A) inhibition of acetylcholine molecules.
B) blockage of acetylcholine receptors.
C) inhibition of acetylcholinesterase.
D) destruction of synaptic vesicles.
E) increase in the amount of acetylcholinesterase.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Multiunit smooth muscle is located in the
A) gastrocnemius.
B) wall of the GI tract.
C) wall of blood vessels.
D) wall of the heart.
E) reproductive system.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The capacity of a muscle cell to shorten forcefully is known as
A) contractility.
B) excitability.
C) extensibility.
D) elasticity.
E) flexibility.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Troponin
A) has two subunits.
B) is part of the myosin myofilament.
C) is a long, flexible protein.
D) has a calcium-binding site.
E) binds to ATP.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calcium ion blocking agents would most likely affect
A) action potential propogation along the transverse tubules.
B) release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) movement of the tropomyosin molecule.
D) release of the myosin head from the G actin molecule.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Callie is a world class marathon runner. Which of the descriptions about her dominant type of skeletal muscle is FALSE?
A) They split ATP slowly.
B) They have large deposits of myoglobin.
C) They are well adapted to anaerobic activity.
D) They have a well-developed blood supply.
E) They have low glycogen stores.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the role of pacemaker cells?
A) They rapidly develop action potentials.
B) They are shallow invaginations of the plasma membrane.
C) They maintain relatively constant tension for a period of time.
D) They are part of the intracellular cytoskeleton.
E) They are enzymes that remove phosphate from myosin.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fascicle
A) is a bundle of reticular fibers.
B) is surrounded by perimysium.
C) is only found in smooth muscle.
D) possesses an external lamina.
E) is a bundle of collagen fibers.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Due to the pattern of innervation of skeletal muscle, one would expect that
A) there are fewer motor neurons than skeletal muscle fibers.
B) there are fewer muscle fibers than motor neurons.
C) the number of muscle fibers and motor neurons is equal.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Movements of the body are usually smooth and occur at differing rates because
A) they are a mixture of isotonic and isometric contractions.
B) motor units contract out of phase at their own particular rates.
C) most muscle contractions closely resemble individual muscle twitches.
D) muscles of different sizes contract at different rates.
E) of the all-or-none principle.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the power stroke?
A) A protein found along the groove of the F-actin double helix
B) A T tubule and two adjacent terminal cisternae
C) The combination of myosin heads with active sites on actin molecules
D) The movement of myosin head while attached to actin myofilament
E) After exercise, the O2 taken in that exceeds the O2 required for resting metabolism
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue has spindle-shaped cells?
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
D) Both skeletal and cardiac muscle are correct.
E) Both cardiac and smooth muscle are correct.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sarcolemma is the
A) plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
B) cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
C) structural and functional unit of the skeletal muscle fiber.
D) contractile thread that extends the length of the muscle fiber.
E) protein strand composed of actin.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tetanus of a muscle is thought to be caused by
A) high Ca2+ concentrations in the sarcoplasm.
B) the rapid movement of Na+ back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) an increase in stimulus strength.
D) increased temperature in the active muscle.
E) decreased amounts of Ca2+ in muscle tissue.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Too much acetylcholinesterase causes
A) continuous stimulation of the muscle fiber.
B) rapid degradation of acetylcholine.
C) voltage-gated Ca2+ channels opening in the presynaptic terminal.
D) an increase in Na+ uptake by the muscle fiber.
E) exocytosis of synaptic vesicles.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acetylcholine binds to a membrane bound receptor and causes ligand-gated sodium channels to open and results in
A) hyperpolarization.
B) depolarization.
C) hypoplarization.
D) no change in membrane potential.
E) There is not enough information to predict the outcome.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Functionally, smooth muscle
A) is well adapted to anaerobic metabolism.
B) exhibits autorhythmic contractions.
C) contracts in response to slow increases in length.
D) is unable to maintain tone.
E) rapidly develops an oxygen deficit.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be caused by a contraction of smooth muscle?
A) Goose bumps
B) Blood leaving the left ventricle of the heart
C) Elevating the eyebrows
D) Blinking the eyelids
E) Deep inspiration
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of respiration rapidly produces ATP for short time periods?
A) Anaerobic respiration
B) Aerobic respiration
C) Both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration are correct.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
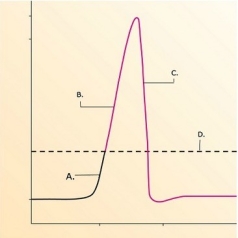 -What does "B" represent on the diagram?
-What does "B" represent on the diagram?
A) Threshold
B) Depolarization
C) Depolarization phase of action potential
D) Repolarization phase of action potential
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 231
Related Exams