A) Spongy bone
B) Compact bone
C) Both "spongy bone" and "compact bone" are correct.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Osteomalacia is
A) bone inflammation that often results from bacterial infection.
B) a disease in adults, especially women, characterized by a reduced amount of bone matrix.
C) a disease in adults characterized by softening of bones resulting from calcium depletion.
D) a disease in children characterized by soft, bowed, and swollen bones.
E) a group of genetic disorders producing very brittle bones that are easily fractured; this occurs because of insufficient collagen development.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
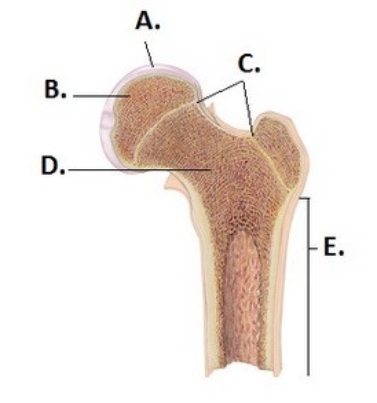 -What does structure "C" represent on the bone diagram?
-What does structure "C" represent on the bone diagram?
A) Spongy bone
B) Diaphysis
C) Epiphyseal lines
D) Articular cartilage
E) Epiphysis
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Woven bone
A) has its collagen fibers randomly oriented.
B) has a porous appearance.
C) is organized into thin sheets of tissue.
D) is very light in weight.
E) is not easily restructured.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two types of bone development formation include endochondral and endosteal bone.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bone remodeling may occur
A) as bones grow.
B) as bones adjust to stress.
C) as fractures heal.
D) constantly during a person's lifetime.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bone cell combines hydroxyapatite and collagen to form extracellular bone matrix?
A) Osteochondral progenitor cell
B) Osteoblast
C) Osteocyte
D) Osteoclast
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What does structure "B" represent on the bone diagram?
-What does structure "B" represent on the bone diagram?
A) Spongy bone
B) Diaphysis
C) Epiphyseal lines
D) Articular cartilage
E) Epiphysis
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The medullary cavity is
A) empty in adult bones.
B) the site where osteoblasts are found.
C) lined with endosteum.
D) filled with fibrocartilage and elastin fibers.
E) dead space in the bone.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which chemical stimulates interstitial cartilage and appositional bone growth?
A) Growth hormone
B) Sex hormones
C) Parathyroid hormone
D) Calcitonin
E) Vitamin D
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bone tissue appears porous?
A) Spongy bone
B) Compact bone
C) Both "spongy bone" and "compact bone" are correct.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Miguel fell out of a tree and broke his fall by putting his arm out, fracturing his radius and ulna. The bones were still aligned at the fracture site. Which specific type of bone fracture is Miguel most likely to have?
A) Stress fracture fracture
B) Nondisplaced fracture
C) Spiral fracture
D) Avulsion fracture
E) None of the choices are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calcitonin
A) decreases osteoblast activity.
B) decreases osteocyte activity.
C) decreases osteochondral progenitor cell activity.
D) is associated with decreased osteoclast activity.
E) has no effect on bone cells.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which substance causes an increase in the blood calcium level?
A) Growth hormone
B) Sex hormones
C) Parathyroid hormone
D) Calcitonin
E) Vitamin D
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an x-ray shows a black area in the region of the epiphyseal plate,
A) the bone is fractured.
B) growth of the bone is complete.
C) marrow is forming in the spongy bone.
D) the epiphyseal plate has not completely ossified.
E) the cartilage is absent.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spaces between developing skull bones that have not ossified are called ________.
A) epiphyseal plates
B) articular cartilages
C) fontanels
D) bone collars
E) medullary cavities
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of lamellae found between osteons (haversian systems) is ________.
A) circumferential
B) concentric
C) interstitial
D) appositional
E) oppositional
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A young boy (10 years old) exhibited the following symptoms: advanced development of secondary sexual characteristics and rapid growth. Which of the following likely caused his condition?
A) Hypersecretion of growth hormone
B) Hypersecretion of testosterone
C) Hypersecretion of estrogen
D) Hyposecretion of estrogen
E) Hypersecretion of vitamin D
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of lamellae that forms the outside surface of compact bone is ________.
A) circumferential
B) concentric
C) interstitial
D) appositional
E) oppositional
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some marrow of long bones is termed "yellow" marrow under normal conditions. The function of yellow marrow is to
A) manufacture blood cells.
B) manufacture tissue cells for the skin.
C) store adipose tissue.
D) store bone-forming cells.
E) make vitamin D.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 178
Related Exams