B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in wealth from a substantial increase in stock prices will move the economy along a fixed aggregate demand curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fear of unwanted price wars may explain why many firms are reluctant to
A) reduce wages when a decline in aggregate demand occurs.
B) reduce prices when a decline in aggregate demand occurs.
C) expand production capacity when an increase in aggregate demand occurs.
D) provide wage increases when labor productivity rises.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If investment increases by $10 billion and the economy's MPC is 0.8, the aggregate demand curve will shift
A) leftward by $50 billion at each price level.
B) rightward by $10 billion at each price level.
C) rightward by $50 billion at each price level.
D) leftward by $40 billion at each price level.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
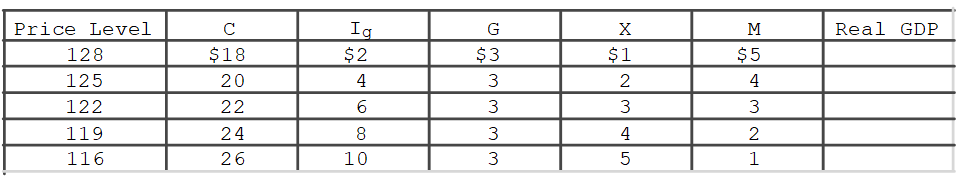 In the accompanying table for a particular country, C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports.All figures are in billions of dollars.A decrease in the interest rate not caused by a change in the price level would
In the accompanying table for a particular country, C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports.All figures are in billions of dollars.A decrease in the interest rate not caused by a change in the price level would
A) increase the values in column Ig and increase aggregate demand.
B) decrease the values in column Ig and increase aggregate demand.
C) increase the values in column C and decrease aggregate demand.
D) decrease the values in column C and decrease aggregate demand.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With cost-push inflation in the short run, there will be
A) an increase in real GDP.
B) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
C) a decrease in real GDP.
D) a decrease in unemployment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
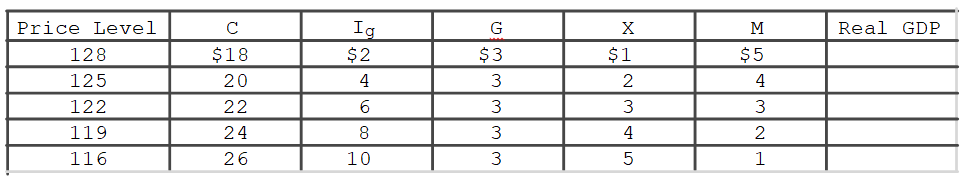 In the accompanying table for a particular country, C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports.All figures are in billions of dollars.If the equilibrium level of real GDP is $43 billion, its level of consumption will be
In the accompanying table for a particular country, C is consumption expenditures, Ig is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures, X is exports, and M is imports.All figures are in billions of dollars.If the equilibrium level of real GDP is $43 billion, its level of consumption will be
A) $20 billion.
B) $22 billion.
C) $24 billion.
D) $26 billion.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a true statement?
A) Firms and resource suppliers generally find it easier to reduce prices than to raise them.
B) As the price level increases, interest rates will rise and therefore consumption and investment spending will also rise.
C) An initial increase in aggregate demand may cause a further increase in aggregate demand because higher prices mean higher incomes.
D) A decline in aggregate demand will primarily affect real output and employment if prices are inflexible downward.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy is employing 2 units of capital, 5 units of raw materials, and 8 units of labor to produce its total output of 640 units.Each unit of capital costs $10; each unit of raw materials, $4; and each unit of labor, $3.If the per-unit price of raw materials rises from $4 to $8 and all else remains constant, the per-unit cost of production will rise by about
A) 100 percent.
B) 50 percent.
C) 40 percent.
D) 30 percent.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in which of the following would not shift the aggregate demand curve?
A) productivity rates
B) foreign-exchange rates
C) real interest rates
D) income tax rates
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not shift the aggregate supply curve?
A) an increase in labor productivity
B) a decline in the price of imported oil
C) a decline in business taxes
D) an increase in the price level
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The foreign purchases effect suggests that an increase in the U.S.price level relative to other countries will
A) increase the amount of U.S.real output purchased.
B) increase U.S.imports and decrease U.S.exports.
C) increase both U.S.imports and U.S.exports.
D) decrease both U.S.imports and U.S.exports.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The expenditure multiplier concept of the aggregate expenditures model
A) is not at all relevant in the AD-AS model.
B) magnifies the shifts of the aggregate demand curve.
C) explains movement up or down the aggregate demand curve.
D) reverses the shift of the aggregate demand curve.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the mid-1970s, changes in oil prices greatly affected U.S.inflation.When oil prices rose, the U.S.experienced
A) cost-push inflation and rising output.
B) demand-pull inflation and rising output.
C) cost-push inflation and falling output.
D) demand-pull inflation and falling output.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If personal income taxes and business taxes increase, then this will
A) increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
B) decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
C) decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply.
D) increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in personal income tax rates will cause a(n)
A) decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand.
B) increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand.
C) decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD) .
D) increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD) .
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which would most likely shift the aggregate supply curve? A change in the prices of
A) domestic products.
B) foreign products.
C) financial assets.
D) resources.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate expenditures model and the aggregate demand curve can be reconciled because, other things equal, in the aggregate expenditures model,
A) changes in the price level have no effect on the equilibrium level of GDP.
B) an increase in the price level increases the real value of wealth.
C) the level of aggregate expenditures and therefore the level of real GDP vary inversely with the price level.
D) the level of aggregate expenditures and therefore the level of real GDP vary directly with the price level.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The shape of the short-run aggregate supply curve indicates that as the general price level rises, output will expand but not by much when the economy reaches full employment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cost-push inflation can be described as a rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 227
Related Exams