A) rarely consider the potential reactions of rivals.
B) experience economies of scale.
C) can increase their profits through collusion.
D) may be either homogeneous or differentiated.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a repeated game with reciprocity, the two players
A) could each earn a higher payoff than if they aggressively countered each other's single-period strategy.
B) tend to earn less than if they aggressively countered each other's single-period strategy.
C) will have less incentive to collude explicitly or tacitly.
D) often end up in a price war.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If three or four homogeneous oligopolists collude, the resulting price and production outcomes will be similar to those of pure monopoly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Limit pricing by a price leader in an oligopoly refers to the strategy of setting a price
A) that blocks the entry of new firms.
B) that ensures profits for the least efficient existing firm in the oligopoly.
C) that maximizes profits for all firms in the oligopoly market.
D) that maximizes profits for the price leader, but not necessarily for the other firms.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clear-cut mutual interdependence with respect to the price-output policies exists in
A) pure monopoly.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) pure competition.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The kinked-demand curve model helps to explain price rigidity because
A) there is a gap in the marginal revenue curve within which changes in marginal cost will not affect output or price.
B) demand is inelastic above and elastic below the going price.
C) the model assumes firms are engaging in some form of collusion.
D) the associated marginal revenue curve is perfectly elastic at the going price.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Negative-sum games do not exist, because neither player has an incentive to play the game.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A potential negative effect of advertising for society is that it can
A) be the major cause of price wars among firms in the industry.
B) reduce mutual interdependence and increase competition.
C) be self-canceling and contribute to economic inefficiency.
D) lower barriers to entry and undermine profits in the industry.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under oligopoly, if one firm in an industry significantly increases advertising expenditures in order to capture a greater market share, it is most likely that other firms in that industry will
A) pursue a strategy to reduce advertising expenditures to maintain profits.
B) decide to increase advertising expenditures even if it means a reduction in profits.
C) make no changes in advertising expenditures because advertising is effective in the short run, but not the long run.
D) increase the price of the product to improve profits and then increase advertising expenditures.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Advertising increases the costs of firms and could be manipulative; therefore, it does not really have a positive economic effect.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
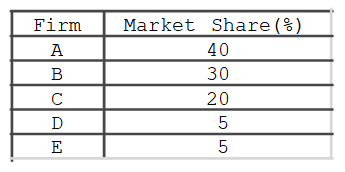 If enforcement of antitrust laws caused the two largest firms in this table to be divided in half, with each half having equal market share, the industry's four-firm concentration ratio would and its Herfindahl index would .
If enforcement of antitrust laws caused the two largest firms in this table to be divided in half, with each half having equal market share, the industry's four-firm concentration ratio would and its Herfindahl index would .
A) fall; fall
B) fall; rise
C) remain the same; rise
D) remain the same; fall
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In game theory, each player is assumed to have the following, except
A) alternative strategies or actions.
B) alternative outcomes or results.
C) alternative payoffs or earnings.
D) alternative partners or coplayers.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The automobile, household appliance, and automobile tire industries are all illustrations of
A) homogeneous oligopoly.
B) monopolistic competition.
C) pure monopoly.
D) differentiated oligopoly.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In game theory, the credibility of a threat
A) determines whether or not a Nash equilibrium to a game exists.
B) influences the degree of cooperation between two rivals.
C) is relevant only in simultaneous games.
D) determines whether or not a firm has a dominant strategy.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effects of advertising on a firm's profits and efficiency
A) are definitely positive.
B) are definitely negative.
C) may be positive or negative.
D) are only observed in oligopoly.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a zero-sum game, the gains by one player will be exactly offset by the losses of the other.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Concentration ratios
A) may overstate the degree of competition because they ignore imported products.
B) may overstate the degree of competition because interindustry competition is ignored.
C) may understate the degree of competition because they ignore imported products.
D) provide detailed insights as to the price and output behavior of firms that compose the various industries.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If oligopolistic firms facing similar cost and demand conditions successfully collude, price and output results in this industry will be most accurately predicted by which of the following models?
A) the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly
B) the price-leadership model of oligopoly
C) the pure monopoly model
D) the monopolistic competition model
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If one player in a game has a dominant strategy, the other player must also have a dominant strategy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
First-mover advantage cannot happen in a one-time simultaneous game.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 260
Related Exams