A) right because C will increase.
B) left because C will decrease.
C) right because Ig will increase.
D) left because Ig will decrease.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy experiences an increase in the price level and an increase in real domestic output.Which is a likely explanation?
A) Interest rates have increased.
B) Business taxes have increased.
C) Wage rates have fallen.
D) Net exports have increased.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply analysis assumes that
A) input prices are fixed, while product prices are variable.
B) input prices are variable, while product prices are fixed.
C) both input and product prices are variable.
D) both input and product prices are fixed.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in consumer spending can be expected to shift the
A) aggregate expenditures curve downward and the aggregate demand curve leftward.
B) aggregate expenditures curve upward and the aggregate demand curve leftward.
C) aggregate expenditures curve downward and the aggregate demand curve rightward.
D) aggregate expenditures curve upward and the aggregate demand curve rightward.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the excess capacity of business expands unintentionally, aggregate
A) demand will increase.
B) demand will decrease.
C) supply will increase.
D) supply will decrease.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The factors that affect the amounts that consumers, businesses, government, and foreigners wish to purchase at each price level are the
A) real-balances, interest-rate, and foreign purchases effects.
B) determinants of aggregate supply.
C) determinants of aggregate demand.
D) sole determinants of the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium real output.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is incorrect?
A) As the U.S.price level rises, U.S.goods become relatively more expensive so that U.S.exports fall and U.S.imports rise.
B) As the price level falls, the demand for money declines, the interest rate declines, and interest-rate-sensitive spending increases.
C) When the price level increases, real balances increase and businesses and households find themselves wealthier and therefore increase their spending.
D) Given aggregate demand, an increase in aggregate supply increases real output and, assuming downward-flexible prices, reduces the price level.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Advanced analysis) Assume that the MPC is 0.8 in an economy that has an aggregate supply curve with a slope of 1.Also, suppose that the price level is flexible downward.A decrease in investment spending of $10 billion will shift the aggregate demand curve leftward by
A) $50 billion and decrease real GDP by $50 billion.
B) $50 billion and decrease real GDP by $25 billion.
C) $10 billion and decrease real GDP by $10 billion.
D) $10 billion and decrease real GDP by $25 billion.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The aggregate supply curve (short run) becomes steeper as the economy moves rightward and upward along it.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the immediate short run, both input and output prices are fixed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve shows the
A) inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP purchased.
B) inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP produced.
C) direct relationship between the price level and real GDP produced.
D) direct relationship between the price level and real GDP purchased.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Last Word) In response to the Great Recession, the federal government engaged in significant deficit-funded spending.What was the result of that spending over the first three years?
A) Neither economic growth nor unemployment responded as well as many economists had predicted.
B) Economic growth responded in accordance with predictions, but unemployment remained much higher than anticipated.
C) Economic growth remained sluggish, but the unemployment rate fell to predicted levels.
D) Both economic growth and the unemployment rate responded well, reaching the fiscal policy targets set by the government.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Consider This) The ratchet effect is the tendency of
A) the price level to increase but not to decrease.
B) nominal GDP to increase more rapidly than real GDP.
C) real interest rates to fall more rapidly than nominal interest rates.
D) consumption to rise year after year regardless of what happens to disposable income.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
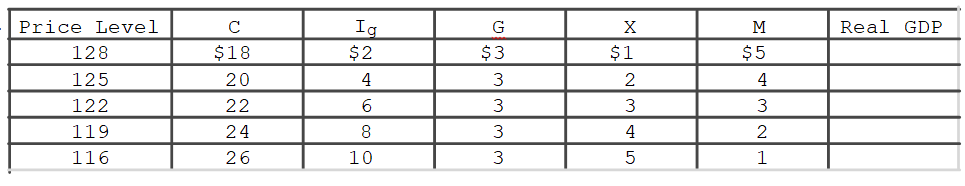 In the accompanying table for a particular country, C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports.All figures are in billions of dollars.A decline in the international value of the dollar would
In the accompanying table for a particular country, C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports.All figures are in billions of dollars.A decline in the international value of the dollar would
A) increase the values in the X and M columns and reduce aggregate demand.
B) decrease the values in the X and M columns and increase aggregate demand.
C) decrease the values in column X increase the values in column M , and reduce aggregate demand.
D) increase the values in column X , decrease the values in column M , and increase aggregate demand.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graphically, the full-employment, low-inflation, rapid-growth economy of the last half of the 1990s is depicted by a
A) rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve along a fixed aggregate supply curve.
B) rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve along a fixed aggregate demand curve.
C) rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve and a rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
D) leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve and a leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest-rate effect suggests that
A) a decrease in the supply of money will increase interest rates and reduce interest-sensitive consumption and investment spending.
B) an increase in the price level will increase the demand for money, reduce interest rates, and decrease consumption and investment spending.
C) an increase in the price level will increase the demand for money, increase interest rates, and decrease consumption and investment spending.
D) an increase in the price level will decrease the demand for money, reduce interest rates, and increase consumption and investment spending.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate supply curve (short run) is upsloping because
A) wages and other resource prices match changes in the price level.
B) the price level is flexible upward but inflexible downward.
C) per-unit production costs rise as the economy moves toward and beyond its full-employment real output.
D) wages and other resource prices are flexible upward but inflexible downward.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in aggregate demand is most likely to be caused by which of the following?
A) an increase in real interest rates
B) a decrease in government spending
C) a decrease in expected returns on investment
D) a decrease in the tax rates on household income
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the
A) productivity level in the economy.
B) shape of the aggregate demand curve.
C) per-unit cost of production in the economy.
D) equilibrium level of real domestic output and prices.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following would increase per-unit production cost and therefore shift the aggregate supply curve to the left?
A) a reduction in business taxes
B) production bottlenecks occurring when producers near full plant capacity
C) an increase in the price of imported resources
D) deregulation of industry
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 227
Related Exams