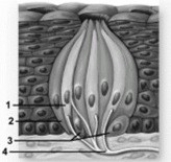 -In this diagram of a taste bud, what structures does number 3 indicate?
-In this diagram of a taste bud, what structures does number 3 indicate?
A) Gustatory microvilli
B) Basal cells
C) Supporting cells
D) Sensory nerves
E) Taste pores
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where would you find olfactory hairs?
A) Scattered among the lamina propria
B) At the apical surface of olfactory neurons
C) Buried within the olfactory glands
D) At the surface of supporting cells
E) Concentrated along basal cells
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Olfactory receptors & their role in smell. 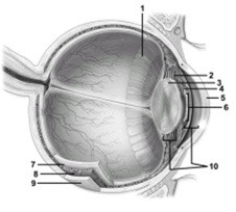 -In this sagittal view of the eye, what space does number 10 indicate?
-In this sagittal view of the eye, what space does number 10 indicate?
A) Scleral venous sinus
B) Anterior cavity
C) Anterior chamber
D) Posterior chamber
E) Posterior cavity
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement accurately describes structures at a taste bud?
A) The gustatory microvillus of a gustatory cell extends through the taste pore of a taste bud.
B) The gustatory villi of basal cells project through the taste bud to the surface of the epithelium.
C) The gustatory microvilus of a papilla projects through the gustatory pore to the gustatory glomerulus.
D) Basal cells contain villi that project through the pore of a papilla to make a taste bud.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The part of the cochlea that converts pressure waves (from sounds) into changes in membrane potentials is the
A) modiolus.
B) scala tympani.
C) spiral organ.
D) scala vestibuli.
E) helicotrema.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 146
Related Exams