B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Giffen good is one in which the quantity demanded rises as the price rises because the income effect
A) reinforces the substitution effect.
B) reinforces and is greater than the substitution effect.
C) counteracts but is smaller than the substitution effect.
D) counteracts and is greater than the substitution effect.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not represent a tradeoff facing a consumer?
A) choosing to purchase more of all goods
B) choosing to spend more time on leisure and less time on work
C) choosing to spend more now and consume less in the future
D) choosing to purchase less of one good in order to purchase more of another good
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-17  -Refer to Figure 21-17.Bundle C represents a point where
-Refer to Figure 21-17.Bundle C represents a point where
A) MRSxy > Py/Px.
B) MRSxy = Px/Py.
C) MRSxy < Px/Py.
D) MRSxy > Px/Py.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-3
In each case,the budget constraint moves from BC-1 to BC-2. 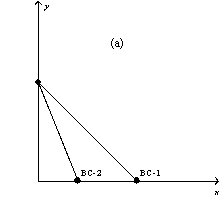
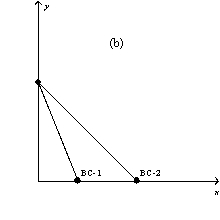
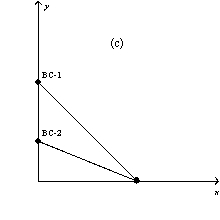
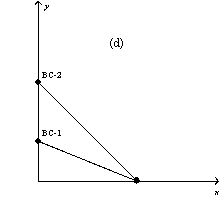 -Refer to Figure 21-3.Which of the graphs in the figure could reflect a simultaneous decrease in the prices of both goods?
(i) Graph a
(ii) Graph b
(iii) Graph c
(iv) Graph d
-Refer to Figure 21-3.Which of the graphs in the figure could reflect a simultaneous decrease in the prices of both goods?
(i) Graph a
(ii) Graph b
(iii) Graph c
(iv) Graph d
A) (i) only
B) (iv) only
C) (ii) or (iii) only
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-5
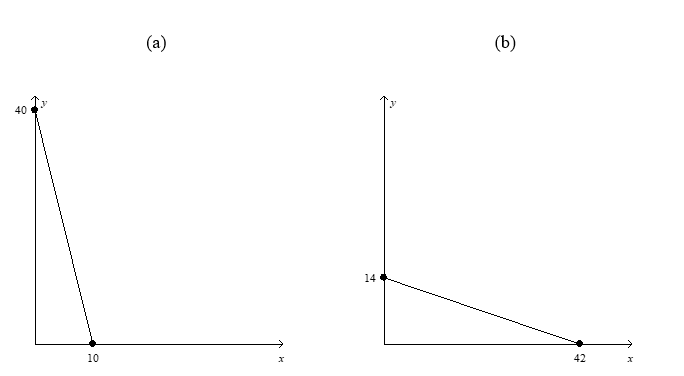 -Refer to Figure 21-5.In graph (b) ,what is the price of good X relative to good Y (i.e. ,Px/Py) ?
-Refer to Figure 21-5.In graph (b) ,what is the price of good X relative to good Y (i.e. ,Px/Py) ?
A) 1/3
B) 1
C) 3
D) 10
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-11 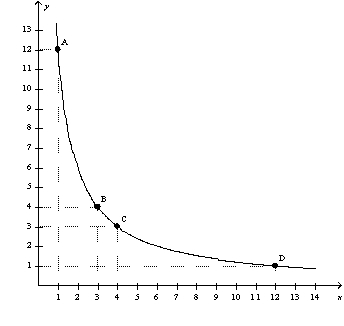 -Refer to Figure 21-11.As the consumer moves from point A to B to C to D,the consumer's total utility
-Refer to Figure 21-11.As the consumer moves from point A to B to C to D,the consumer's total utility
A) remains constant.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) first increases,then decreases.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) Reducing taxes on interest income might encourage people to save more.
B) Reducing taxes on interest income might reduce saving.
C) A price increase will create income and substitution effects that will both always work to reduce consumption of the good.
D) Utility is maximized when the marginal rate of substitution between any two goods equals the relative prices of the two goods.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Energy drinks and granola bars are normal goods.When the price of energy drinks decreases,the income effect causes
A) the consumer to feel richer,so the consumer buys more granola bars.
B) the consumer to feel richer,so the consumer buys fewer granola bars.
C) granola bars to be relatively more expensive,so the consumer buys more granola bars.
D) granola bars to be relatively less expensive,so the consumer buys fewer granola bars.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bob enjoys fishing and hunting.He divides his leisure hours between the two outdoor activities.Suppose we were to draw Bob's indifference curves for the two activities,placing fishing on the horizontal axis and hunting on the vertical axis.If Bob's indifference curves are bowed inward,then
A) the rate at which he is willing to give up an hour of hunting for an hour of fishing changes depending on how many hours of each activity he has done.For example,if Bob has already fished a lot in one week,he will be more willing to give up an hour of fishing for an hour of hunting than if he has only fished a little that week.
B) the rate at which he is willing to give up an hour of hunting for an hour of fishing is constant because he must derive the same enjoyment out of each activity.
C) the rate at which he is willing to give up an hour of hunting for an hour of fishing changes depending on how many hours of each activity he has done.For example,if Bob has already fished a lot in one week,he will be less willing to give up an hour of fishing for an hour of hunting than if he has only fished a little that week.
D) Bob's indifference curves will not cross.When indifference curves are bowed outward,the indifference curves must cross.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Giffen goods have positively-sloped demand curves because they are
A) inferior goods with no substitution effect.
B) normal goods with no substitution effect.
C) inferior goods for which the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
D) inferior goods for which the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer likes two goods: pizza and beer.The four bundles shown in the table below lie on the same indifference curve for the consumer. 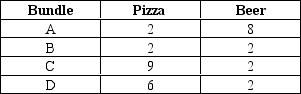 Which of the following statements regarding these bundles is correct?
Which of the following statements regarding these bundles is correct?
A) The goods are perfect substitutes for this consumer.
B) The goods are perfect complements for this consumer.
C) These bundles illustrate the property that indifference curves are bowed inward.
D) These bundles violate the property that indifference curves do not cross.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-16 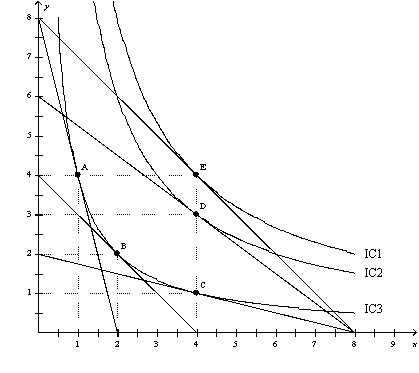 -Refer to Figure 21-16.When the price of X is $40,the price of Y is $40,and income is $160,Steve's optimal choice is point B.Then Steve's income increases to $320,and his optimal choice is point E.For Steve,
-Refer to Figure 21-16.When the price of X is $40,the price of Y is $40,and income is $160,Steve's optimal choice is point B.Then Steve's income increases to $320,and his optimal choice is point E.For Steve,
A) good X is a normal good,and good Y is an inferior good.
B) good X is an inferior good,and good Y is a normal good.
C) both good X and good Y are normal goods.
D) good Y is a normal good;good X is neither a normal nor an inferior good.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Jessica regards cheese and crackers as perfect complements,then
A) her indifference curves slope upward.
B) her indifference curves are straight lines.
C) Jessica prefers lower indifference curves to higher ones.
D) for Jessica a bundle of 5 crackers and 5 ounces of cheese is just as good as a bundle of 5 crackers and 8 ounces of cheese.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of a good increases,all else equal,the higher price
A) reduces the consumer's set of buying opportunities.
B) leads to a parallel shift of the budget constraint.
C) will necessarily lead to an increase in the consumption of goods whose price did not change.
D) generally discourages the consumption of inferior goods.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A budget constraint illustrates bundles that a consumer prefers equally,while an indifference curve illustrates bundles that are equally affordable to a consumer.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Violations of the law of demand are assumed to occur
A) regularly.
B) only when goods are Giffen goods.
C) only when the substitution effect dominates the income effect.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer chooses an optimal consumption point where the
A) marginal rate of substitution equals the relative price ratio.
B) slope of the indifference curve equals the slope of the budget constraint.
C) ratio of the marginal utilities equals the ratio of the prices.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-14 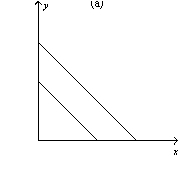
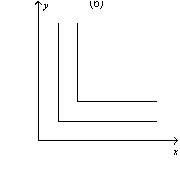
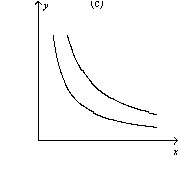 -Refer to Figure 21-14.Which of the following statements is correct?
-Refer to Figure 21-14.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The indifference curves represented in graph a are perfect substitutes.
B) The indifference curves represented in graph b are perfect complements.
C) The indifference curves represented in graph c are neither perfect substitutes not perfect complements.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A family on a trip budgets $800 for meals and hotel accommodations.Suppose the price of a meal is $40.In addition,suppose the family could afford a total of 8 nights in a hotel if they don't buy any meals.How many meals could the family afford if they gave up two nights in the hotel?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 5
D) 8
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 492
Related Exams