A) K-related
B) density-independent
C) environmental resistance
D) density-dependent
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The statistical study of populations including sex ratio, age structure, and predicting growth rates is called _________.
A) ethology
B) demography
C) population genetics
D) biometrics
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a species with r-selected adaptations?
A) house fly
B) blue whale
C) gorilla
D) horse
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the graph is true?
A) Oysters live longer than Hydra.
B) Hydra and humans have parallel life spans.
C) Humans and oysters have similar life spans.
D) Humans have low mortality rates early in life.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following expressions from the logistic equation (dN/dt = rN ((K - N) /K) represents the proportion of unused resources remaining for use by the population?
A) the carrying capacity (K)
B) the population size (N)
C) the biotic potential (rN)
D) (K - N) /K
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small group of mice are released on an island without mice but with abundant food for mice and no predators.Initially, the growth of the mouse population will be limited mainly by what?
A) the carrying capacity
B) the biotic potential
C) only density-dependent factors
D) only density-independent factors
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under which condition will a population experience growth?
A) when N equals K
B) when N is less than K
C) when dN/dt equals zero
D) when r equals zero
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are three aspects of entire populations that are important and often studied.Select the best choice from the ones listed.
A) a population's range, the pattern of spacing of individuals within the range, and the size that the population attains
B) a population's range, the amount of food available within the range, and the size that the population attains
C) a population's range, the parental care received by each offspring within the population, and the size that the population attains
D) a population's range, the size home range of an individual in the population, and the parental care expended for each offspring
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Populations of endotherms that live in colder climates tend to have shorter ears and limbs than populations of the same species in warm climates.This is called ____________ Rule.
A) Allen's
B) the K-Selected
C) the r-Selected
D) Edward's
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are not many species of fish living deep in the oceans, but the deep-sea fish occasionally pulled up by fisherman have been bizarre creatures, such as the deep-sea anglerfish with its giant fangs and bioluminescent lure.Why have these fascinating deep-sea fish never been shown live on exhibit in an aquarium?
A) Their diet is too specialized.
B) They are adapted to cold temperatures and total darkness.
C) They might frighten visitors.
D) They are adapted for high pressure, and will die at low pressure. Clarify question:
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the sigmoid growth curve, the carrying capacity of the environment is indicated by what symbol?
A) ri
B) N
C) K
D) dN/dt
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are population pyramids used to show?
A) death rates
B) birth rates
C) competition
D) age composition of a population
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The trade-off between investments in current reproduction and in growth that promotes future reproduction is referred to as the total cost of what?
A) adaptation
B) selection
C) reproduction
D) genetic change
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clumped or patched populations that undergo local periodic extinction and recolonization are called what?
A) randomly spaced populations
B) uniformly spaced populations
C) metapopulations
D) over-sized populations
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group of international students is having a heated discussion in the dining hall."Your country needs to get its population under control!" asserts a student from the United States."Perhaps," replies the Indian student, "but your country ______________________."
A) has the highest per capita resource consumption, ten times greater than mine
B) also has a big population overgrowth problem
C) has a much higher birth rate
D) has the lowest infant mortality rate
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You construct a life table for a plant species and find that in all cases about the same proportion of the cohort survive to the beginning of the next time interval.What would you call this?
A) a Type I survivorship curve
B) a Type II survivorship curve
C) a Type III survivorship curve
D) a semelparous life history adaptation
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure included shows the body temperature of lizards versus air temperature in two different habitats-open and shaded forest.Which one of the following conclusions is best supported by these data. 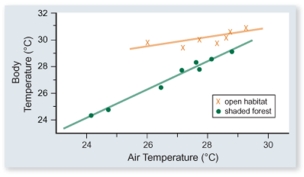
A) Lizards are more active in open habitats.
B) Lizards sunbathe more in open habitats.
C) Lizards in shaded forest habitats eat more to maintain their temperature.
D) The body temperature of lizards is more constant in open than in shaded forest habitats.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demographic studies include all of the following except what?
A) age structure
B) growth rates
C) mortality and survivorship curves
D) sex ratio
E) measurements of interspecific competition
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many times species are composed of networks of distinct populations called metapopulations.When do metapopulations occur?
A) When a population is large and uniformly distributed.
B) When a population in poor habitat continually sends out dispersers to bolster populations in better habitats.
C) When a population in a better habitat does not send out colonizers into less suitable habitats.
D) When suitable habitat is patchily distributed and separated by areas of unsuitable habitat.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate at which a population of a given species will increase when no limits are placed on its rate of growth is called its
A) maximum growth.
B) carrying capacity.
C) biotic potential.
D) optimal growth.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams