A) velocity of money.
B) monetary multiplier.
C) equation of exchange.
D) monetary rule.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the view of real-business-cycle theory, an increase in the long-run aggregate supply would lead to a(n)
A) increase in aggregate demand by an equal amount, so real output would increase and the price level would be unchanged.
B) increase in aggregate demand by an equal amount, so real output and the price level would increase.
C) decrease in aggregate demand, so real output would increase and the price level would decrease.
D) decrease in aggregate demand, so real output and the price level would increase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
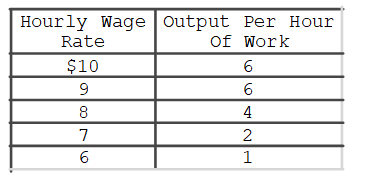 Refer to the table.At the $8 wage, labor cost per unit of output is
Refer to the table.At the $8 wage, labor cost per unit of output is
A) $1.25.
B) $1.50.
C) $2.00.
D) $1.67.Type: Table
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The equation of exchange is MV = PQ.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetarists say
A) that, because P is stable, a change in M will change Q proportionately in the opposite direction.
B) a change in the money supply will change aggregate demand and therefore the nominal GDP.
C) a change in the money supply will change velocity, which in turn will change nominal GDP.
D) a change in the money supply will change the interest rate, which will change investment spending and nominal GDP.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of rational expectations calls for monetary policy rules because
A) of past policy errors.
B) policy tends to be countercyclical.
C) of the inability to time policy decisions.
D) of the reaction of the public to the expected effects of policy.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the equation of exchange, if V is stable, an increase in M will necessarily increase
A) the demand for money.
B) the price level.
C) nominal GDP.
D) real GDP.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which economic perspective typically views the market system as less than fully competitive, and therefore subject to macroeconomic instability?
A) monetarism
B) mainstream economics
C) real-business-cycle theory
D) rational expectations theory
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Real-business-cycle theory focuses on factors affecting
A) aggregate demand.
B) aggregate supply.
C) the velocity of money.
D) consumer spending.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monetarists say the velocity of money is highly variable and there is no close link between the money supply and the level of economic activity.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a full-employment economy, a rise in M will cause inflation unless
A) V rises in proportion to the increase in M.
B) the quantity of goods produced declines proportionately.
C) tax reductions accompany the increase in the money supply.
D) the velocity of money diminishes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Targeting the forecast" is the policy that best describes which of the following views?
A) real-business-cycle theory
B) rational expectations theory
C) market monetarism
D) the Keynesian view
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the rational expectations view, the best approach to fiscal policy is for the government to
A) cut taxes.
B) balance its budget.
C) eliminate transfer payments.
D) fix government spending.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to new classical economists, the
A) short-run demand for labor curve is vertical.
B) short-run aggregate demand curve is vertical.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most mainstream macroeconomists oppose a strict requirement to balance the federal budget annually because they conclude that such a requirement would
A) increase real interest rates and drive out investment spending.
B) eliminate monetary policy as a stabilization tool.
C) force government to undertake expansionary fiscal policy during inflation and contractionary fiscal policy during recession.
D) expand the size of the federal government.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to rational expectations theory, observed instability in the private economy would most likely be due to
A) changes in aggregate supply.
B) inappropriate monetary policy.
C) the instability of investment spending in the economy.
D) unanticipated aggregate demand and aggregate supply shocks in the short run.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mainstream economists have adopted some ideas from RET, and some rational expectations assumptions are being incorporated into current macroeconomic models.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Coordination failures occur when people lack some way to jointly coordinate their actions to reach a(n)
A) unanticipated price level change.
B) fully anticipated price level change.
C) mutually beneficial equilibrium.
D) insider-outsider relationship.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a component of the equation of exchange?
A) consumption
B) the interest rate
C) investment
D) the velocity of money
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rational expectations theory considers the aggregate
A) demand curve to be vertical.
B) supply curve to be vertical.
C) supply curve to be horizontal.
D) demand curve to be horizontal.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 225
Related Exams