A) fitness
B) selection
C) mutations
D) adaptations
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reproductive success of an individual is known as:
A) variation.
B) adaptive makeup.
C) fitness.
D) microevolution.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gene flow, defined as the movement of genes from one population to another, can take place by migration, as well as
A) physical movement of genes within an individual by transposons.
B) removing the barriers between the populations.
C) mating between individuals of adjacent populations.
D) mating with certain trait-containing individuals.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a small population of cockroaches living in your kitchen, only a few roaches mate in one year.This can lead to random changes in allele frequency in the population through ______
A) nonrandom mating.
B) selection.
C) genetic drift.
D) mutation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
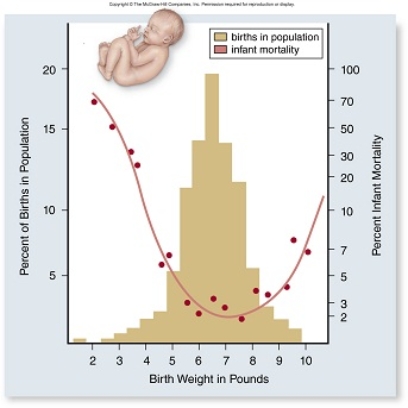 In the graph above, which baby characteristics would explain the percent infant mortality curve and any subsequent effects on fitness?
In the graph above, which baby characteristics would explain the percent infant mortality curve and any subsequent effects on fitness?
A) The smaller the baby the better the chance of survival.
B) The baby needs to be small enough to survive after birth, but large enough for a safe delivery.
C) The baby needs to be large enough to survive after birth, but small enough for a safe delivery.
D) There is no correlation between birth weight and survival.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a forest, trees that get more sunlight grow taller than other nearby trees.This is a form of ______
A) natural selection.
B) directional selection.
C) artificial selection.
D) disruptive selection.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Antigens on red blood cells are hereditary traits that allow blood to be typed in different ways.One system is based on a gene with two alleles, M and N.If the frequency of the M allele in a population is 0.4, then according to the Hardy-Weinberg rule, the expected frequency of the heterozygous MN genotype is ___.
A) 0.16
B) 0.24
C) 0.36
D) 0.48
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for natural selection to occur within a population, certain conditions must be met.One such condition is
A) heterozygosity must be very low.
B) frequent mutations that are inherited.
C) phenotypic differences resulting from environmental conditions.
D) phenotypic variations that are genetic.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two parents who do not have sickle cell anemia have a child that has the disease.The parents are both:
A) homozygous for the sickle cell allele.
B) heterozygous for the sickle cell allele.
C) homozygous for the normal allele.
D) epistatic for the sickle cell allele.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The disease, sickle-cell anemia is common in malaria-infested areas because individuals that are heterozygous for the gene (AS) have enhanced resistance to malaria over normal individuals (AA) .Individuals with severe sickle-cell anemia (SS) usually die before reproduction.If this population moves to an area without malaria, what will happen to the allele frequency of the A allele over time?
A) It will go up because there is no sickle cell anemia.
B) It will go down because there is no malaria.
C) It will go down because there is no sickle cell anemia.
D) It will go up because there is no malaria.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a gene with two alternative alleles, A (with a frequency of p) and B (with a frequency of q) , the term in the algebraic form of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for the heterozygote genotype frequency is
A) p2.
B) q2.
C) 2pq.
D) (p+q) 2.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, p and q are _____.
A) genotypes
B) mutation rates
C) phenotypes
D) allele frequencies
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals that select mates that are phenotypically similar will have _____ when compared with Hardy-Weinberg predictions.
A) fewer homozygotes
B) more homozygotes.
C) less natural selection
D) more mutations
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People homozygous for the sickle-cell anemia allele develop a life threatening disease, while those homozygous for the normal allele are at the highest risk of dying from malaria.Carriers have some resistance to malaria, but do not develop sickle cell anemia.This is an example of ____
A) founder effect.
B) genetic bottleneck.
C) heterozygosity.
D) heterozygote advantage.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
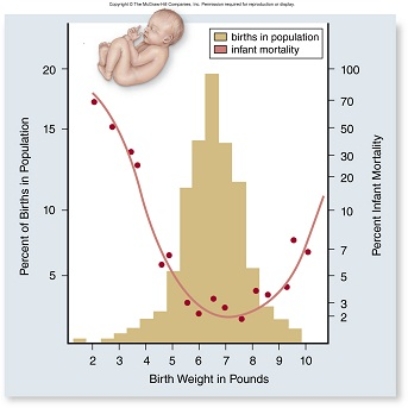 In the graph above, how can the change in infant mortality be explained as birth weight increases from 2 to 7 pounds?
In the graph above, how can the change in infant mortality be explained as birth weight increases from 2 to 7 pounds?
A) A larger baby will have more developed organs and thus have greater fitness.
B) A baby closer to 7 pounds will have more developed organs and thus have lower mortality.
C) A baby closer to 2 pounds will not be able to be delivered safely and thus have lower mortality.
D) A baby closer to 7 pounds will have more developed organs and thus have higher motality.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Female cardinals select male mates in part based on their bright red color.What effect would this have on a cardinal population that was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) The red allele frequencies would decrease because of equilibrium.
B) The frequency of red alleles would be less than those predicted by Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
C) The frequency of red alleles would be greater than those predicted by Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
D) The frequency of red alleles would be equal to those predicted by Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
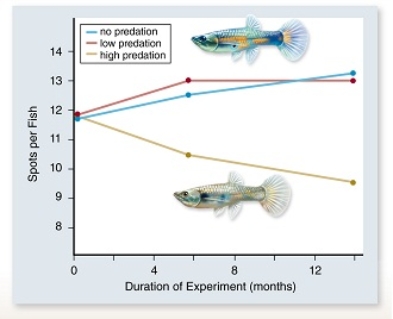 In the experiment above, guppy color patterns (spots) were measured in populations exposed to increasing amounts of predation.From this you could conclude that ____ .
In the experiment above, guppy color patterns (spots) were measured in populations exposed to increasing amounts of predation.From this you could conclude that ____ .
A) evolutionary changes take millions of years to appear
B) predators are less likely to catch and eat brightly colored guppies
C) predators are more likely to catch and eat brightly colored guppies
D) brightly colored guppies are more likely to reproduce in the presence of predators
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An island is on the migration route of sea birds.This island also has abundant tree nesting birds that live on the island permanently and are not found on any other island.The tree nesting birds are more likely than the sea birds to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium because:
A) the sea bird population is larger.
B) there are fewer mutations in the sea birds.
C) mating is random in the tree nesting birds.
D) of high immigration in the sea bird population.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
______ could not be involved in gene flow.
A) Hybridization between neighboring populations
B) Gametes dispersed by ocean currents
C) Disassortative mating within a population
D) Wind-blown pollen
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hardy-Weinberg pointed out that the original proportions of the genotypes in a population would remain constant from generation to generation if certain assumptions are met.Which one of the following is not a Hardy-Weinberg condition?
A) No gene flow occurs.
B) Random mating occurs.
C) No polymorphic loci exist in the population.
D) No selection occurs.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 57
Related Exams