A) relaxation of the muscle fiber.
B) contraction with no relaxation.
C) muscle hypertrophy.
D) fibrosis of the muscle.
E) an imbalance of blood calcium.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plasma membrane of an excitable cell is more permeable to K+ because
A) of its positive electrical charge.
B) there are more leak ion channels for K+ than Na+.
C) protein molecules cannot exit through the plasma membrane.
D) calcium ions block Na+ and Cl- channels.
E) there are more gated channels for K+.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen deficit represents
A) the amount anaerobic metabolism must increase after exercise.
B) the amount of O2 converted to lactate during exercise.
C) the amount of CO2 that cells need to eliminate.
D) conversion of pyruvate to lactate.
E) the amount of O2 that cells need to replenish ATP supplies after exercise.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following helps explain the increased tension seen in multiple wave summation?
A) Increased motor unit recruitment
B) Increased concentration of Ca2+ around the myofibrils
C) Exposure of more active sites on myosin myofilaments
D) The breakdown of elastic elements in the cell
E) Decreased stimulus frequency
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) I band - contains only actin
B) M line - middle of the H zone
C) Z disk - structure between adjacent sarcomeres
D) Myosin myofilaments - thin myofilaments
E) Actin myofilaments - thin myofilaments
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are reasons that shivering raises body temperature? (Check all that apply.)
A) Shivering decreases warm blood flow to the core while increasing flow to the muscles.
B) Shivering depresses metabolism.
C) Shivering increases heat production up to 18 times that of resting levels.
D) The process of muscle contraction produces heat.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Drugs called calcium channel blockers may be used to lower blood pressure by causing arteries to vasodilate. How do you suppose these drugs work?
A) They prevent calcium from entering the sarcoplasmic reticulum of smooth muscle.
B) They stimulate the calcium pump in smooth muscle, thus removing calcium from the calmodulin.
C) They prevent calcium from exiting the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle.
D) They prevent calcium from entering cardiac muscle, thus slowing down the heart rate.
E) They prevent calcium from entering smooth muscle, thus allowing the muscle to relax.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which muscle(s) can contract without the need for nervous stimulation?
A) Skeletal muscle only
B) Smooth muscle only
C) Cardiac muscle only
D) Smooth and cardiac muscle
E) Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue would cause flexion and extension of the arm?
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
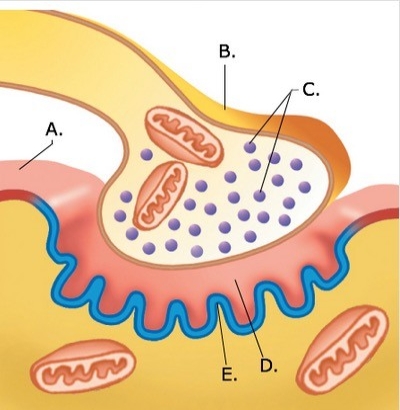 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "C" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "C" represent?
A) Synaptic vesicles
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Sarcolemma
D) Presynaptic terminal
E) Postsynaptic membrane
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sites where a chemical substance is transmitted from the presynaptic terminal of an axon to the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber are called
A) neuromuscular junctions.
B) sarcomeres.
C) myofilaments.
D) Z disks.
E) cell bodies of neurons.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If one nerve stimulus arrives at a muscle fiber so soon that the fiber does NOT relax at all from the previous twitch, the most likely result will be ________.
A) fatigue
B) spasm
C) incomplete tetanus
D) complete tetanus
E) wave summation
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue causes peristalsis?
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An eccentric contraction is described as
A) action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
B) a muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
C) a muscle produces an increasing tension during contraction.
D) a muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
E) a muscle produces tension, but the length of the muscle is increasing.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscle myofibrils
A) are found in the sarcolemma.
B) extend from the sarcolemma to the T-tubule.
C) contain myosin and actin myofilaments.
D) hold muscle fibers together.
E) do not appear striated.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Synaptic vesicles in the neuromuscular junction contain
A) calcium.
B) ATP.
C) acetylcholine.
D) acetylcholinesterase.
E) sodium.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Athletes who train at high altitudes increase their red blood cell count, which increases their oxygen supply during exercise. Increased oxygen supply results in
A) increased glycolysis.
B) increased use of myokinase.
C) longer aerobic respiration.
D) longer anaerobic respiration.
E) reduced ATP consumption.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Epimysium
A) surrounds individual muscles.
B) separates muscle fibers.
C) connects muscles to bone.
D) is a type of muscle tissue.
E) is a type of nerve tissue.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete tetanus
A) is the time during which the tissue cannot respond again.
B) results in complete and incomplete tetanus.
C) is the condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions.
D) is the condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations.
E) is the constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After contraction has occurred, the Ca2+ are
A) destroyed by cholinesterase.
B) chemically bound to the cross bridges.
C) secreted by the Golgi apparatus to the outside of the cell.
D) released from troponin.
E) returned to the sarcolemma.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 231
Related Exams