A) reduce output quantity, increase total revenue, and increase total cost.
B) reduce output quantity, increase total revenue, and decrease total cost.
C) raise output quantity, decrease total revenue, and increase total cost.
D) reduce output quantity, decrease total revenue, and decrease total cost.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pure monopolist
A) will realize an economic profit if price exceeds ATC at the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing level of output.
B) will realize an economic profit if ATC exceeds MR at the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing level of output.
C) will realize an economic loss if MC intersects the downsloping portion of MR.
D) always realizes an economic profit.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The profit-maximizing output of a pure monopoly is not socially optimal, because in equilibrium
A) price equals minimum average total cost.
B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) marginal cost exceeds price.
D) price exceeds marginal cost.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As a monopolist lowers the price of its product from a high level, it finds that its total revenue may at first increase and then, below a certain price, its total revenue begins to decrease.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a pure monopolist is charging a price of $12 and the associated marginal revenue is $9.We thus know that
A) demand is inelastic at this price.
B) the firm is maximizing profits.
C) total revenue is increasing.
D) total revenue is at a maximum.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A dilemma of regulation is that
A) the regulated price that achieves allocative efficiency is also likely to result in persistent economic profits.
B) the regulated price that results in a "fair return" restricts output by more than would unregulated monopoly.
C) regulated pricing always conflicts with the "due process" provision of the Constitution.
D) the regulated price that achieves allocative efficiency is also likely to result in losses.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue
A) may be either greater or less than $35.
B) will also be $35.
C) will be less than $35.
D) will be greater than $35.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Price discrimination is not viable if consumers can resell the products they purchase to other consumers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Because of the ability to influence price, a pure monopolist can increase price and increase volume of sales simultaneously.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which one of the following market models is X-inefficiency most likely to be the greatest?
A) pure competition
B) oligopoly
C) monopolistic competition
D) pure monopoly
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
"Price maker" means that a monopoly can decide whatever price it wants to, in order to sell a specific given quantity of its product.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The region of demand in which the monopolist will choose a price-output combination will be
A) inelastic because, as price declines and output increases, total revenue will increase.
B) inelastic because, as price declines and output increases, total revenue will decrease.
C) elastic because, as price declines and output increases, total revenue will decrease.
D) elastic because, as price declines and output increases, total revenue will increase.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Large minimum efficient scale of plant combined with limited market demand may lead to
A) natural monopoly.
B) patent monopoly.
C) government franchise monopoly.
D) shared monopoly.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nondiscriminating pure monopolist is generally viewed as
A) productively efficient but allocatively inefficient.
B) productively inefficient but allocatively efficient.
C) both productively and allocatively inefficient.
D) both productively and allocatively efficient.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A patent for a new product or a new business process is typically granted for a hundred years.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the short run a pure monopolist will charge the highest price the market will bear for its product.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
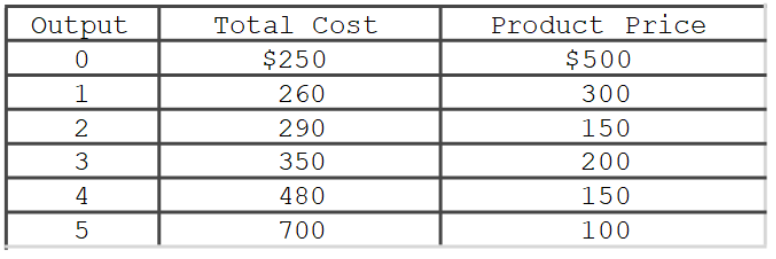 If the profit-maximizing pure monopolist whose information is in the accompanying table is able to price discriminate, charging each customer the price associated with each given level of output, how much profit will the firm earn?
If the profit-maximizing pure monopolist whose information is in the accompanying table is able to price discriminate, charging each customer the price associated with each given level of output, how much profit will the firm earn?
A) $120.
B) $250.
C) $300.
D) $420.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve of a pure monopolist
A) is that portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above average variable cost.
B) is the same as that of a purely competitive industry.
C) is its average variable cost curve.
D) does not exist because prices are not "given" to a monopolist.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve confronting a nondiscriminating pure monopolist is
A) horizontal.
B) the same as the industry's demand curve.
C) more elastic than the demand curve confronting a competitive firm.
D) derived by vertically summing the individual demand curves for the buyers.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a natural monopoly, the fair-return price
A) is allocatively efficient; the socially optimal price is allocatively inefficient.
B) is allocatively inefficient; the socially optimal price is allocatively efficient.
C) and the socially optimal price are both allocatively inefficient.
D) and the socially optimal price are both allocatively efficient.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 204
Related Exams