A) Michael reaction
B) Robinson reaction
C) Hoffman reaction
D) Dieckmann reaction
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true?
A) Equilibrium favors the products with aldehydes; equilibrium favors the starting materials with ketones.
B) Equilibrium favors the starting materials with aldehydes; equilibrium favors the products with ketones.
C) Equilibrium favors the products with both aldehydes and ketones.
D) Equilibrium favors the starting materials with both aldehydes and ketones.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following reaction is an example of what type of reaction?
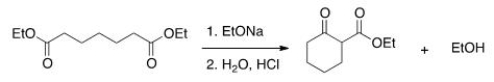
A) Claisen condensation
B) Mixed Aldol reaction
C) Robinson annulation
D) Dieckmann condensation
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are several variations of the Aldol reaction.Which of the following types of reactants leads to only one possible product with the Aldol condensation reaction?
A) Two different aldehydes with a-hydrogens are able to form a single aldol condensation product.
B) Two different ketones with a-hydrogens are able to form a single aldol condensation product.
C) Any aldehyde and ketone mixed together can react to form a single condensation product.
D) Any pair of aldehyde or ketone reactants where one of the reactants has no a-hydrogens will lead to a single aldol product.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The b-hydroxy carbonyl product of an Aldol reaction is oftentimes not the final isolated product; what is the explanation for this result?
A) It undergoes elimination, since water is a good leaving group.
B) The hydroxy group is oxidized to a carbonyl.
C) The hydroxy group reacts with the carbonyl to form a ketal.
D) Hydroxide is eliminated via an enolate intermediate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What cyclic product is formed in the intramolecular Aldol condensation when the following compound is treated with aqueous NaOH?
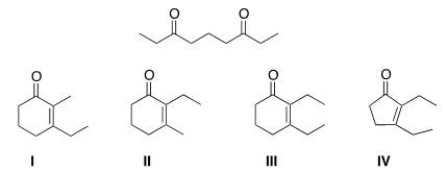
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete this statement: A major difference between the Aldol condensation and the Claisen condensation reactions is that
A) the Aldol reaction involves substitution while the Claisen reaction involves addition.
B) the Aldol reaction is acid catalyzed while the Claisen reaction is base-catalyzed.
C) the Aldol reaction is base catalyzed while the Claisen reaction requires a full equivalent of base.
D) the Aldol reaction is base catalyzed while the Claisen reaction is acid-catalyzed.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the carbonyl compounds; (1) benzaldehyde, (2) acetophenone and (3) dicyclohexyl ketone, which compound has noa-hydrogens?
A) Benzaldehyde
B) Acetophenone
C) Acetone
D) All of these compounds contain a-hydrogens.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the unsaturated carbonyl compound formed in the dehydration of the following b-hydroxy carbonyl compound?
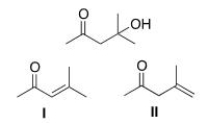
A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) None of the choices
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under basic conditions, the Aldol reaction is reversible, but dehydration is not.What is the reason for this difference in reactivity?
A) The initial Aldol product is an alkoxide, so the reaction is not energetically downhill in either direction.
B) The initial Aldol product is an alkoxide, so the reaction is energetically downhill going toward the product.
C) The initial Aldol product is an alkoxide, so the reaction is energetically downhill going toward the starting materials.
D) Water is a stable molecule.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Would this crossed Aldol reaction work well? Why or why not?
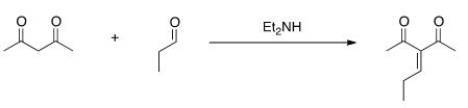
A) Yes, the diketone is significantly more acidic, so this enolate can be formed selectively.
B) Yes, the aldehyde is significantly more acidic, so this enolate can be formed selectively.
C) No, the aldehyde is significantly more acidic, so this enolate cannot be formed selectively.
D) No, the diketone is significantly more acidic, so this enolate cannot be formed selectively.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the Aldol addition product formed from the reaction of acetone, (CH3) 2CO, with itself?
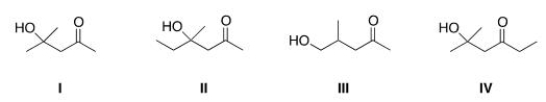
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following bicyclic ring systems can be prepared by an intermolecular Robinson annulation?
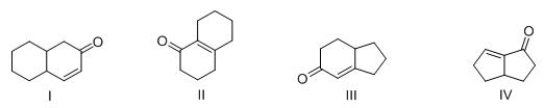
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the general name for the class of products formed in an Aldol condensation reaction?
A) b,g-Unsaturated carbonyl compound
B) a,b-Unsaturated carbonyl compound
C) a,g-Unsaturated carbonyl compound
D) b-Hydroxy carbonyl compound
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the Aldol addition product formed from reaction of the following compound with itself?
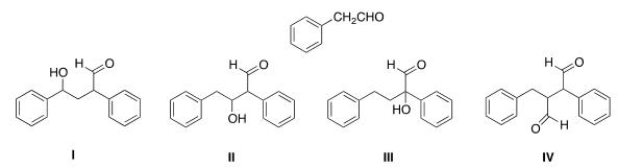
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When is a crossed Aldol reaction said to be synthetically useful?
A) When both carbonyl compounds have a hydrogens
B) When both carbonyl compounds have no a hydrogens
C) When one carbonyl compound has no a hydrogens
D) When one carbonyl compound has no b hydrogens
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When is a crossed Claisen reaction between two different esters synthetically useful?
A) When only one of the esters has a hydrogen atoms
B) When both esters have a hydrogen atoms
C) When only one of the esters has b hydrogen atoms
D) When both esters lack a hydrogen atoms
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is the Aldol reaction often called an Aldol condensation?
A) The initially formed b-hydroxy carbonyl compound loses a hydroxyl group.
B) The initially formed b-hydroxy carbonyl compound loses an oxygen atom.
C) The initially formed b-hydroxy carbonyl compound loses a hydrogen atom.
D) The initially formed b-hydroxy carbonyl compound loses water.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the correct order, what are the three steps in the mechanism of an Aldol reaction?
A) Protonation, enolate formation, nucleophilic addition
B) Enolate formation, protonation, nucleophilic addition
C) Enolate formation, nucleophilic addition, protonation
D) Nucleophilic addition, enolate formation, protonation
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the cyclic product formed in the intramolecular Aldol condensation when the following compound is treated with aqueous NaOH?
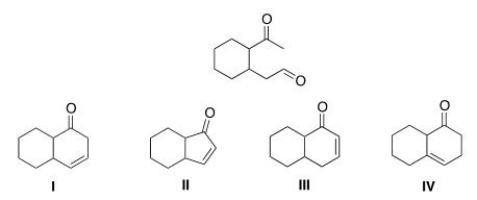
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 45
Related Exams