A) shows the relationship between the total quantity of labor supplied by all firms in the economy and the wage rate.
B) shows that, all things being equal, more workers will want to work when wages are higher and fewer will want to work when wages are lower.
C) has a negative slope.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jennifer has a PhD in economics and has been working for three years as a part-time instructor, but she would like to be hired as a full-time faculty member. Jennifer is best described as:
A) a discouraged worker.
B) unemployed.
C) underemployed.
D) overemployed.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of supply and demand, unemployment is:
A) a surplus of labor.
B) a shortage of labor.
C) an increase in the quantity of labor demanded.
D) a decrease in the quantity of labor supplied.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A minimum wage is:
A) the lowest wage a firm is legally allowed to pay its workers.
B) the wage that firms must pay unionized labor.
C) what every high school student will earn upon employment.
D) the national average for wages paid to low-skilled workers.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Henry Ford offered his employees:
A) a contract promising safer working conditions.
B) efficiency wages.
C) minimum wages.
D) unemployment benefits.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor demand curve shows:
A) the number of workers firms want to hire at each given wage.
B) the number of people who want to work at each given wage.
C) the number of workers who are willing and able to work at higher wages.
D) that the number of people who want to work increases as the wage increases.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Weizhe just quit his job as a phone salesman and is looking for work as an accountant. Weizhe is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 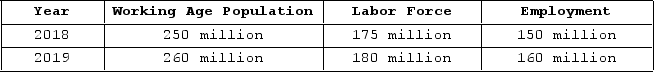 The unemployment rate in 2019 was _______ percentage points _______ than in 2018.
The unemployment rate in 2019 was _______ percentage points _______ than in 2018.
A) 3; higher
B) 3; lower
C) 14; higher
D) 11; lower
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of an economic policy that affects the level of unemployment?
A) Minimum wage law
B) Efficiency wages
C) At-will employment policies
D) Incentives for underemployed workers to find more gainful employment.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pattern of recession and recovery is called:
A) the liquidity cycle.
B) the business cycle.
C) structural unemployment.
D) inflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment insurance could affect unemployment by:
A) increasing the equilibrium level of unemployment.
B) decreasing the amount of frictional unemployment.
C) changing the incentives of those unemployed and looking for work.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After an economic boom, the new equilibrium wage will be _______ because the labor demand curve shifts to the _______.
A) lower; left
B) higher; left
C) lower; right
D) higher; right
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment occurs when someone:
A) wants to work but cannot find a job.
B) is not working full-time.
C) should be working but chooses not to.
D) is not utilizing their full set of skills.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the economy slows down:
A) the demand for labor stays the same, then increases as firms expand their operations.
B) the demand for labor decreases.
C) the demand for labor stays the same.
D) the demand for labor increases.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We would expect, all else equal, that _______ on wage income would _______ unemployment.
A) lower taxes; reduce
B) higher taxes; reduce
C) taxes; have no effect on
D) taxes; be negatively related to
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discouraged workers are people who have:
A) looked for work in the past year but have given up looking because of the condition of the labor market.
B) not looked for work in the past year but would take a job if one was offered to them.
C) looked for work in the past year but have since decided to leave the labor market to go back to school, retire, or be a stay-at-home parent.
D) spent longer than a year looking for work.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true when the prevailing market wage is above equilibrium?
A) The surplus of labor reflects the amount of unemployment in the market.
B) The difference between the quantity supplied and the quantity of labor demanded is unemployment.
C) Unemployment occurs.
D) All of these are true when the market wage is above equilibrium.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There is evidence that the presence of unions in a labor market _______ non-union wage earners in the same market.
A) can increase wages for
B) can keep wages low for
C) has no effect on the wages of
D) can increase employment rates of
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Liam just quit his job as a librarian to pursue his lifelong dream of becoming a teacher. Liam is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) seasonally unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 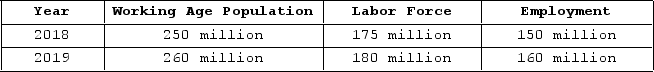 What was the labor force participation rate in 2019?
What was the labor force participation rate in 2019?
A) 70 percent
B) 80 percent
C) 69 percent
D) 26 percent
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 115
Related Exams