A) marine animals.
B) insects.
C) plants.
D) snakes, spiders, and fishes.
E) Batesian mimics.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cardiac glycosides, molecules causing a drastic effect on vertebrate heart function, are produced as defensive chemicals by plants belonging to
A) the milkweed and dogbane families.
B) the mustard family.
C) the grass family.
D) the poison ivy, oak, and sumac families.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual niche the organism is able to occupy in the presence of competitors is called its
A) fundamental niche.
B) realized niche.
C) interference niche.
D) intraspecific niche.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Following their respective breeding seasons, several species of hummingbirds occur at the same locations in North America and several hummingbird flowers bloom simultaneously in these habitats.These flowers seem to have converged to a common morphology and color.Birds have the most visual sensitivity to the color red.Following their breeding season, these species of hummingbirds are
A) allopatric.
B) sympatric. Clarify question:
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of commensalism?
A) a tapeworm living in the intestines of a mule deer
B) barnacles hitching a ride on the skin of a whale
C) a female mosquito sucking blood from a musk oxen
D) wood-digesting flagellates living in the gut of termites
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aposematic, or warning coloration, serves to protect an animal or plant by signaling to potential ________ to stay away.
A) competitors
B) predators
C) mates
D) rivals
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cattle egrets follow African ungulates such as African buffalo around and catch insects that the buffalo flush out.Oxpeckers perch on the backs of buffalo and feed on ectoparasites that infest the buffalo.Which one of the following shows the ecological interaction that the buffalo has with each bird?
A) cattle egret: mutualism; oxpecker: commensalism
B) cattle egret: commensalism; oxpecker: mutualism
C) cattle egret: competition; oxpecker: mutualism
D) cattle egret: mutualism; oxpecker: mutualism
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Resource partitioning would be most likely to occur between allopatric populations of species with similar ecological niches.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lakes become eutrophic by
A) accumulation of organic matter.
B) loss of organic matter.
C) circulation of water in the lake.
D) free exchange of water with outside sources.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In _______ mimicry, unprotected species resemble others that are distasteful.
A) Müllerian
B) competitive
C) Batesian
D) aposematic
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Chemical compounds produced by plants that are not components of major metabolic pathways.
Correct Answer

verified
secondary chemical compounds
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alligators excavate holes in the bottom of bodies of water.During times of severe drought these holes act as refugia for various aquatic organisms that might perish if there were no water available.Thus, alligators in this system can be classified as a(n)
A) keystone species.
B) symbiotic species.
C) sympatric species.
D) allopatric species.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When there are high levels of disturbance in a community, the number of K-selected species should increase along with the overall diversity of the community.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement correctly interprets the graph? 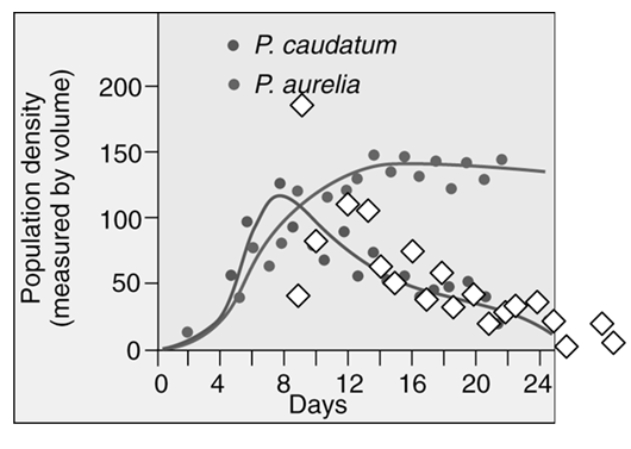
A) Paramecium caudatum drives Paramecium aurelia to near extinction.
B) Paramecium aurelia drives Paramecium caudatum to near extinction.
C) Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia are able to compete for the same resource and their population densities are not affected.
D) Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia are unable to exist and both populations go extinct after 24 days.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in the fundamental niche and the realized niche is
A) the fundamental niche is the actual niche that a species occupies while the realized niche is the potential area that the species is capable of inhabiting.
B) the fundamental niche is the entire niche that a species is capable of using while the realized niche is just what is being occupied.
C) the fundamental niche is smaller than the realized niche.
D) the realized niche is theoretical while the fundamental niche is the entire niche that an organism can use.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the differences between Batesian mimicry and Müllerian mimicry?
A) In Batesian mimicry the model must behave differently than the mimic; in Müllerian mimicry they behave the same.
B) In Batesian mimicry the model must be more dangerous than the mimic; in Müllerian mimicry they are both dangerous.
C) Batesian mimicry does not differ from Müllerian mimicry.Two different scientists discovered these two types at the same time, and they disagreed on what to call it.
D) Batesian mimicry differs from Müllerian mimicry in that they occur on different continents-Batesian on the North American and Müllerian on the European.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two of Darwin's finches display a character displacement when they occur as sympatric species.Which of the statements correctly interprets the graph? 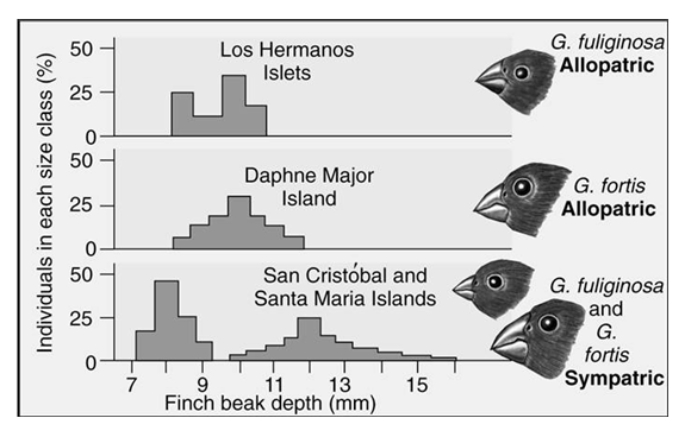
A) Both species have the same size beak on Santa Maria Island.
B) Both species have the same size beaks on Daphne Major.
C) Both species have the same size beaks on Los Hermanos Island.
D) The two species have different beak sizes when they occur on the same island.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Competition between species is called ____________ competition.
A) interspecific
B) exploitative
C) interference
D) fundamental
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A species that plays a critical role in maintaining the structure of an ecological community and helps to determine the types and numbers of various other species in the community is known as
A) a predator.
B) a keystone species.
C) the primary species.
D) the dominant species.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have been studying the relationship between jackals and tigers in India.Until recently, the only relationship you have observed is that jackals will associate themselves with a particular tiger and follow it at a safe distance in order to feed on the big cat's kills.However, recently you observed a jackal alerting a tiger to a kill with a loud cry.If you continue to observe this alerting behavior, you might change the categorization of the jackal/tiger relationship from ___________ to __________________.
A) mutualism; parasitism
B) mutualism; commensalism
C) commensalism; mutualism
D) parasitism; mutualism
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 44
Related Exams