A) instinct
B) free will
C) consciousness
D) operance
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The modification of behavior as a result of experience is called
A) association.
B) behavior modification.
C) habituation.
D) learning.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a scientist is conducting a study of how an animal's senses provide a physiological basis for a particular behavior, what type of causation is she exploring?
A) ultimate causation
B) proximate causation
C) stereotyped causation
D) ethnological causation
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By evaluating and selecting mates with superior qualities, an animal can increase its
A) reproductive success.
B) learning.
C) competitive strategies.
D) foraging efficiency.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Male Mormon crickets choose larger females as their mates.Which of the following statements best interprets the graph? 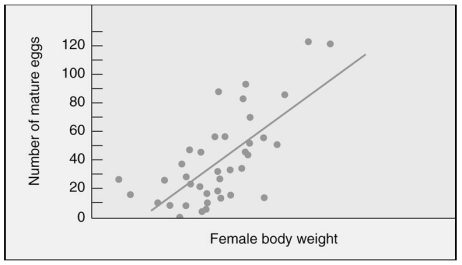
A) Larger females live longer and thus produce more eggs.
B) Larger females are capable of storing sperm.
C) Larger females reproduce earlier than smaller females.
D) Larger females lay more eggs.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an unrelated stimulus, such as the ringing of a bell, was presented at the same time as the meat powder, over repeated trials, a dog would salivate in response to the sound of the bell alone.This kind of response is called
A) behavioral learning.
B) classical conditioning.
C) deviant behavior.
D) operant conditioning.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a behavior has evolved by natural selection, it must have ______________.
A) benefits for both males and females
B) reduced the predation rate on the animal
C) evolved the same way in each species
D) a genetic basis
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following genes would most likely play a role in promoting kin selection?
A) wingless -- critical for the formation of wings in fruit flies
B) SRY -- the gene that initiates male sex determination
C) Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) genes -- allow mammals to recognize related individuals
D) the genes important for the development of large antlers in the caribou Clarify question:
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals tend to feed on prey that maximize their net energy intake.This is called the __________ theory.
A) competitive exclusion
B) maximal consumption
C) optimal foraging
D) optimization
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the flash pattern used by female fireflies to attract males of their species an example of?
A) a sign stimulus
B) an innate releasing mechanism
C) a supernormal stimulus
D) sexual imprinting Clarify question:
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A study finds a positive correlation between the number of spots on the tail of male peacocks and their mating success.What would be the best followup experiment?
A) Count the number of spots on female tails and measure mating success.
B) Remove spots or add artificial spots to male tails and determine female responses.
C) Measure the sperm count of males and compare to spot count.
D) Inject testosterone and observe changes in spot count. Clarify question:
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One spring, your friend living in Minnesota eagerly sets up her new hummingbird feeders, and is thrilled to watch hummingbirds feeding on the nectar.However, she is disappointed when after just a week or two the hummingbirds disappear.What advice would you give her?
A) Set up a bell (conditioned stimulus) near the feeders so the hummingbirds make an association with the food.
B) Set up flashing red lights that mimic the male neck feathers -- that should attract more males to the area.
C) Set up the feeders again in the fall.The hummingbirds may have briefly traveled through during their annual spring migration.
D) Wait till next year -- hummingbirds are a high-metabolism, semelparous species and have already reproduced and died. Clarify question:
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As an animal matures, it forms attachments to other individuals and develops preferences.This process is called
A) instinct.
B) imprinting.
C) associational learning.
D) habituation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Due to reproductive isolation, a new species of weaver bird is evolving.Is it likely to use a social or solitary nesting strategy?
A) It depends on whether it lives in the forest or the open savanna.
B) It depends on whether it lives in near water or near the desert.
C) It depends on how many similar species it is competing with.
D) It depends on how many eggs it lays. African weaver birds, which construct nests from vegetation, provide an excellent example of the relationship between ecology and social organization.Their roughly 90 species can be divided according to the type of social group they form.One group of species lives in the forest and builds camouflaged, solitary nests.Males and females are monogamous; they forage for insects to feed their young.The second group of species nests in colonies in trees on the savanna.They are polygynous and feed in flocks on seeds.The feeding and nesting habits of these two groups of species are correlated with their mating systems.In the forest, insects are hard to find, and both parents must cooperate in feeding the young.The camouflaged nests do not call the attention of predators to their brood.On the open savanna, building a hidden nest is not an option.Rather, savanna-dwelling weaver birds protect their young from predators by nesting in trees, which are not very abundant.This shortage of safe nest sites means that birds must nest together in colonies.Because seeds occur abundantly, a female can acquire all the food needed to rear young without a male's help.The male, free from the duties of parenting, spends his time courting many females-a polygynous mating system.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
True or False: Haplodiploidy is necessary for eusociality.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Platys and swordtails are related tropical freshwater fish.In studies, researchers have shown that female platys prefer males with swordtails, even though males of their own species do not have them.This was discovered by attaching artificial swordtails to platys males.What does this suggest about the origin of the swordtail feature?
A) Female preference for swords may have predated the origin of the feature itself.
B) Evolution of swords later led to evolution of female preference for swords.
C) The same gene that causes sword development also causes development of neural circuits for female preference.
D) Adjacent genes on the same chromosome cause sword development and development of neural circuits for female preference. Clarify question:
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who conducted the famous "imprinting" experiment on geese?
A) Mendel
B) Russel
C) Lorenz
D) Darwin
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your study buddy asks, "would you please explain the difference between home range and territory?" What is the best response?
A) Territory is the entire area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food, and mates.Home range is near its nest or den.
B) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates and will defend against other members of its species.Home range is near its nest or den.
C) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates, and will defend against other members of its species.Home range is the area that an animal may roam over on a daily basis.
D) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates, and will defend against others members of its species.Home range is a smaller area within the territory that the animal is found in when it is resting or hiding from predators.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a research conference, you meet a graduate student who studies the hormonal underpinnings of mating behavior in two species of squirrel."It turns out the difference between my two squirrel species is similar to the difference between the prairie and the montane voles," he says.You nod knowingly, and reply...
A) "Oh, so the promiscuous species has a lot of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbus, blocking pair bonding, and the monogamous species doesn't?"
B) "Oh, so the monogamous species has a lot of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
C) "Oh, so the polyandrous species has a lot of serotonin and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
D) "Oh, so the monogamous species has a lot of serotonin and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?" Clarify question:
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals that acquire energy efficiently during foraging will increase their fitness by having more energy available for _______________.
A) competition
B) defenses
C) respiration
D) reproduction
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 79
Related Exams