A) dehydration
B) synthesis
C) hydrolysis
D) reversible
E) oxidation
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the reversible reaction, CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-, a decrease in respiration rate will increase the concentration of CO2 in the blood. What will this do to the amount of H+ in the blood?
A) H+ will increase.
B) H+ will decrease.
C) H+ will be unchanged.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
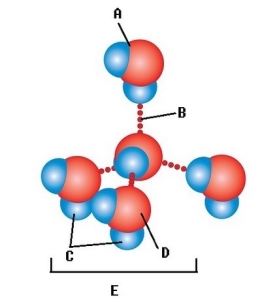 -Water accounts for 50% of the weight of a young adult female and 60% of a young adult male. What kind of molecule is found at "E"?
-Water accounts for 50% of the weight of a young adult female and 60% of a young adult male. What kind of molecule is found at "E"?
A) Hydrogen bond
B) Water molecule
C) Oxygen atom
D) Hydrogen atom
E) Polar covalent bond
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Phospholipids are important components of the plasma membrane. What does "D" represent on the diagram?
-Phospholipids are important components of the plasma membrane. What does "D" represent on the diagram?
A) Phosphorus
B) Oxygen
C) Nitrogen
D) Polar (hydrophilic) region
E) Nonpolar (hydrophobic) region
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical substances that dissolve in water or react with water to release ions are known as ________.
A) buffers
B) enzymes
C) bases
D) inorganic compounds
E) electrolytes
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cellulose is the
A) storage carbohydrate in animals.
B) storage carbohydrate in plants.
C) nondigestible plant polysaccharide.
D) major nutrient for most body cells.
E) sugar found in RNA.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electrolyte is
A) a combination of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
B) a positively charged ion.
C) a negatively charged ion.
D) a substance that conducts electricity when placed in solution.
E) the alteration in the three-dimensional structure of a protein.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neutral atom will become a cation if it
A) gains electrons.
B) gains protons.
C) loses electrons.
D) loses protons.
E) gains neutrons.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors will influence the rate of chemical reactions?
A) Temperature
B) Concentration of reactants
C) Presence of catalysts
D) Presence of enzymes
E) All of these factors will influence the rate of chemical reactions.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Covalent bonds form when
A) atomic nuclei fuse.
B) molecules become ionized.
C) neutrons are transferred from one atom to another.
D) protons are lost from atoms.
E) electrons are shared between two atoms.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two solutions, A and B, have the same osmolality. What does that mean?
A) Solution A has more solute particles than solution B.
B) Solution B has more solute particles than solution A.
C) Both solutions have the same number of solute particles.
D) Solution A is water and sugar; solution B is water and salt.
E) Solution A is pure water, and solution B is water and salt.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
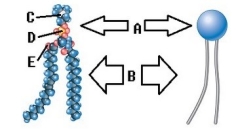
 -Phospholipids are important components of the plasma membrane. What does "C" represent on the diagram?
-Phospholipids are important components of the plasma membrane. What does "C" represent on the diagram?
A) Phosphorus
B) Oxygen
C) Nitrogen
D) Polar (hydrophilic) region
E) Nonpolar (hydrophobic) region
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glycogen is the
A) storage carbohydrate in animals.
B) storage carbohydrate in plants.
C) nondigestible plant polysaccharide.
D) major nutrient for most body cells.
E) sugar found in RNA.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eicosanoids
A) are structural proteins.
B) are fat-soluble vitamins.
C) are components of the plasma membrane.
D) comprise the genetic material.
E) play a role in the response of tissues to injuries.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Metabolic water refers to the water molecules produced during normal cellular metabolism. Which types of metabolic reactions are important for the production of metabolic water?
A) Dehydration reactions
B) Hydrolysis reactions
C) Catabolic reactions
D) Reversible reactions
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sodium has an atomic number of 11 and an atomic mass of 23. Sodium has ________.
A) 12 neutrons and 11 protons
B) 12 protons and 11 neutrons
C) 12 electrons and 11 neutrons
D) 12 protons and 11 electrons
E) 12 electrons and 11 protons
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a use of x-ray imaging?
A) Breast cancer screening in mammography
B) Upper digestive tract abnormalities following barium ingestion
C) Brain tumor progression
D) Vertebrae fractures
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes RNA?
A) RNA is found outside a cell.
B) RNA contains the base thymine.
C) RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
D) RNA molecules are antiparallel.
E) RNA is a double helix.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a synthesis reaction?
A) Two amino acids are bonded together to form a dipeptide.
B) Sucrose is chemically separated to form one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose.
C) Sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
D) Several dipeptide chains are formed from digestion of a long polypeptide chain.
E) ATP is converted to ADP.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Potential energy is
A) the form of energy that actually does work.
B) movement of ions or electrons.
C) energy that flows between objects with different temperatures.
D) stored energy that could do work but is not doing so.
E) energy that moves in waves.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 207
Related Exams