A) Riskless investment and stock purchase
B) Stock purchase and call option
C) Call option and riskless investment
D) Riskless investment and writing a put
E) Call option, stock purchase, and riskless investment
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The shareholders of a firm will benefit the most from a positive net present value project when the delta of the call option on the firm's assets is:
A) equal to one.
B) between zero and one.
C) equal to zero.
D) between zero and minus one.
E) equal to minus one.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the put-call parity formula, the present value of the exercise price is computed using the:
A) nominal market rate.
B) real market rate.
C) real inflation rate.
D) nominal inflation rate.
E) risk-free rate.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
J&N stock has a current market price of $51.97 a share and the annual risk-free rate is 4.2 percent, compounded continuously. The 1-year call on this stock with a strike price of $55 is priced at $2.30. What is the price of the one-year put with a strike price of $55?
A) $3.07
B) $2.86
C) $3.22
D) $2.94
E) $2.99
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The one-year call on TLM stock with a strike price of $65 is priced at $2.20 while the one-year put with a strike price of $65 is priced at $11.18. The annual risk-free rate is 3.8 percent, compounded continuously. What is the current price of TLM stock?
A) $53.60
B) $48.90
C) $56.70
D) $50.10
E) $47.65
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the risk-free rate increases. This change will ________ the value of call options and ________ the value of put options on shares of stock.
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
E) not affect; not affect
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements related to options is correct?
A) American stock options can be exercised but not resold.
B) A European call is either equal to or less valuable than a comparable American call.
C) European puts can be resold but can never be exercised.
D) European options can be exercised on any dividend payment date.
E) American options are valued using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the risk-free rate increases by one percent. Which one of the following measures the effect this change will have on the value of a firm's stock options?
A) Theta
B) Vega
C) Delta
D) Rho
E) Gamma
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of these is most equivalent to e− ᴿᵗ?
A) −2.71828ᴿᵗ
B) −1/2.71828ᴿᵗ
C) 1/2.71828ᴿᵗ
D) 1 − 2.71828ᴿᵗ
E) 1/2.71828Rᵗ
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Day's End stock is selling for $43 a share. The 6-month call with a strike price of $45 is priced at $.30. Risk-free assets are currently returning 4.1 percent per year, compounded continuously. What is the price of a 6-month put with a strike price of $45?
A) $1.39
B) $1.46
C) $1.28
D) $1.51
E) $1.32
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paying off a firm's debt is comparable to ________ on the assets of the firm.
A) purchasing a put option
B) purchasing a call option
C) exercising an in-the-money put option
D) exercising an in-the-money call option
E) writing a put option
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of the risky debt of a firm is equal to the value of:
A) a call option plus the value of a risk-free bond.
B) a risk-free bond plus a put option.
C) the equity of the firm minus a put.
D) the equity of the firm plus a call option.
E) a risk-free bond minus a put option.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following cannot be either used by or calculated by the Black-Scholes option pricing model?
A) Risk-free rate of return
B) Premium on an American call option
C) Time to maturity greater than one year
D) Underlying asset value
E) An exercise price equal to the face value of a firm's debt
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under European put-call parity, the present value of the strike price is equivalent to the present value of:
A) the current value of the stock minus the call premium.
B) the market value of the stock plus the put premium.
C) a U.S. Treasury coupon bond with a face value equal to the strike price.
D) a U.S. Treasury bill with a face value equal to the strike price.
E) any risk-free security with a face value equal to the strike price and a coupon rate equal to the risk-free rate of return.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information below to answer the following question. 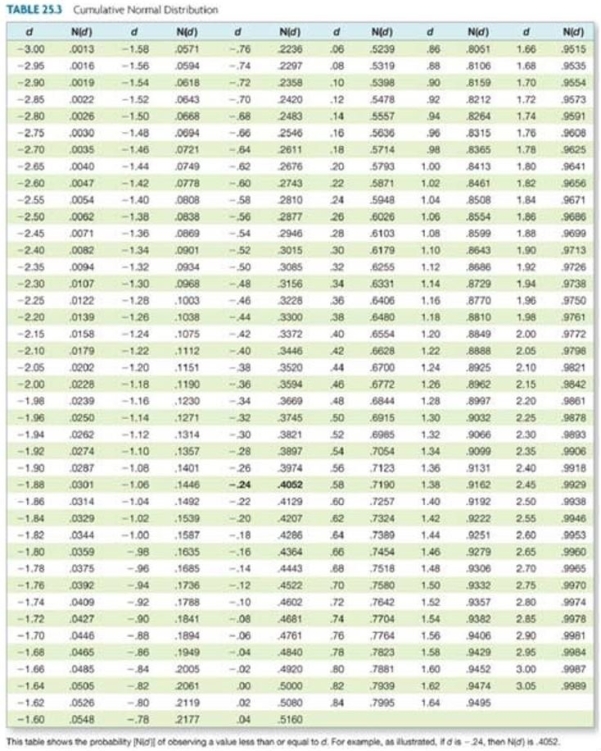 Assume a stock price of $88; risk-free rate of 4 percent per year, compounded continuously; time to maturity of five months; standard deviation of 48 percent per year; and a put and call exercise price of $85. What is the delta of the put option?
Assume a stock price of $88; risk-free rate of 4 percent per year, compounded continuously; time to maturity of five months; standard deviation of 48 percent per year; and a put and call exercise price of $85. What is the delta of the put option?
A) −.6850
B) −.3742
C) −.3158
D) −.0525
E) −.4685
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a stock price of $21.80, an exercise price of $20, three months to expiration, a risk-free rate of 3.40 percent, standard deviation of 46 percent, and a d₁ value of .52664. What is the value of d₂ as it is used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model?
A) .31218
B) .31225
C) .29664
D) .29535
E) .31340
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A) The value of a call option decreases as the time to expiration increases.
B) A decrease in the risk-free rate decreases the value of a put option.
C) Increasing the risk-free rate decreases the value of a call option.
D) The value of a put option increases when the standard deviation of the returns on the underlying stock increase.
E) Increasing the strike price decreases the value of a put option.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the value of a 6-month put with a strike price of $27.50 if the stock price is $22.60, the 6-month $27.50 call is priced at $1.46, and the risk-free rate is 3.5 percent, compounded continuously?
A) $4.71
B) $5.43
C) $5.24
D) $5.88
E) $6.62
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
WT Foods stock is selling for $38 a share. The 6-month $40 call on this stock is selling for $2.01 while the 6-month $40 put is priced at $3.60. What is the continuously compounded risk-free rate of return?
A) 2.7 percent
B) 2.4 percent
C) 1.8 percent
D) 1.5 percent
E) 2.1 percent
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A) Mergers benefit shareholders but not creditors.
B) Positive NPV projects will automatically benefit both creditors and shareholders.
C) There may be conflicts between the interests of bondholders and shareholders.
D) Creditors prefer negative NPV projects while shareholders prefer positive NPV projects.
E) Mergers rarely affect bondholders.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 78
Related Exams