A) fossil record
B) homology
C) convergent evolution
D) biogeography
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some of the most dramatic evidence for evolution has come from human agriculture.One of the most highly artificially selected crop plants is
A) peas.
B) tomatoes.
C) potatoes.
D) corn.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows results of bristle number in Drosophila flies after 35 generations of artificial selection.This figure suggests that 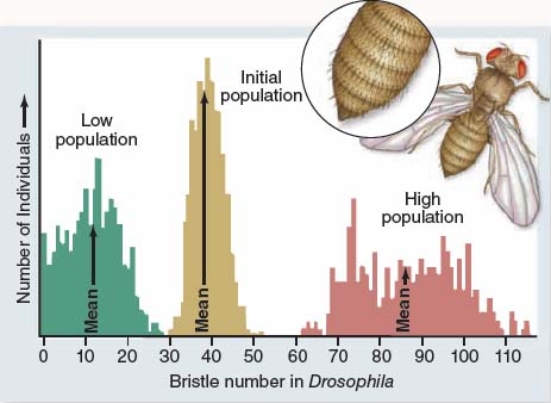
A) bristle number has evolved beyond the original range of phenotypic variation for this trait.
B) after 35 generations of selection, populations no longer exhibit variation in bristle number.
C) natural selection cannot lead to large phenotypic changes.
D) at the end of the experiment, "high population" flies were unable to interbreed with "low population" flies.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following features of Archaeopteryx clearly demonstrates that it was on the evolutionary line leading from dinosaurs to birds?
A) egg-laying ability
B) teeth
C) feathers
D) bony tail
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A new plant species is introduced to Daphne Major and produces small, thin seeds.This plant species is highly adapted to drought and after 5 years has replaced over 80% of the native plants that produce large seeds.How will this change affect the evolution of beak size in the medium ground finch population?
A) Small beaks will be favored under all rainfall conditions.
B) Small beaks will be favored in wet years and large beaks will be favored in dry years.
C) Large beaks will be favored in wet years and small beaks will be favored in dry years.
D) Large beaks will be favored under all rainfall conditions.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A technique used in dating a rock can be used to accurately predict the age of the fossils occurring in the rocks.This technique involves
A) fossil dating.
B) successive rock layering.
C) radioactive isotope decay.
D) structural geology.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing the evolution of domesticated dogs to the evolution of wolves over the same time period illustrates what relationship between artificial and natural selection?
A) Artificial selection is slower than natural selection.
B) Artificial selection is reversible; natural selection is not.
C) Artificial selection is more likely to produce maladaptive structures than natural selection.
D) Artificial selection cannot produce changes as large as changes produced by natural selection.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rock contains 18 mg of the radioactive isotope carbon-14.The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,600 years.How many half-lives and years will it take before the carbon-14 decays to less than 4 mg?
A) 1 half-lives; 5,600 years
B) 2 half-lives; 11,200 years
C) 3 half-lives; 16,800 years
D) 4 half-lives; 22,400 years
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The side toes of a horse, the pelvis of the whale, and the human appendix are all examples of structures that resemble structures of presumed ancestors, which are known as
A) analogous structures.
B) homologous structures.
C) vestigial structures.
D) homeotic mutations.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inhabitants of oceanic islands resemble forms of the nearest mainland but show some differences.This is an example of
A) the fossil record.
B) homology.
C) convergent evolution.
D) biogeography.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural selection has favored the dark form of the peppered moth in areas subject to severe air pollution, perhaps because on darkened trees, moth-eating birds see them less easily.As pollution abated, the light forms increased in the population because
A) light moths had lower fitness than dark moths.
B) light moths were able to produce more offspring than dark moths.
C) light moths were more genetically variable than dark moths.
D) birds ate more light moths.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It could be said that today's Australian marsupials and today's placental mammals have
A) undergone divergent evolution.
B) undergone selective advantage.
C) undergone heterozygote advantage.
D) undergone convergent evolution.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plants in the desert-adapted families Cactacea (cactus) and Euphorbia (euphorbs) share many of the same physical characteristics, such as succulent stems that store water and CAM photosynthesis, but they do not share a recent common ancestor.This evidence suggests that these families are an example of
A) convergent evolution.
B) homologous structures.
C) vestigial structures.
D) divergent evolution.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Industrial melanism involving the peppered moths (Biston sp.) is cited as an example of natural selection that has been observed in the last one hundred years.Recall that the peppered moth exhibits two distinct morphological types with dark and light colored wings.Which of the following statements about changes in these two types of moths as a result of industrial melanism is true?
A) The dark forms are selected against in nonpolluted forests.
B) The dark forms are distasteful to birds and are thus safe in polluted forests.
C) The light forms are selected against in nonpolluted forests.
D) Birds prey more on the dark forms in polluted forests
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Homologous structures are
A) structures of animals that appear to have evolved from different parts of their bodies.
B) structures of animals that have different appearances and functions but seem to have evolved from the same body part in a common ancestor.
C) structures of animals that have the same appearances and functions but obviously no common ancestor.
D) structures of animals that have different appearances and functions but different ancestors.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Industrial melanism is a term
A) describing the color change induced by living in industrialized areas.
B) explaining that the darker moths have higher mutation rates because of industrialization.
C) describing the evolutionary process in which initially light-colored organisms become dark as a result of natural selection.
D) explaining that the darker moths having higher reproductive success because of their pigmentation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement factors into artificial but not natural selection?
A) Most organisms are capable of producing more offspring than typically survive.
B) Phenotypic variation of a species has variable appeal to humans interested in that species.
C) Phenotypic variation exists within populations.
D) Phenotypic variation can influence reproductive success.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which "alternate" hypothesis might also explain industrial melanism?
A) Dark moths are more resistant to the toxic effects of pollution than light moths.
B) Dark moths emigrate out of polluted areas to escape the pollution.
C) Pollution kills important tree species that peppered moths depend on for egg laying.
D) Because dark moths absorb more heat, they are more active and better able to avoid bird predation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2006, scientists discovered a fossil that had scales and gills, a flat head with eyes on top like a crocodile, and fin and neck bones that would allow it to prop itself out of the water.The best explanation for this fossil is that it is
A) a transitional fossil between fish and amphibians.
B) a transitional fossil between amphibians and reptiles.
C) a ray-finned fish.
D) a modern amphibian.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Considerably more phenotypic variation exists in domesticated varieties of species like dogs and cabbages than exists in non-domesticated species like lions and maple trees.Which one of the following statements best explains why this is true?
A) There is no selection and mating is random under domestication.
B) During domestication, very high rates of mutation are induced.
C) Genetic drift is important because domestication involves small populations.
D) Many domesticated varieties would not survive in the natural world.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 44
Related Exams