A) action reaction.
B) power stroke.
C) recovery stroke.
D) muscle tone.
E) action potential.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Substance A is found to be a competitor with acetylcholine. Which step of muscle contraction physiology would be directly affected by this substance?
A) Exposure of the active sites on G actin
B) Release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic terminal
C) Generation of an action potential at the sarcolemma
D) Release of the myosin head following the power stroke
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Atrophy at the neuromuscular junction that naturally occurs with age would have what effect on muscles?
A) It would stimulate the nervous system to increase the speed in which it sends action potentials to the muscle fiber.
B) It would stimulate muscle cramps.
C) It would decrease the number of action potentials sent to the muscle fiber.
D) It would cause an increase in the amount of ACh released by the neurons to compensate.
E) It would have no effect on the muscles.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does muscle activity affect the temperature of the body?
A) The rate of chemical reactions increases in muscle fibers during contraction, so the rate of heat production also increases.
B) Muscle contraction generates pyrogens which reset the body's internal thermostat to a higher temperature.
C) Muscle activity directs more warm blood to the muscles away from the central core causing a cooling effect on your internal organs.
D) Increased muscle activity causes a rise in adipose stores which increases the insulation value of the body.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is part of a thin myofilament?
A) ATP-binding site
B) Globular (G) actin
C) Calcium
D) Myosin
E) Sarcolemma
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a function of skeletal muscle?
A) Body movement
B) Maintenance of posture
C) Respiration
D) Constriction of organs
E) Production of heat
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Actin myofilaments
A) resemble bundles of minute golf clubs.
B) contain both myosin and tropomyosin.
C) are held in place by the M line.
D) contain strands of fibrous actin.
E) are the thickest proteins in muscle.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myosin phosphatase
A) activates myosin kinase.
B) forms the cross-bridge.
C) removes phosphate from myosin.
D) binds to calcium-calmodulin complex.
E) opens Ca2+-channels.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a property of the myosin head?
A) They form cross-bridges with the active sites of actin.
B) They have a hinge region to bend and straighten.
C) They bind to troponin.
D) They have ATPase activity.
E) They bind to ATP.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As muscle activity increases, the body temperature ________.
A) decreases
B) increases
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of muscle fatigue known as "psychological fatigue" is the result of
A) depleted ATP reserves.
B) increased Ca2+ concentration in the sarcoplasm.
C) decreased levels of acetylcholine.
D) the emotional state of an individual.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When repolarization of the plasma membrane is complete, the
A) cell dies.
B) cell regenerates.
C) cell no longer has a potential difference across its membrane.
D) cell is no longer responsive.
E) original polarity of the cell is restored.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Endomysium is a delicate network of loose connective tissue that
A) surrounds each muscle fiber.
B) forms a sheath around a fascicle.
C) is composed of elastic fibers.
D) separates individual muscles.
E) penetrates muscle fibers.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will respond to a threshold stimulus with an all-or-none contraction?
A) A single muscle fiber
B) A single motor unit
C) A whole muscle
D) Both a single muscle fiber and a single motor unit are correct.
E) A single muscle fiber, a single motor unit, and a whole muscle are all correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is composed of myosin molecules?
A) Thick myofilaments
B) I bands
C) Z disks
D) Sarcolemma
E) Tropomyosin
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Channels that open or close in response to changes in the electrical charge or voltage across the plasma membrane are called
A) ligand-gated ion channels.
B) leak ion channels.
C) relegated ion channels.
D) voltage-gated ion channels.
E) obligated ion channels.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Concentric contractions occur when
A) the muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
B) the tension and length of the muscle remain constant during a contraction.
C) tension in a muscle is maintained while the muscle increases in length.
D) the muscle produces tension while the length of the muscle increases.
E) isometric contractions occur.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
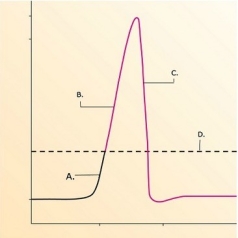 -What does "A" represent on the diagram?
-What does "A" represent on the diagram?
A) Threshold
B) Depolarization
C) Depolarization phase of action potential
D) Repolarization phase of action potential
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is tropomyosin?
A) A protein found along the groove of the F-actin double helix
B) A T tubule and two adjacent terminal cisternae
C) The combination of myosin heads with active sites on actin molecules
D) The movement of myosin head while attached to actin myofilament
E) After exercise, the O2 taken in that exceeds the O2 required for resting metabolism
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Na+ cannot enter a muscle fiber in response to a stimulus,
A) contraction cannot occur.
B) relaxation cannot occur.
C) Na+ will be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum instead.
D) the active sites are left exposed.
E) the action potential travels into the muscle anyway.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 231
Related Exams