A) 70 percent
B) 75 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 69 percent
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 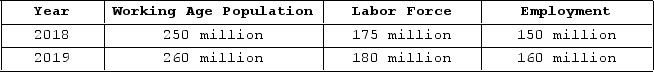 What was the unemployment rate in 2018?
What was the unemployment rate in 2018?
A) 14 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 17.5 percent
D) 15 percent
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment insurance is:
A) often more extensive in times of economic expansion.
B) a subsidy offered by the government to private insurance companies to insure the unemployed.
C) money that is paid by the government to people who are unemployed.
D) All of these are true.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor force does not include people in the working-age population who are:
A) employed.
B) not actively trying to find a job.
C) retired, a full-time student, or a stay-at-home parent.
D) employed part time.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economic growth _______, unemployment tends to _______.
A) slows; increase
B) speeds up; increase
C) slows, decrease
D) slows; stay the same
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After the financial crisis in 2007, many firms laid off workers who struggled to find new work during the recession. These workers experienced:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 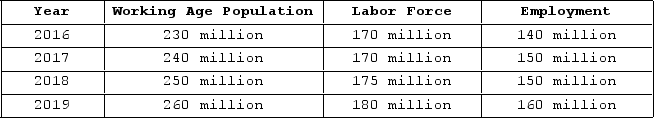 In which year was unemployment the highest?
In which year was unemployment the highest?
A) 2016
B) 2017
C) 2018
D) 2019
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists report changes in unemployment as:
A) percentage points, not percentages.
B) percentages, not percentage points.
C) percentage points or percentages, interchangeably.
D) nominal figures.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is generally more profitable for a firm to pay workers more than the going wage rate:
A) in sectors where skills are scarce.
B) in industries in which worker motivation doesn't really matter.
C) in areas for which turnover is not very costly.
D) in cities where there is a surplus of labor.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All else equal, if unemployment rises to 8 percent after a 3.5 percentage point increase, this indicates that:
A) 35 out of every 100 in the labor force have lost a job.
B) 35 out of every 1,000 in the labor force have lost a job.
C) 8 out of every 1,000 in the labor force can't find a job.
D) 8 out of every 100 in the labor force have stopped looking for work.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The unemployment rate may_______ the effect of a recession on unemployment because some people ______ the labor force.
A) understate; leave
B) understate; enter
C) overstate; leave
D) overstate; enter
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wages tend to be "sticky" because:
A) contracts are often negotiated for long periods of time and cannot be easily changed.
B) workers are less likely to work hard if their pay may be cut due to market performance.
C) changing wages create uncertainty and cost employers a lot of time and energy.
D) All of these are reasons why wages might be sticky.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How might labor unions affect the labor market?
A) Wage rates could rise above equilibrium level.
B) Wage rates could fall below equilibrium level.
C) Unemployment could reach zero.
D) Unemployment could grow to unsustainable levels.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Miguel is a corrections officer at a local prison, but he would like to go back to school to train to become a police officer someday. According to the BLS, Miguel is:
A) a discouraged worker.
B) unemployed.
C) underemployed.
D) employed.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lian has a master's degree in writing and currently works full-time as a second grade classroom helper. She submits articles for the local paper on occasion, and gets paid only when the editor agrees to publish a submission. Lian would love to work full-time as a news reporter. Lian is best described as _______ and the BLS would classify Lian as _______.
A) underemployed; employed
B) employed; employed
C) discouraged; underemployed
D) underemployed; underemployed
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price of labor is called:
A) the wage.
B) income.
C) opportunity cost.
D) the leisure trade-off.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Millennials are stereotyped as changing jobs frequently to find their "dream" career. What type of unemployment is caused by these movements?
A) Frictional
B) Real-wage
C) Cyclical
D) Structural
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor force participation rate:
A) tells us what fraction of the working-age population wants employment, whether or not they actually have a job.
B) typically rises during times of recession, as more people need work.
C) is used to assess the health of the overall economy.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the United States, the working-age population includes people:
A) in prison.
B) in the military.
C) who are less than 16 years of age.
D) aged 16 years or older.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment insurance is paid:
A) by the government to people who are unemployed.
B) to the government by employers who lay off employees.
C) by private insurance companies to people who have purchased insurance and are unemployed.
D) by the government to employers so that they can retain workers.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 115
Related Exams